The short answer is that film thickness is not measured directly, but is calculated by analyzing how light waves interact with the film. Specialized instruments measure the interference pattern created by light that is either reflected from or transmitted through the film, and sophisticated algorithms then use this pattern to calculate a precise thickness value.
The core principle is thin-film interference. The choice of measurement method—and therefore the specific calculation—depends entirely on whether the material beneath the film (the substrate) is opaque or transparent.
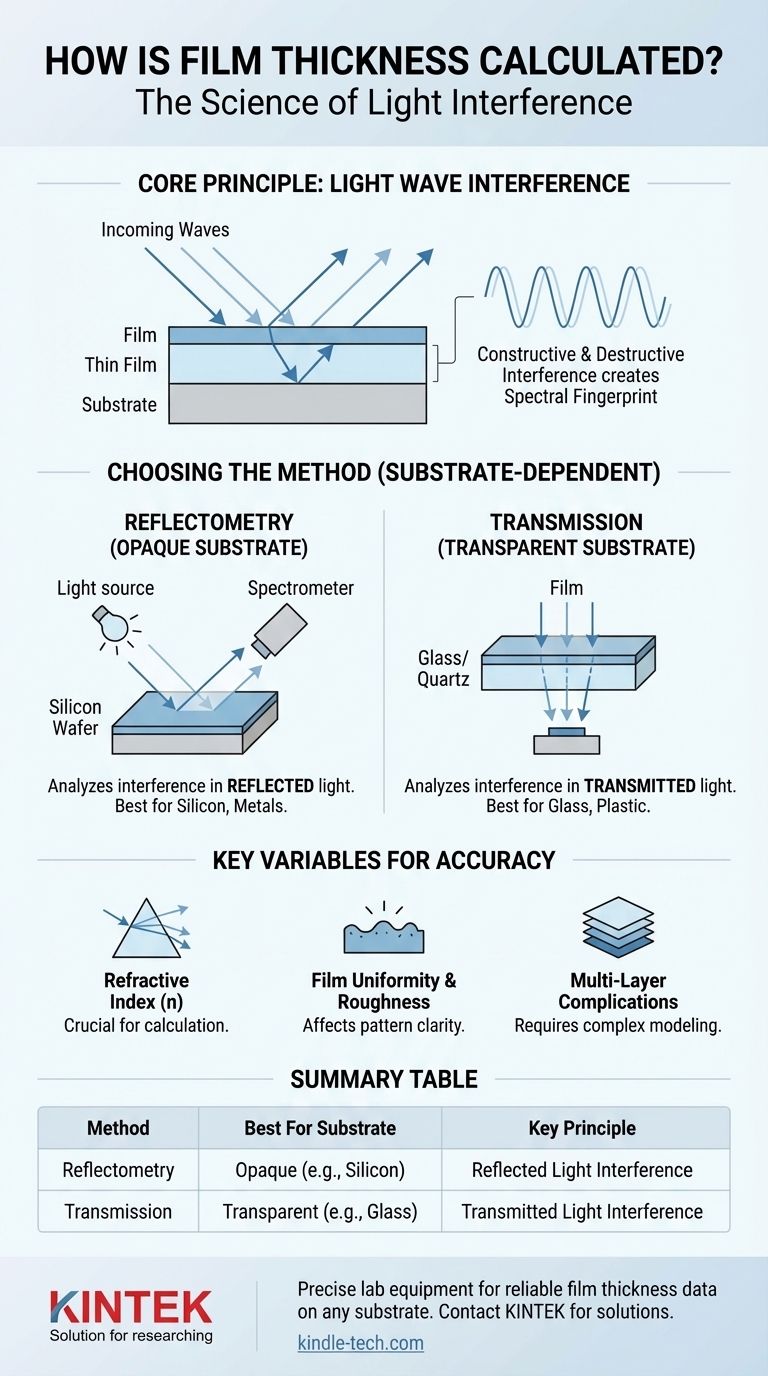
The Core Principle: Light Wave Interference
To understand how thickness is calculated, you must first understand the phenomenon of light wave interference. This is the foundation upon which all modern optical thickness measurements are built.
