In short, sintering increases grain size. This process uses heat to fuse particles together, and a direct consequence of this atomic diffusion and boundary migration is that smaller grains are consumed by larger ones, leading to an overall growth in the average grain size of the material. The primary factors you can control to influence this growth are temperature and time.
Sintering is fundamentally a balancing act. The goal is to reduce porosity and increase density, but the very mechanisms that achieve this—heat and time—also inherently cause grains to grow, which critically alters the final properties of the material.
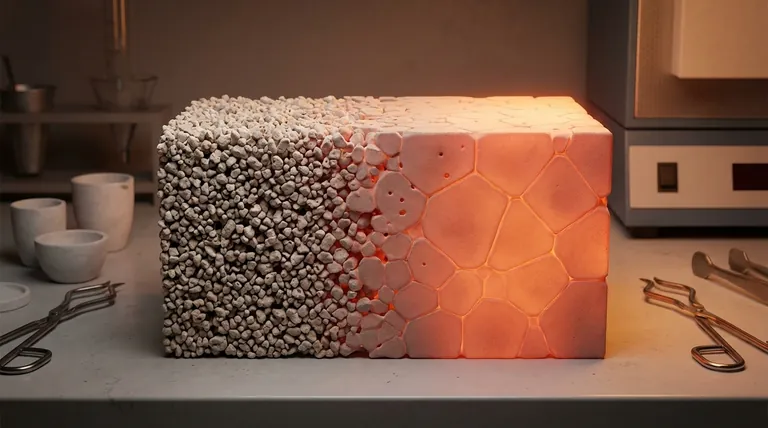
The Core Mechanism: How Sintering Drives Grain Growth
Sintering is more than just heating a material. It is a thermally activated process designed to transform a loosely packed powder compact into a dense, solid object. This transformation happens at the microscopic level, directly impacting the grain structure.
The Role of Temperature
Higher sintering temperatures provide more thermal energy to the atoms within the material. This energy allows atoms to diffuse more easily across the boundaries between individual grains.
As a result, larger, more energetically stable grains grow at the expense of smaller ones, increasing the average grain size.
The Influence of Time
The duration of the sintering process is the second key variable. The longer the material is held at a high temperature, the more time there is for atomic diffusion to occur.
This extended period allows the process of grain coalescence and growth to continue, leading to a progressively larger average grain size until it eventually begins to stabilize.
The Link Between Grains and Pores
The primary goal of sintering is densification—the elimination of empty spaces, or pores, between the initial particles.
As grains grow and their boundaries migrate, they sweep over and eliminate these pores. This is how the material becomes stronger and more solid.
Why Grain Size Control is Critical
The microstructure, particularly the grain size, dictates the final performance characteristics of the sintered part. Understanding this link is essential for engineering materials to meet specific demands.
Impact on Mechanical Strength
Grain size has a profound effect on a material's strength and hardness. In many materials, smaller grains result in higher strength.
This is because the boundaries between grains act as obstacles that impede the movement of dislocations, which is the primary mechanism of plastic deformation. More boundaries mean more obstacles and a stronger material.
Influence on Other Properties
Beyond strength, grain size affects a wide range of characteristics. It can influence a material's durability, electrical conductivity, and even its optical properties.
For example, in some advanced ceramics, achieving a specific, uniform grain size is necessary to create a transparent final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing a sintering process is rarely straightforward. It often involves navigating a critical conflict between achieving full density and preventing undesirable grain growth.
The Density vs. Grain Size Dilemma
To eliminate porosity and achieve maximum density, you often need higher temperatures or longer sintering times. However, these very conditions also promote significant grain growth.
This can lead to a situation where you create a very dense part that unfortunately lacks the mechanical strength it would have had with a finer grain structure.
Reaching a Plateau
As noted in material studies, grain growth is not infinite. After a certain duration at a given temperature, the rate of growth slows down and tends to stabilize.
Understanding this behavior is key to process control. It allows engineers to hold a part at temperature long enough to achieve target density without letting the grains grow uncontrollably.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal sintering parameters depend entirely on the desired properties of the final component. Your primary application dictates how you should approach the density-grain size trade-off.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and hardness: Prioritize keeping grains small by using the lowest possible temperature and shortest time required to achieve the necessary component density.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and stability: You may need to accept larger grain growth by using higher temperatures or longer times, especially if ultimate mechanical strength is not the most critical factor.
Ultimately, mastering the sintering process is about precisely controlling the material's final microstructure to achieve its intended function.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on Grain Size | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Higher temperature = Larger grains | More thermal energy accelerates atomic diffusion. |
| Time | Longer time = Larger grains | Extended exposure allows for more grain growth. |
| Goal | Strength (Small Grains) vs. Density (Large Grains) | A critical trade-off that dictates sintering parameters. |
Need precise control over your material's microstructure?
The sintering process is a delicate balance. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and expert support you need to achieve the perfect grain size and density for your specific application—whether you're developing high-strength components or materials with specialized properties.
Let us help you optimize your sintering process. Contact our experts today to discuss your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is a 1000°C+ furnace needed for LLZO/LLTO? Mastering High-Temperature Sintering for Ceramic Electrolytes
- What is the temperature of vacuum casting? Mastering the Thermal Profile for Flawless Parts
- What is the temperature of a vacuum brazing furnace? Key metrics for precision joining
- What is the effect of hardening on mechanical properties? A Guide to Strength vs. Toughness
- Which heat treatment is best? Choose the Right Process for Your Metal's Properties
- What does sintering do to metal? Transform Powder into Durable, High-Performance Parts
- Can you heat treat metal twice? Correct Flaws and Adapt Parts with Multiple Cycles
- How is heat transfer in liquids different from that in a vacuum? Mastering Thermal Management for Your Lab



















