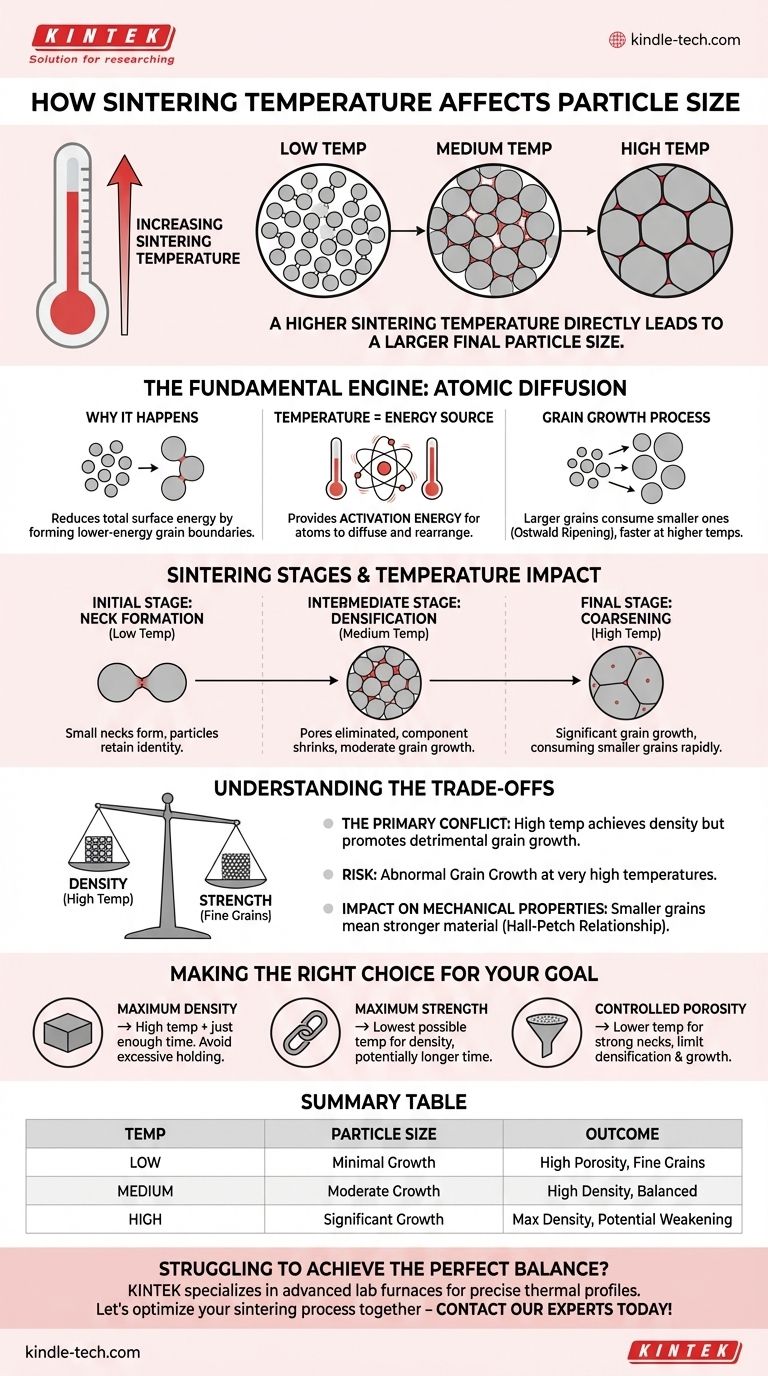
In short, a higher sintering temperature directly leads to a larger final particle size. Sintering uses thermal energy to drive atomic diffusion, causing individual particles to bond and grow into larger crystalline domains, or "grains." As you increase the temperature, you dramatically accelerate this diffusion process, promoting faster and more extensive grain growth.
The core challenge in any sintering process is managing a fundamental trade-off. While higher temperatures are necessary to achieve high density by eliminating pores, they also aggressively promote grain growth, which can be detrimental to the final material's mechanical properties.

The Fundamental Engine: Atomic Diffusion
To control particle size, you must first understand the underlying mechanism that drives the entire sintering process. It's not about melting; it's about atoms moving in a solid state.
Why Sintering Happens at All
A powder compact is a high-energy system due to its vast amount of surface area. Nature always seeks the lowest energy state.
