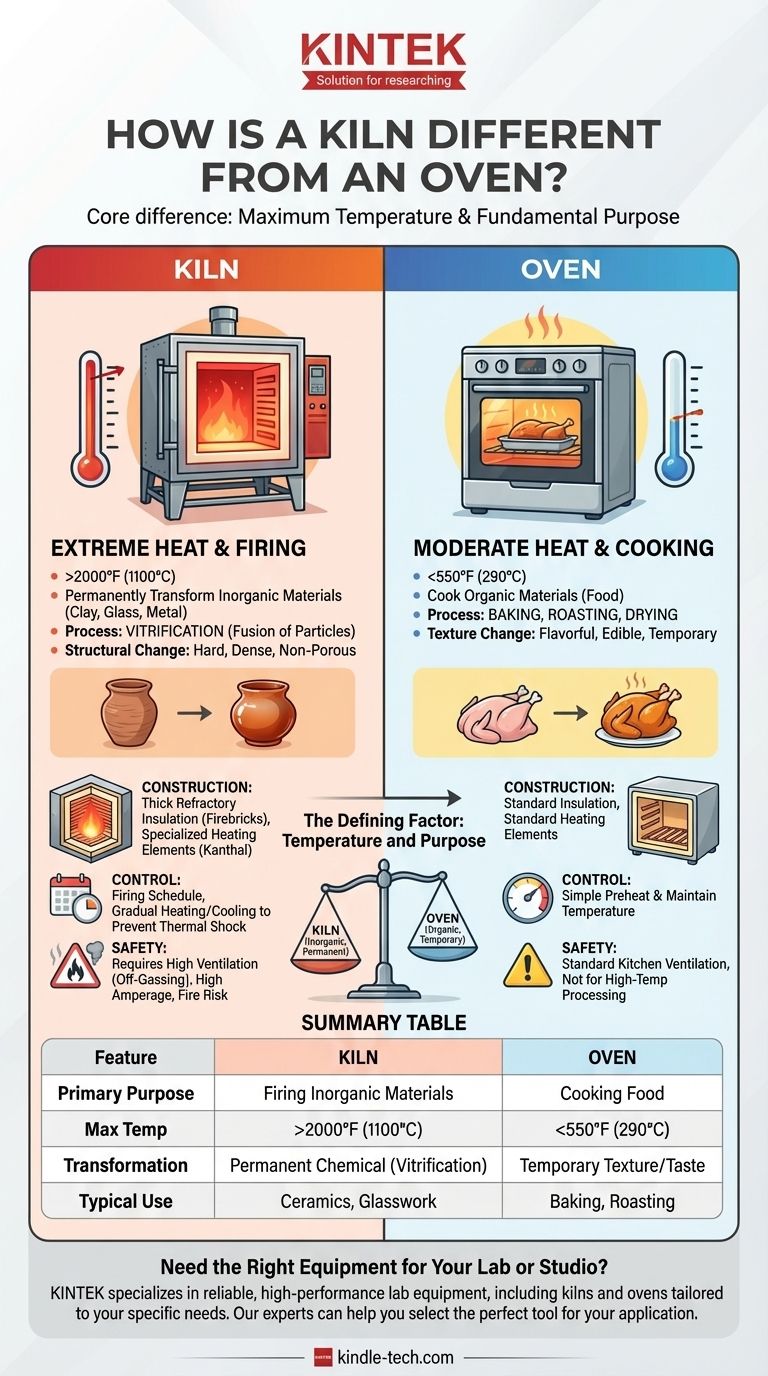
In short, a kiln is differentiated from an oven by its maximum temperature and its fundamental purpose. A kiln is engineered to reach extremely high temperatures (often exceeding 2000°F or 1100°C) to permanently and chemically transform inorganic materials like clay, glass, and metal. An oven operates at much lower temperatures (typically below 550°F or 290°C) to cook food through baking, roasting, or drying.
The core difference isn't just about the level of heat; it's about the nature of the transformation. An oven applies heat to cook organic material, while a kiln applies extreme heat to fire inorganic material, inducing a permanent structural change that an oven is physically incapable of producing.

The Defining Factor: Temperature and Purpose
The most significant distinction lies in what each device is designed to accomplish, which is a direct result of its temperature range.
