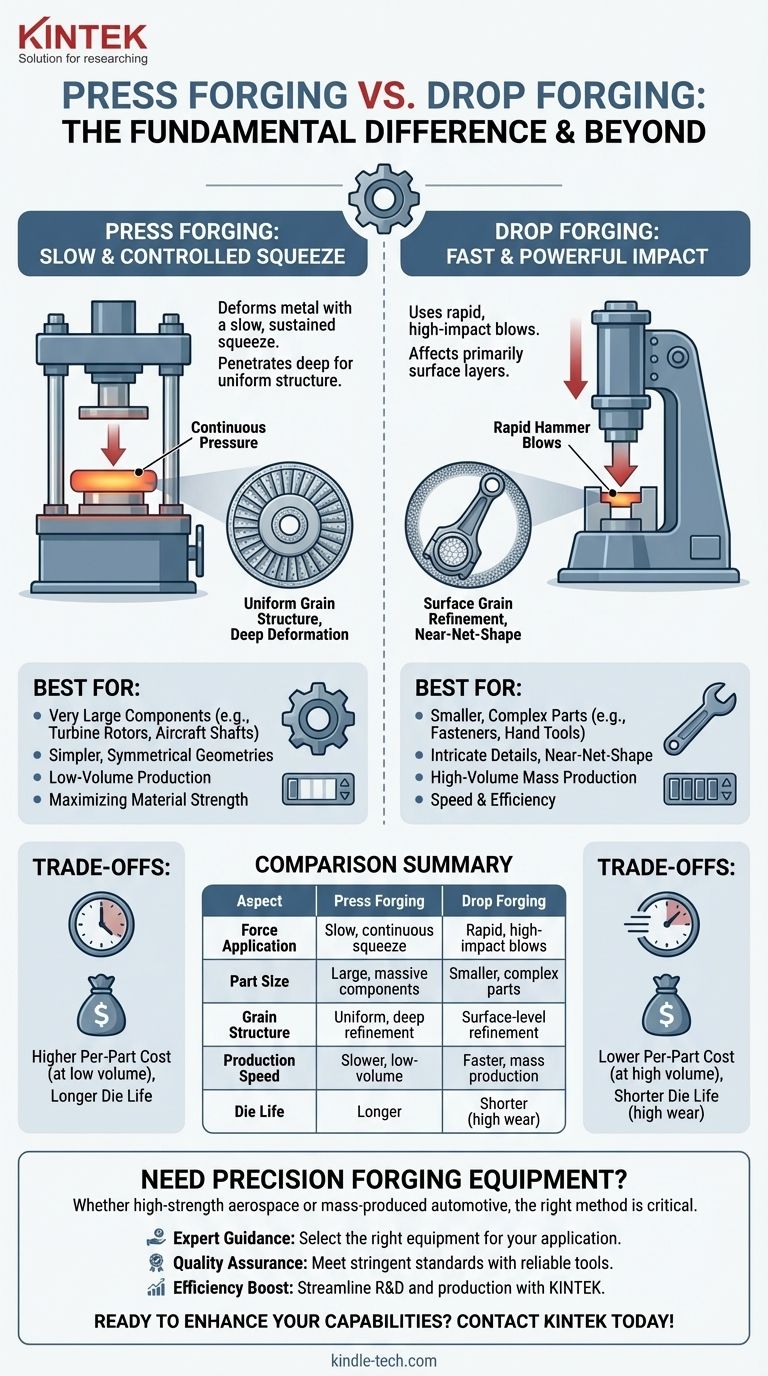
The fundamental difference between press forging and drop forging lies in the application of force. Press forging uses a slow, continuous, and controlled pressure to shape the metal, whereas drop forging uses a rapid, high-impact blow from a falling hammer. This single distinction in force application leads to significant differences in material properties, production speed, and suitable applications.
The core decision is not about which process is superior, but which is appropriate for the task. Drop forging excels at mass-producing smaller, complex parts at high speed, while press forging is the definitive choice for large components where deep, uniform material deformation is critical for strength.

The Mechanics of Force Application
Understanding how force is transmitted to the workpiece is the key to grasping the differences between these two foundational forging methods. The entire process, from tooling design to final material properties, is dictated by this initial action.
Press Forging: Slow and Controlled Squeeze
In press forging, a hydraulic or mechanical press applies gradual and sustained pressure to the workpiece. Think of it as slowly squeezing clay in your hand.
This continuous force penetrates deep into the center of the metal, causing uniform plastic deformation throughout the entire volume. The dies remain in contact with the workpiece for a longer period, which also allows for more significant and controlled material flow.
Drop Forging: Fast and Powerful Impact
Drop forging, also known as hammer forging, uses the force of a falling ram or hammer to strike the workpiece in a series of short, extremely rapid blows. This is more like hitting clay with a hammer.
