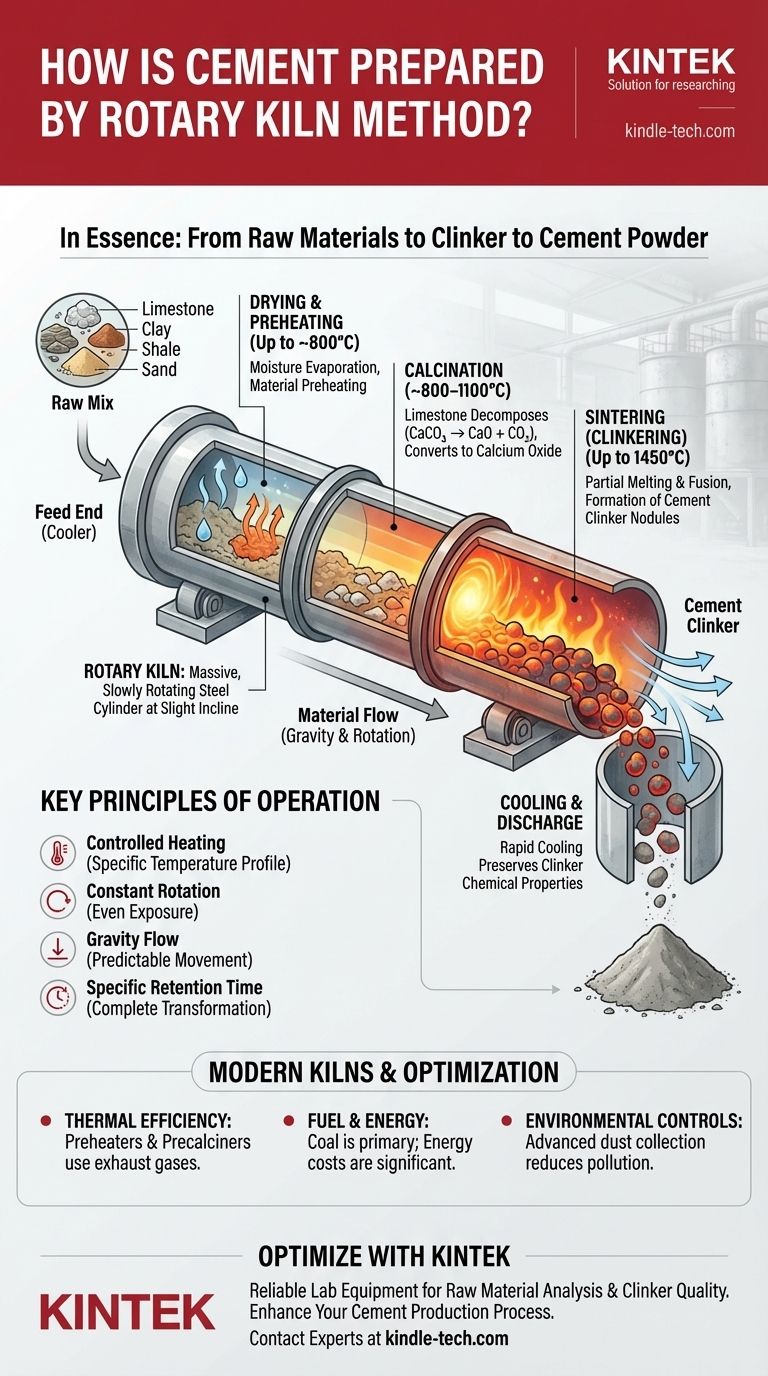
In essence, a rotary kiln prepares cement by heating a precise mixture of raw materials, like limestone, to extremely high temperatures inside a long, rotating cylinder. This intense heating process triggers specific chemical reactions, transforming the raw feed into a new substance called "clinker." This clinker is the fundamental intermediate product that, once cooled and ground, becomes the final cement powder.
The rotary kiln is the heart of modern cement manufacturing. Its core function is to facilitate a precise, high-temperature chemical transformation of raw materials into clinker through a combination of controlled heating, constant motion, and specific retention times.

How the Rotary Kiln System Works
A rotary kiln is a massive, slowly rotating steel cylinder lined with heat-resistant brick. It is mounted at a slight incline to allow gravity to guide materials through it from one end to the other.
The Principle of Operation
The kiln's primary job is to heat solid materials to a point where a desired chemical reaction or physical change occurs. It is designed to hold the material at a very specific temperature for a precise amount of time to ensure the transformation is complete.
