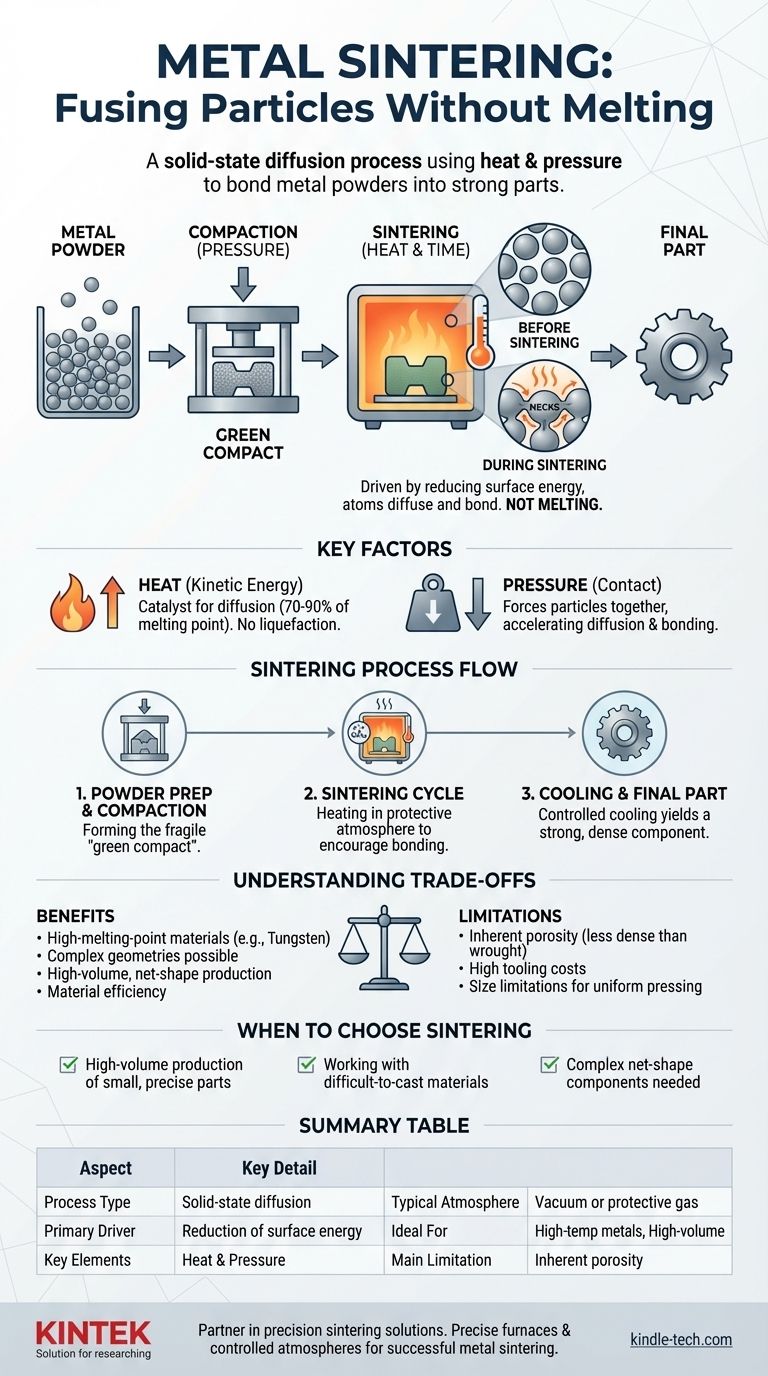
In short, metal sintering is a manufacturing process that uses heat and pressure to fuse metal particles into a solid, functional part. Critically, this is achieved without reaching the metal's melting point. Instead of liquefying the material, sintering encourages the atoms on the surfaces of individual powder grains to diffuse and bond with neighboring grains, creating a dense and strong metallic structure.
Sintering is not a melting process; it is a solid-state diffusion process. Its primary value lies in creating strong, precise parts from materials—especially those with very high melting points—that are difficult or impossible to form using traditional casting methods.

The Core Principle: Atomic Diffusion, Not Melting
To truly understand sintering, you must shift your thinking from melting and casting to the atomic level. The process is driven by fundamental physics that encourages solid particles to bond together.