The force is instantaneous and intense, primarily affecting the surface layers of the material. The die contact time is measured in milliseconds, and the final shape is achieved through one or more successive impacts.
Impact on Material and Part Characteristics
The method of force application directly influences the final component's size, complexity, and, most importantly, its internal metallurgical structure.
Grain Structure and Deformation
The slow squeeze of press forging deforms the material uniformly from the surface to the core. This creates a highly refined and consistent grain structure throughout the part, which is ideal for high-strength, fatigue-resistant applications.
The sudden impact of drop forging primarily refines the grain structure near the component's surface. While it produces a strong part, the deformation may not be as uniform or deep as in press forging.
Precision and Complexity
Drop forging is exceptionally well-suited for producing intricate and complex shapes with high precision. The rapid blow forces the metal to fill every detail of the die cavity, often creating near-net-shape parts that require minimal secondary machining.
Press forging is generally used for simpler, often symmetrical geometries like discs, rings, and large blocks, where the primary goal is bulk deformation rather than intricate detail.
Part Size and Scale
Press forging is the dominant process for manufacturing very large components. The immense, continuous force of a forging press is necessary to deform massive ingots weighing many tons into parts like turbine rotors, large-scale industrial shafts, and aircraft structural components.
Drop forging is typically limited to smaller parts, from hand tools and automotive connecting rods to small fittings and fasteners. The energy of the hammer blow is insufficient to forge extremely large workpieces effectively.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Production and Cost
Your choice of forging method will have direct and significant consequences for production speed, tooling costs, and the overall economics of your project.
Production Speed and Volume
Drop forging is a much faster process. The rapid cycle of hammer blows makes it the clear choice for high-volume, mass production where thousands or millions of identical parts are required.
Press forging is a slower, more deliberate process. Its cycle times are significantly longer, making it better suited for lower-volume production runs or one-off manufacturing of specialized, large-scale components.
Tooling and Die Life
The repeated, high-intensity impacts of drop forging are extremely harsh on the dies. This leads to more rapid wear and a shorter operational life for the tooling, which must be factored into the overall cost.
The controlled squeezing action of press forging is much gentler on the dies, resulting in significantly longer tool life.
Initial Investment and Cost per Part
While the dies may wear out faster, drop forging equipment (hammers) generally has a lower initial capital cost than the massive hydraulic presses required for press forging.
For mass-produced items, the high speed of drop forging leads to a much lower cost per part, even with higher tooling maintenance. For large, specialized parts, the efficiency of press forging makes it the only viable and cost-effective option.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct process requires aligning the method's strengths with your primary design and production goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of small, complex parts (e.g., automotive components): Drop forging is the superior choice for its speed, precision, and lower per-part cost at scale.
- If your primary focus is creating very large, critical components (e.g., aerospace discs, power generation shafts): Press forging is the only method that can achieve the necessary deep, uniform deformation and grain refinement.
- If your primary focus is maximum control over the internal grain structure for a fatigue-critical application: The slow, controlled deformation of press forging provides more precise metallurgical control throughout the entire part.
- If your primary focus is producing near-net-shape parts to minimize subsequent machining: Drop forging generally offers a higher degree of precision and complexity for smaller components.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental difference between a sudden impact and a controlled squeeze is the key to selecting the forging process that ensures the performance and economic viability of your design.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Press Forging | Drop Forging |
|---|---|---|
| Force Application | Slow, continuous, controlled pressure | Rapid, high-impact hammer blows |
| Best For Part Size | Large components (e.g., turbine rotors) | Smaller, complex parts (e.g., fasteners) |
| Grain Structure | Uniform deformation from surface to core | Surface-level refinement |
| Production Speed | Slower, suited for low-volume runs | Faster, ideal for mass production |
| Die Life | Longer due to gentler force | Shorter due to high-impact wear |
Need Precision Forging Equipment for Your Lab or Production Line?
Whether you're developing high-strength aerospace components or mass-producing intricate automotive parts, the right forging method is critical to your success. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust lab equipment and consumables tailored to your metalworking and material testing needs.
Let us help you achieve superior results:
- Expert Guidance: Our team can help you select the right equipment for press or drop forging applications.
- Quality Assurance: Ensure your materials meet stringent standards with our reliable tools.
- Efficiency Boost: Streamline your R&D or production process with KINTEK's solutions.
Ready to enhance your forging capabilities? Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory or production goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates Split Manual Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More
- What is a hydraulic hot press? A Guide to Precision Heat and Pressure for Manufacturing
- What is a hydraulic hot press machine? A Guide to Force and Heat for Material Transformation
- How does a hydraulic hot press machine work? Unlock Precision in Material Bonding and Forming
- What is the purpose of using a laboratory hydraulic press for LGVO synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Solid Electrolytes



















