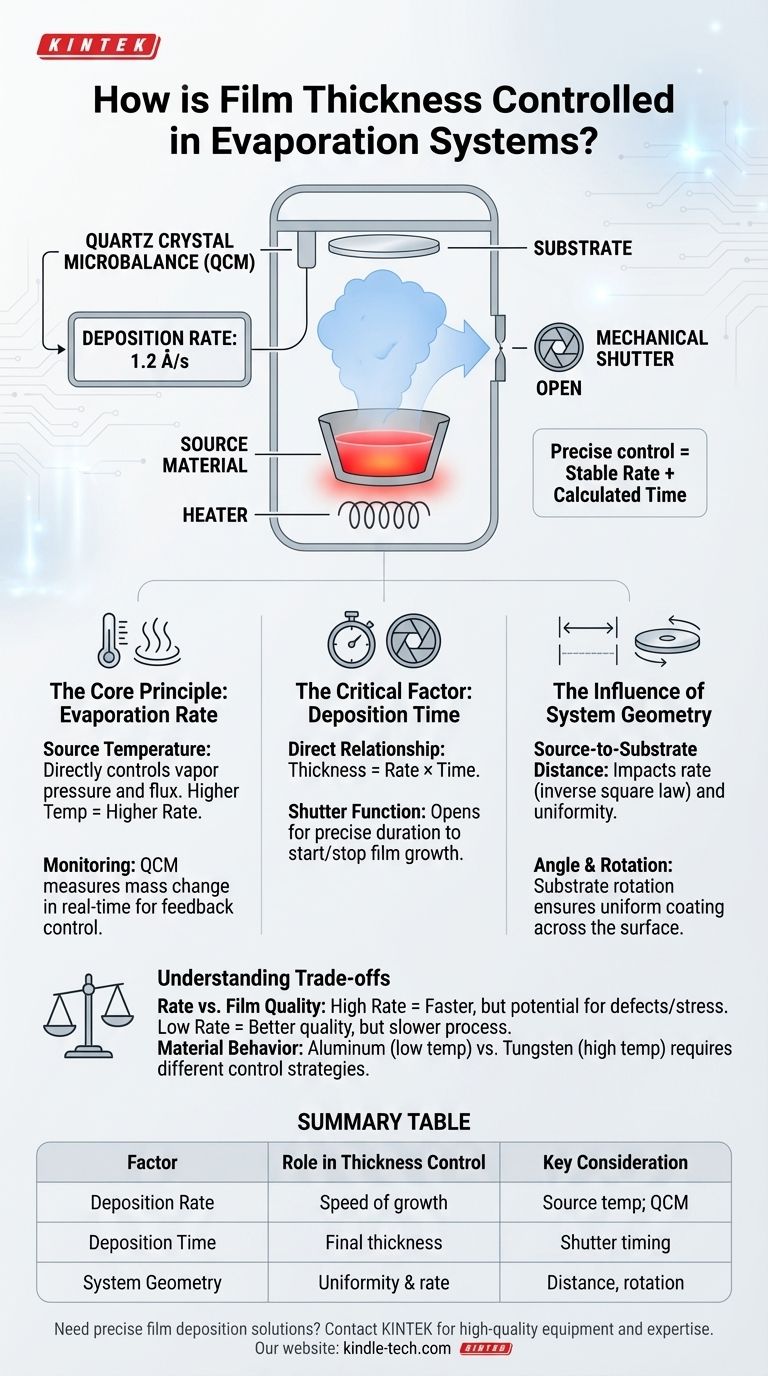
In short, film thickness in an evaporation system is controlled by three primary factors. These are the rate of deposition (which is driven by the source material's temperature), the total duration of the deposition process, and the physical geometry of the system, specifically the distance from the source to the substrate.
Precise thickness control is not about manipulating a single setting. It's about achieving a stable, known deposition rate and then exposing the substrate for a precisely calculated amount of time.