The Two-Wave Interaction
When light hits a thin film, some of it reflects off the top surface. The rest of the light enters the film, travels through it, and reflects off the bottom surface (the film-substrate interface).
These two separate reflected light waves then travel back and recombine. Because one wave traveled a longer path (down through the film and back up), it is out of phase with the first wave.
Constructive and Destructive Interference
Depending on the film's thickness and the wavelength of the light, these two recombining waves will either reinforce each other (constructive interference) or cancel each other out (destructive interference).
This interference creates a unique spectral "fingerprint" of peaks (constructive) and valleys (destructive) at different wavelengths of light. The distance between these peaks is directly proportional to the film's thickness.
Choosing the Right Measurement Method
The substrate—the material the film is deposited on—is the single most important factor in determining which measurement technique to use.
For Opaque Substrates: Reflectometry
If the film is on an opaque substrate like a silicon wafer, you must use reflectometry.
An instrument shines a light source onto the sample and a detector (spectrometer) measures the intensity of the light that reflects back across a range of wavelengths. By analyzing the interference pattern in this reflected light, software can calculate the film thickness.
For Transparent Substrates: Transmission
If the film is on a transparent substrate like glass or quartz, you can use the transmission method.
Here, light is shone through the entire sample, and the detector measures the light that makes it all the way through. This method analyzes the interference patterns in the transmitted light to determine thickness.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Variables
Simply measuring a spectrum is not enough. The calculation is a modeling process that relies on critical assumptions. An error in these assumptions will lead to an incorrect result.
The Importance of Refractive Index (n)
The calculation is inextricably linked to the film material's refractive index (n), which describes how fast light travels through it.
You cannot accurately calculate thickness without knowing the refractive index. If you provide an incorrect refractive index value to the analysis software, it will return an incorrect thickness value.
Film Uniformity and Roughness
Optical measurement techniques work best on films that are smooth and uniform.
If the film surface is rough or its thickness varies significantly across the measurement spot, the interference pattern will be muted or distorted, making an accurate calculation difficult or impossible.
Multi-Layer Complications
When dealing with a stack of multiple thin films, the light reflects from every interface. This creates a highly complex interference pattern that requires more advanced modeling software to deconstruct and accurately calculate the thickness of each individual layer.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The method you choose is dictated by your sample, but accuracy depends on understanding the entire system.
- If your primary focus is on films on silicon or metal: You will be using reflectometry. Focus on ensuring your material's refractive index is well-characterized.
- If your primary focus is on films on glass or plastic: You can use transmission measurements, which are often less sensitive to back-surface reflections and can provide cleaner data.
- If your primary focus is absolute accuracy: You must validate not only the thickness but also the optical constants (like refractive index) of your material, as the two are calculated together.
Ultimately, mastering film thickness measurement is about controlling the variables that influence how light interacts with your material.
Summary Table:
| Measurement Method | Best For Substrate Type | Key Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Reflectometry | Opaque (e.g., Silicon Wafer) | Analyzes interference pattern in reflected light. |
| Transmission | Transparent (e.g., Glass, Quartz) | Analyzes interference pattern in transmitted light. |
Need to accurately measure film thickness in your lab? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing precise tools for reflectometry and transmission measurements. Our expertise ensures you get reliable data for your films on silicon, glass, or complex multi-layer stacks. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs and achieve superior measurement accuracy.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Buchner Funnel and Triangular Funnel
- Laboratory manual slicer
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of laminating? Protect and Enhance Your Documents for Long-Term Use
- Why is a vacuum hot-pressing furnace preferred for C_fiber/Si3N4 composites? Achieve High Density & Fiber Protection
- What is the advantage by using hot press forming? Achieve Stronger, More Complex Parts
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of hot pressing? Choose the Right Powder Metallurgy Process
- What is hot press moulding? Achieve Superior Density and Complex Shapes with Heat and Pressure