The Driving Force: Reducing Surface Energy
Imagine a collection of individual soap bubbles. They have a large total surface area. When they touch, they merge to form larger bubbles, reducing the overall surface area and thus lowering their total surface energy.
Metal powders behave in a similar way. Each tiny particle has a high surface energy. When heated, the system naturally seeks a lower energy state by reducing this surface area. It achieves this by forming solid bonds, or "necks," between particles, effectively merging them.
The Role of Heat
Heat is the catalyst for sintering. It does not melt the metal, but it gives the atoms enough kinetic energy to move and migrate across the particle surfaces. This atomic movement, known as solid-state diffusion, is what allows the bonds between particles to form and grow, gradually eliminating the pores between them.
The Role of Pressure
While some sintering can occur with heat alone (pressureless sintering), applying external pressure is common. Pressure compacts the metal powder, forcing the particles into intimate contact. This increases the number of contact points and significantly accelerates the diffusion and bonding process.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process
While there are variations, the conventional powder metallurgy sintering process follows a few key stages.
Step 1: Powder Preparation and Compaction
First, fine metal powder is placed into a die or mold that has the shape of the final part. In some cases, a small amount of a polymeric binder is mixed in to help the particles stick together. A press then applies immense pressure to compact the powder into a fragile, precisely shaped object known as a "green compact."
Step 2: The Sintering Cycle
The green compact is transferred to a high-temperature furnace. The atmosphere inside the furnace is critical. To prevent the hot metal surfaces from oxidizing, sintering is performed in a vacuum or a controlled protective atmosphere, such as an endothermic gas.
The part is heated in a controlled manner to a temperature below its melting point, typically around 70-90% of it. It is held at this temperature for a set amount of time, allowing atomic diffusion to bond the particles and densify the part. If a binder was used, it is carefully burned out at a lower temperature in a preliminary "debinding" step.
Step 3: Cooling and Final Part
After the sintering stage, the part is cooled in a controlled manner. The result is a solid, dense component that is much stronger than the initial green compact and has properties approaching those of the bulk metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sintering is a powerful technique, but it is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Inherent Porosity
While sintering dramatically reduces the empty space between particles, it rarely eliminates it completely. This residual porosity can make a sintered part slightly less dense and strong than a part forged or machined from a solid billet of the same metal.
Tooling and Volume Costs
The dies used for compacting metal powders are made from hardened steel and can be very expensive to produce. This high initial cost means sintering is most economical for high-volume production runs, where the cost of the tooling can be spread across thousands or millions of parts.
Part Size and Geometry
Pressing powders uniformly can be challenging for very large or highly complex shapes. Therefore, sintering is typically best suited for producing relatively small, though often intricate, components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if sintering is the correct approach for your project.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing parts from high-melting-point materials like tungsten or molybdenum: Sintering is often the only viable and cost-effective method available.
- If your primary focus is the high-volume production of small, precise metal components: Sintering offers excellent consistency and net-shape capabilities, minimizing waste and the need for secondary machining.
- If your primary focus is achieving the absolute maximum strength and fatigue resistance for a critical component: A forged or fully wrought material may be a better choice, as it avoids the potential for residual porosity.
By understanding sintering as a process of atomic diffusion, you can leverage its unique capabilities to solve complex manufacturing challenges.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Solid-state diffusion (not melting) |
| Primary Driver | Reduction of surface energy |
| Key Elements | Heat (70-90% of melting point) & Pressure |
| Typical Atmosphere | Vacuum or protective gas (e.g., endothermic) |
| Ideal For | High-melting-point metals (e.g., tungsten), high-volume production |
| Main Limitation | Inherent porosity (less dense than wrought metal) |
Ready to leverage sintering for your high-volume production or challenging materials? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the precise furnaces and controlled atmospheres essential for successful metal sintering. Our expertise helps you create strong, complex parts efficiently. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering needs and enhance your manufacturing process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity, Strength, and Performance
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Superior Density for Nanocrystalline Fe3Al
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve high-density NTC ceramics with superior stability.
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics
- How does a vacuum environment system contribute to the hot pressing sintering of B4C-CeB6? Unlock Peak Ceramic Density



