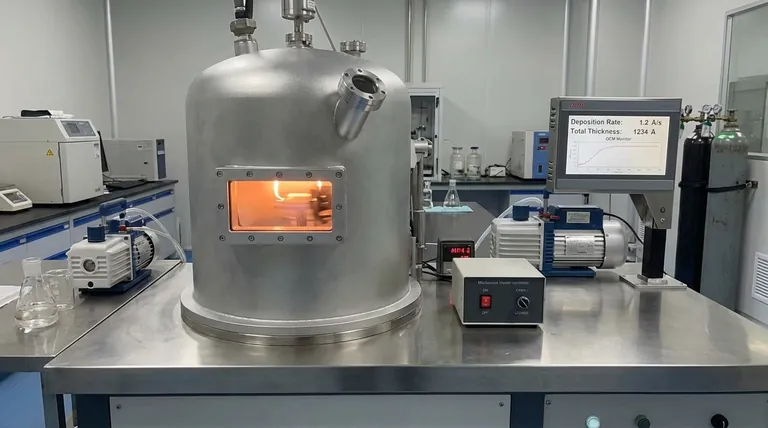

The Core Principle: Evaporation Rate
The foundation of thickness control is establishing a steady and predictable rate at which your material builds up on the substrate. This rate is not set directly; it's a result of other physical parameters.
The Role of Temperature
The temperature of the source material (the evaporant) is the primary engine of the process.
Heating the source increases its vapor pressure. This is the pressure at which the material is in equilibrium between its solid/liquid and gas phases.
A higher temperature leads to a much higher vapor pressure, causing significantly more atoms or molecules to leave the source and travel through the vacuum chamber. This directly increases the deposition rate.
Monitoring and Stabilizing the Rate
To achieve a specific thickness, you must first achieve a stable rate. Minor fluctuations in source temperature will cause the rate to drift, compromising the final thickness.
Advanced systems use a quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) to monitor the deposition rate in real-time, allowing for feedback control to maintain a constant rate.
The Critical Factor: Deposition Time
Once a stable deposition rate is established, time becomes the most direct and simple variable to control.
A Direct Relationship
The relationship is straightforward: Final Thickness = Deposition Rate × Time.
For example, if you establish a stable rate of 1 Angstrom per second (Å/s), a 100-second deposition will yield a 100 Å thick film.
The Function of the Shutter
Nearly all evaporation systems use a mechanical shutter positioned between the source and the substrate.
The shutter remains closed while you heat the source and stabilize the deposition rate. When you are ready, the shutter opens for the precise duration required, then closes to abruptly stop film growth.
The Influence of System Geometry
The physical layout of the deposition chamber has a profound and often overlooked impact on the final film.
Source-to-Substrate Distance
The distance between the evaporation source and the substrate is critical. The flux of evaporated material decreases with distance, generally following an inverse square law.
Increasing this distance lowers the deposition rate, meaning a longer deposition time is needed for the same thickness. However, a greater distance often improves the uniformity of the film across the substrate.
Angle of Incidence
The angle at which the material vapor arrives at the substrate also affects thickness. Areas of the substrate directly above the source will receive more material and grow a thicker film than areas at the edge.
This is why many systems incorporate substrate rotation to average out these geometric effects and achieve better uniformity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Controlling film thickness involves balancing competing factors to achieve the desired outcome.
Rate vs. Film Quality
A high deposition rate is faster and ideal for high-throughput applications. However, it can sometimes lead to films with higher stress, more structural defects, or lower density.
A slow deposition rate generally produces higher-quality, denser films but increases the process time and the risk of incorporating contaminants from the vacuum chamber.
Material-Specific Behavior
Every material has a unique vapor pressure curve. Materials like aluminum evaporate at relatively low temperatures, making rate control easier.
Refractory metals like tungsten or tantalum require extremely high temperatures, making stable rate control much more challenging.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Your specific goal will determine which variables you should prioritize for optimization.
- If your primary focus is high precision and quality: Use a QCM for real-time rate monitoring, opt for a slower, more stable deposition rate, and ensure your temperature control is rock-solid.
- If your primary focus is high throughput: Work to find the fastest possible deposition rate that still provides acceptable film quality for your application.
- If your primary focus is film uniformity: Increase the source-to-substrate distance and implement substrate rotation during the deposition.
Mastering film thickness control is a matter of systematically balancing these interconnected variables to meet the demands of your material and application.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Role in Thickness Control | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Deposition Rate | Determines speed of film growth | Controlled by source temperature; monitored with a QCM |
| Deposition Time | Directly sets final thickness | Precisely managed using a mechanical shutter |
| System Geometry | Affects uniformity and effective rate | Optimize source-to-substrate distance and use substrate rotation |
Need precise and reliable film deposition for your research or production? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including evaporation systems and consumables, designed to give you unparalleled control over film thickness and quality. Our experts can help you select the right system and optimize your process for your specific material and application. Contact our team today to discuss your laboratory needs and achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- How does PACVD equipment improve DLC coatings? Unlock Low Friction and High Heat Resistance
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies



















