In essence, heat treatment is a controlled process of heating and cooling a material, most often a metal, to deliberately alter its internal microstructure. This manipulation dissolves, rearranges, and precipitates elements within the material's crystal lattice, fundamentally changing the size, shape, and composition of its internal grains. These microscopic changes are directly responsible for macroscopic shifts in mechanical properties like hardness, strength, and ductility.
The core purpose of heat treatment is not simply to heat metal, but to precisely navigate the trade-off between hardness and brittleness. By controlling the thermal cycle, you are making a deliberate choice about the material's final atomic structure, tailoring its performance for a specific engineering purpose.
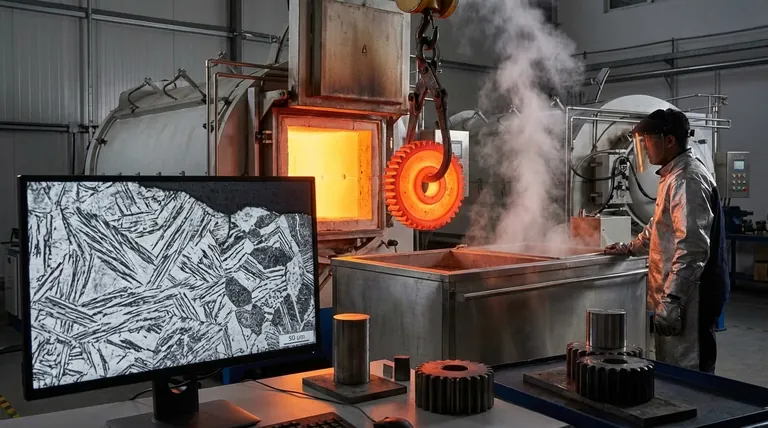
The Foundation: Phase Transformations in Steel
To understand the effect of heat treatment, you must first understand how steel behaves at high temperatures. The entire process hinges on a critical phase transformation.
Austenite: The Starting Point
When you heat steel above its critical temperature (typically between 727°C and 912°C, depending on carbon content), its crystal structure changes. The iron atoms rearrange into a face-centered cubic (FCC) lattice known as austenite.
The most important feature of austenite is its ability to dissolve a significant amount of carbon. This creates a uniform, single-phase solid solution, effectively "resetting" the microstructure and preparing it for transformation.
The Critical Role of Cooling Rate
The microstructure that forms when the steel cools from the austenitic state is almost entirely dependent on one variable: the cooling rate.
The speed of cooling dictates how much time carbon atoms have to move, or diffuse, out of the iron crystal lattice to form new structures. This is the central mechanism that heat treatment controls.
Key Processes and Their Resulting Microstructures
Different cooling rates produce distinct microstructures, each with a unique set of mechanical properties.
Annealing (Slow Cooling): Creating Softness and Ductility
By cooling the steel very slowly (e.g., by leaving it in a turned-off furnace), atoms are given maximum time to diffuse into their most stable, low-energy state.
This process results in a microstructure called coarse pearlite, which is a layered structure of soft ferrite and hard iron carbide (cementite). Annealed steel is soft, highly ductile, and easily machined, making it ideal for preparing a material for further forming operations.
Normalizing (Air Cooling): Refining Grain Structure
Normalizing involves cooling the steel in still air, which is faster than furnace cooling but much slower than quenching.
This intermediate cooling rate produces fine pearlite. The structure is similar to that from annealing, but the finer grains result in slightly higher strength and hardness while retaining good ductility. It's often used to create a more uniform internal structure.
Quenching (Rapid Cooling): Achieving Maximum Hardness
Quenching is the process of cooling the material extremely rapidly by submerging it in a medium like water, brine, or oil.
This rapid cooling gives the dissolved carbon atoms no time to diffuse out of the lattice. The carbon becomes trapped, distorting the crystal structure into a body-centered tetragonal (BCT) form known as martensite. Martensite is exceptionally hard and strong, but also extremely brittle.
Tempering (Reheating After Quenching): Restoring Toughness
A component made of pure martensite is often too brittle for practical use; it could shatter under impact. Tempering is a secondary heat treatment performed after quenching.
The part is reheated to a precise temperature below the critical point and held there. This allows some of the trapped carbon to precipitate out, relieving internal stresses and transforming the brittle martensite into a more refined structure called tempered martensite. This process reduces hardness slightly but dramatically increases toughness and ductility.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat treatment is never about achieving a single property in isolation. It is always a game of balance.
The Price of Hardness
The pursuit of maximum hardness through quenching invariably leads to maximum brittleness. A martensitic steel file is excellent at cutting other metals, but it will snap if you try to bend it. This inverse relationship is the most fundamental trade-off in metallurgy.
The Need for Toughness
Toughness is a material's ability to absorb energy and deform without fracturing. For components like gears, shafts, or structural bolts, toughness is often more critical than absolute hardness. A brittle gear would shatter on its first shock load, while a tough gear will endure years of service.
Tempering: The Engineered Compromise
Tempering is the most common tool for navigating this trade-off. By carefully selecting the tempering temperature, an engineer can dial in the exact balance of hardness and toughness required for an application, sacrificing a small amount of wear resistance to gain a large amount of impact resistance.
Matching the Process to the Engineering Goal
The right heat treatment is not universal; it is dictated entirely by the component's intended function.
- If your primary focus is maximum machinability or formability: Choose full annealing to produce the softest, most ductile microstructure (coarse pearlite).
- If your primary focus is a uniform, refined grain structure with balanced properties: Use normalizing for a cost-effective improvement in strength and consistency.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance: You must quench to form martensite, but it almost always requires a subsequent tempering step to be useful.
- If your primary focus is creating a tough, durable component that can withstand impact: The combination of quenching followed by tempering is the definitive path to achieving high strength with necessary toughness.
Ultimately, mastering heat treatment means understanding how to deliberately manipulate a metal's atomic structure to produce a material perfectly engineered for its purpose.
Summary Table:
| Process | Cooling Rate | Resulting Microstructure | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Very Slow (Furnace Cool) | Coarse Pearlite | Soft, Ductile, Machinable |
| Normalizing | Moderate (Air Cool) | Fine Pearlite | Balanced Strength & Ductility |
| Quenching | Very Fast (Water/Oil) | Martensite | Extremely Hard, Strong, Brittle |
| Tempering | Reheat after Quench | Tempered Martensite | Tough, Durable, Less Brittle |
Ready to Engineer Your Materials for Peak Performance?
Understanding the science of heat treatment is the first step. Applying it precisely in your lab is what delivers results. The right equipment is critical for controlling the thermal cycles that define your material's final microstructure and properties.
KINTEK is your partner in precision. We specialize in high-quality lab furnaces and thermal processing equipment, helping researchers and engineers in materials science, metallurgy, and manufacturing achieve consistent, reliable outcomes.
Let us help you master the trade-off between hardness and toughness. Whether you need a furnace for annealing, quenching studies, or precise tempering, our solutions are designed for accuracy and repeatability.
Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect equipment for your lab's needs.
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals can be joined by brazing? Discover the Versatility of Modern Brazing Techniques
- Why would you braze instead of weld? Preserve Material Integrity and Join Dissimilar Metals
- What are the factors that affect the strength of a brazed joint? Master the 4 Keys to a Perfect Bond
- What is the major advantage that brazing has over welding? Joining Dissimilar Metals with Ease
- What is vacuum brazed? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity Metal Joining



