Sintering is the process by which the system reduces its total surface energy by replacing solid-vapor interfaces (particle surfaces) with lower-energy solid-solid interfaces (grain boundaries).
Temperature as the Energy Source
For atoms to move and rearrange themselves to form these new boundaries, they need energy. This is called activation energy.
Temperature provides this thermal energy. A higher temperature gives more atoms the energy needed to break their bonds, diffuse across surfaces or through the particle lattice, and re-bond in a more stable configuration. It is the accelerator pedal for the entire process.
The Process of Grain Growth
As particles bond and pores shrink, distinct crystalline regions called grains are formed. The interface between two grains is a grain boundary.
Grain growth occurs as these boundaries migrate. To reduce energy further, larger grains consume smaller, less stable ones in a process known as Ostwald Ripening. Higher temperatures make this boundary migration happen much faster, leading to a coarser (larger-grained) final microstructure.
How Temperature Controls the Sintering Stages
The effect of temperature becomes clearer when looking at the distinct stages of sintering. Higher temperatures accelerate every stage, but its impact on the final stage is most critical for controlling particle size.
Initial Stage: Neck Formation
At relatively lower temperatures, the first thing that happens is the formation of "necks" at the contact points between adjacent particles.
This initial bonding reduces some surface area, but the particles largely retain their original identity.
Intermediate Stage: Densification
As temperature increases, diffusion rates climb significantly. Pores begin to shrink and are eliminated as material is transported to fill the voids.
This is the primary stage for densification, where the component shrinks and its density approaches its theoretical maximum. Grain growth also occurs here, but densification is often the dominant process.
Final Stage: Coarsening and Grain Growth
Once the material is nearly dense (typically >92% theoretical density), the remaining pores are isolated. The primary mechanism for further energy reduction is now significant grain growth.
At high sintering temperatures, this stage proceeds rapidly. Grain boundaries sweep through the material, consuming smaller grains and drastically increasing the average particle or grain size. If held at a high temperature for too long, this effect can be extreme.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Manipulating sintering temperature is never about a single outcome. It's about balancing competing objectives to achieve the desired final properties.
The Primary Conflict: Density vs. Grain Size
This is the most critical trade-off. To get a fully dense, pore-free material, you often need high temperatures. However, those same high temperatures will inevitably lead to larger grains.
For many applications, particularly structural ones, you need both high density and a fine grain structure. Achieving this requires precise control over the temperature and time profile.
The Risk of Abnormal Grain Growth
At very high temperatures, or with certain material compositions, a few grains can grow disproportionately large at the expense of all others. This "abnormal" or "runaway" grain growth creates a non-uniform microstructure and is almost always detrimental to performance.
The Impact on Mechanical Properties
For most metals and ceramics, mechanical strength is inversely proportional to the grain size. This is described by the Hall-Petch relationship.
Smaller grains mean more grain boundaries, which act as obstacles to dislocation movement, making the material stronger and harder. Therefore, excessive grain growth from high sintering temperatures often results in a weaker, more brittle final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your ideal sintering temperature is not a fixed number; it is dictated entirely by the end-goal for your material.
- If your primary focus is maximum density: Use a relatively high temperature combined with just enough time to close porosity, but avoid holding it at peak temperature for too long to limit excessive grain coarsening.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength (fine-grained structure): Use the lowest possible temperature that can still achieve the necessary density, potentially over a longer period. Advanced techniques like Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) or the use of grain growth inhibitors may also be necessary.
- If your primary focus is controlled porosity (e.g., for filters or implants): Use a lower sintering temperature sufficient to form strong necks between particles but not high enough to cause significant densification or grain growth.
Ultimately, mastering sintering is about precisely applying thermal energy to control atomic motion, guiding the material toward its desired final form.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Temperature | Effect on Particle/Grain Size | Primary Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Low | Minimal Growth | High Porosity, Fine Grains |
| Medium | Moderate Growth | High Density, Balanced Properties |
| High | Significant/Excessive Growth | Maximum Density, Potential Weakening |
Struggling to achieve the perfect balance of density and strength in your sintered materials? The precise control of sintering temperature is critical. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab furnaces and equipment that deliver the exact thermal profiles needed for consistent, high-quality results. Our solutions help you master the sintering process, whether your goal is maximum density, superior strength, or controlled porosity. Let's optimize your sintering process together – contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.



