This process is governed by a temperature profile, which is carefully calculated based on the chemical properties of the raw materials being processed.
The Role of Rotation and Tilt
The kiln rotates slowly on its axis, typically between one and three revolutions per minute. This rotation continuously tumbles the material, ensuring every particle is evenly exposed to the intense heat.
The slight incline of the kiln ensures a continuous, predictable flow of material from the higher "feed" end to the lower "discharge" end.
The Step-by-Step Production of Cement Clinker
The creation of cement clinker inside the kiln is a continuous process broken down into distinct thermal zones that the raw material passes through.
Step 1: Feeding the Raw Mix
A carefully proportioned mixture of raw materials, primarily limestone (calcium carbonate) mixed with clay, shale, or sand, is fed into the upper, or "cooler," end of the kiln.
Step 2: The Drying and Preheating Zone
As the raw mix enters the kiln, it first encounters hot gases flowing in the opposite direction. In this initial zone, any remaining moisture is evaporated, and the material is preheated to several hundred degrees Celsius.
Step 3: The Calcination Zone
As the material tumbles further down the kiln, it enters the calcination zone, where temperatures rise above 800°C (1470°F). Here, the intense heat drives carbon dioxide out of the limestone, converting it to calcium oxide. This is a critical chemical change.
Step 4: The Sintering (Clinkering) Zone
The material then enters the hottest part of the kiln, the sintering zone, with temperatures reaching up to 1450°C (2640°F). At this extreme heat, the materials partially melt and fuse together, forming new mineral compounds.
This fusion process, known as sintering, results in the formation of hard, rounded nodules called cement clinker. These nodules are typically 3-25 mm in diameter.
Step 5: Cooling and Discharge
The red-hot clinker then exits the kiln and enters a cooler, where it is rapidly cooled with air. This rapid cooling is essential for preserving the chemical properties that give cement its strength.
Modern Kilns and Key Considerations
Modern rotary kilns are the product of decades of engineering focused on increasing efficiency and capacity. They are central to the energy consumption and environmental footprint of a cement plant.
Focus on Thermal Efficiency
Advances in kiln technology are driven by the need to save energy. Modern systems are thermally sophisticated, often incorporating preheaters and precalciners that use the hot exhaust gases from the kiln to begin processing the raw materials before they even enter the main cylinder.
Fuel and Energy Sources
The trend in the industry is toward using coal as the primary energy source for firing the kiln. The intense heat required for clinker formation makes energy one of the most significant costs in cement production.
Environmental Controls
The cement-making process generates significant dust. Modern plants are equipped with advanced dust collection systems that capture particulate matter, reducing air pollution and often returning the captured dust to the production process to minimize waste.
Key Principles of the Rotary Kiln Method
To summarize the role and function of the kiln, consider the core requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is process understanding: The key is the controlled, high-temperature transformation of a raw mix into clinker through the combined action of heat, rotation, and gravity.
- If your primary focus is industrial importance: The rotary kiln is indispensable because it is the only technology that can reliably and continuously provide the extreme, stable heat required for the chemical reactions that define cement's properties.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln is a highly specialized reactor designed for a single, critical purpose: forging the fundamental building blocks of cement.
Summary Table:
| Kiln Zone | Temperature Range | Key Process | Material Transformation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drying & Preheating | Up to ~800°C | Moisture evaporation, material preheating | Raw mix is dried and heated |
| Calcination | ~800-1100°C | Decomposition of limestone (CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂) | Limestone converts to calcium oxide |
| Sintering (Clinkering) | Up to 1450°C | Partial melting and fusion of materials | Formation of cement clinker nodules |
| Cooling | Rapid cooling from 1450°C | Preserves clinker's chemical properties | Clinker is stabilized for grinding |
Optimize Your Cement Production Process with KINTEK
Understanding the intricacies of the rotary kiln is crucial for efficient and high-quality cement production. Whether you are scaling up operations or optimizing an existing plant, having reliable equipment and expert support is key.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust laboratory equipment and consumables that help you analyze raw materials, monitor clinker quality, and ensure your process meets the highest standards. Our solutions are designed to support the demanding needs of the cement industry, from research and development to quality control.
Ready to enhance your cement manufacturing process?
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's precision equipment can help you achieve superior clinker quality and operational efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product



