Ovens: The Realm of Cooking
Ovens are designed for culinary applications. Their typical maximum temperature of around 550°F (290°C) is ideal for processes like the Maillard reaction and caramelization, which make food flavorful and safe to eat.
The goal of an oven is to heat food thoroughly without destroying it. The changes it makes are primarily about texture and palatability, not a fundamental restructuring of the material itself.
Kilns: The Realm of Firing
Kilns are industrial tools for a process called firing. This process uses intense heat to achieve vitrification in clay—the point at which clay particles fuse together, becoming hard, dense, and non-porous like stone or glass.
This transformation requires temperatures that start where ovens top out and go much higher. For example, earthenware clay is fired at around 1800°F (1000°C), while stoneware and porcelain require temperatures of 2200-2400°F (1200-1300°C).
Why an Oven Can't Fire Pottery
Placing a clay pot in a kitchen oven, even at its highest setting, will do little more than make it very hot and dry. The temperature is thousands of degrees too low to initiate the chemical and physical fusion that turns clay into durable ceramic.
How Construction Dictates Function
The vast difference in operating temperature necessitates completely different designs and materials.
Insulation: Containing Extreme Heat
A kiln is essentially a super-insulated box. It is lined with refractory materials like insulating firebricks or ceramic fiber blankets that can withstand and contain extreme heat for many hours.
An oven uses far less robust insulation, sufficient only for cooking temperatures and to keep the exterior safe to touch. This is why a kiln is vastly more energy-efficient at holding high temperatures than an oven would be.
Heating Elements: Built for the Extremes
Electric kilns use thick coils made of specialized metal alloys, like Kanthal, which can glow red-hot for thousands of hours without degrading.
An oven's heating elements are designed for a much lower workload and would quickly fail if forced to operate at kiln-level temperatures.
Control: The Firing Schedule
Firing ceramics is not just about reaching a peak temperature; it's about controlling the rate of temperature change. A kiln is programmed with a firing schedule that dictates how slowly to heat up and cool down.
Ramping the temperature too quickly causes thermal shock, which will crack or shatter the ceramic. An oven’s controls are simple by comparison, designed only to preheat to a set temperature and maintain it.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Dangers
Using these tools interchangeably is not just ineffective—it is dangerous.
Off-Gassing and Ventilation
Firing clay and glazes releases water, sulfur compounds, and other fumes. Kilns must be used in a highly ventilated area, often with a dedicated vent hood, to safely exhaust these gases.
A kitchen oven is not equipped for this, and attempting to fire materials in one could release hazardous fumes into your living space.
Fire Safety and Energy Use
A kiln is a significant fire risk if not installed and maintained properly. It requires dedicated, high-amperage electrical circuits and must be placed far from any combustible materials.
Its energy consumption during a single firing, which can last 8-12 hours or more, is substantial and far exceeds that of any standard home appliance. Trying to push an oven to its limits for prolonged periods creates a serious fire hazard.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice is dictated entirely by the material you intend to heat and the transformation you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is cooking food: An oven is the correct, safe, and efficient tool designed specifically for this task.
- If your primary focus is hardening clay into ceramic: You absolutely require a kiln to reach the necessary vitrification temperatures safely and effectively.
- If your primary focus is curing polymer clay: A conventional or toaster oven is appropriate, as this material cures at very low temperatures (typically 230-275°F or 110-135°C).
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental purpose of each tool—cooking versus permanent transformation—is the key to using them safely and effectively.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Kiln | Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Firing inorganic materials (clay, glass, metal) | Cooking food (baking, roasting) |
| Max Temperature | >2000°F (1100°C) | <550°F (290°C) |
| Material Transformation | Permanent chemical change (vitrification) | Temporary texture/taste change |
| Typical Use Case | Ceramics, pottery, glasswork | Baking, roasting, food preparation |
Need the Right Equipment for Your Lab or Studio?
Whether you're firing ceramics, curing materials, or conducting high-temperature experiments, choosing the correct heating device is critical for safety and success. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable, high-performance lab equipment, including kilns and ovens tailored to your specific needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect tool for your application, ensuring precise temperature control and optimal results.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory or studio with the right heating solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
People Also Ask
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products



















