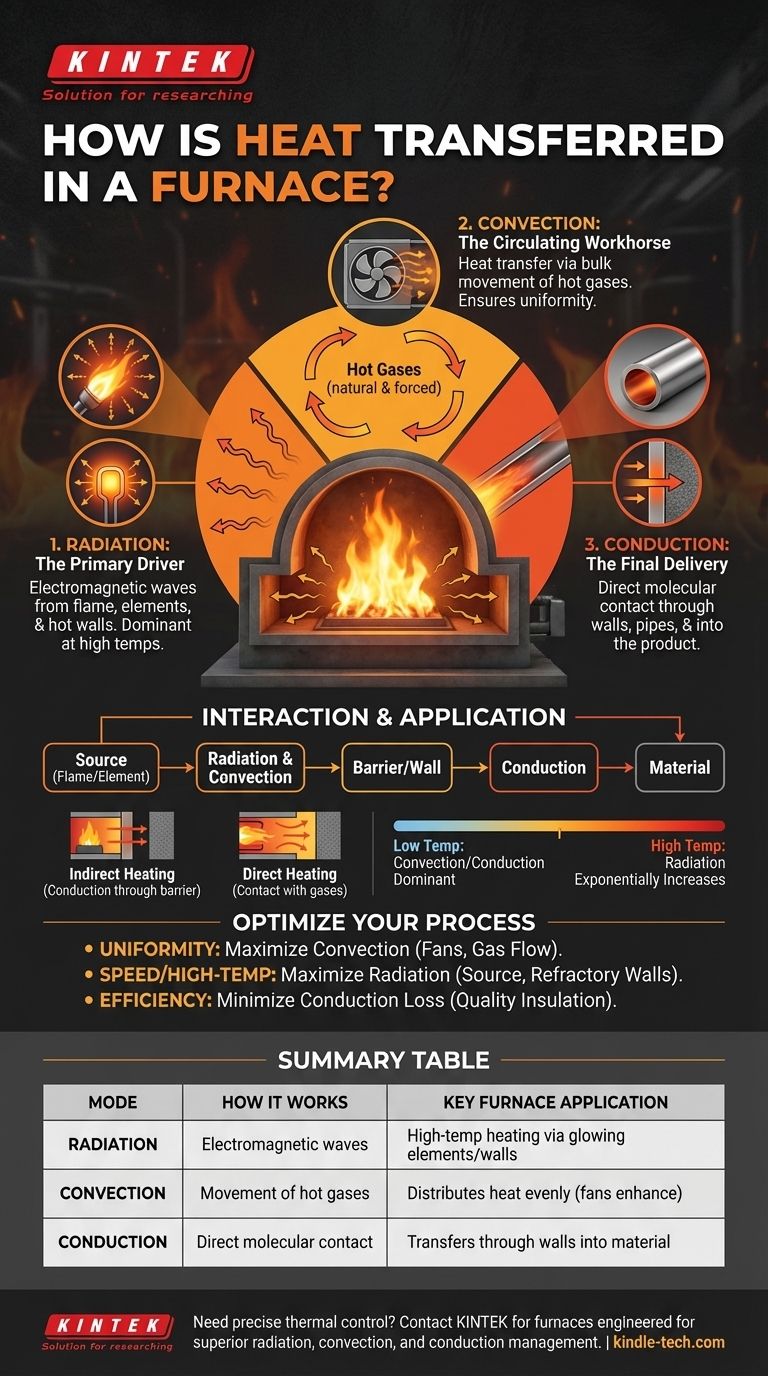
In any furnace, heat is transferred through a combination of three fundamental physical processes. These are radiation, convection, and conduction, which work in concert to move thermal energy from the initial source—whether a flame or an electric element—to the material being processed.
While furnaces create heat through combustion or electricity, the real challenge is moving that heat effectively. Understanding how radiation, convection, and conduction interact is the key to controlling temperature, ensuring product quality, and optimizing energy use.

The Three Pillars of Furnace Heat Transfer
Every furnace, regardless of its design or fuel source, relies on the same three mechanisms to move heat. The efficiency and uniformity of your heating process depend entirely on how these three modes are balanced.
Radiation: The Primary Driver
Radiation transfers heat via electromagnetic waves, just like a campfire warms your hands from a distance without air needing to move.
In a furnace, the flame, glowing electric elements, and hot interior walls all radiate thermal energy in all directions. This mode of transfer requires no medium and can even occur across a vacuum.
At the very high temperatures found in many industrial furnaces, radiation is often the single most dominant mode of heat transfer.
Convection: The Circulating Workhorse
Convection is heat transfer through the bulk movement of fluids—in this case, the hot gases inside the furnace.
As combustion gases or heated air become hot and less dense, they rise and circulate, carrying thermal energy with them. This natural circulation distributes heat throughout the chamber.
Many modern furnaces use fans to create forced convection, which dramatically improves the speed and uniformity of heating by ensuring hot gases reach every surface.
Conduction: The Final Delivery
Conduction is heat transfer through direct molecular contact, like the way heat travels up the handle of a metal spoon left in a hot drink.
Heat conducts through the solid metal walls of the furnace, through any pipes or tubes containing the material, and into the core of the product itself.
This mechanism is also what you fight against with insulation. Good insulation is simply a material that conducts heat very poorly, keeping the energy inside the furnace where it belongs.
Understanding How These Modes Interact
These three modes do not operate in isolation. They form a continuous chain of energy transfer from the source to the final product.
The Chain of Transfer: An Example
Imagine a common industrial heater. A flame first radiates heat to a metal tube and also heats the surrounding air.
That hot air then circulates around the tube, transferring additional heat via convection.
Finally, all of that energy must conduct through the solid wall of the tube to heat the fluid or material moving inside it.
The Impact of Temperature
The dominant mode of transfer changes with temperature. At lower temperatures, convection and conduction often play the most significant roles.
As the furnace temperature rises, however, the contribution from radiation increases exponentially. In high-temperature applications like steel reheating, radiation from the walls and flame becomes the primary mechanism for heating the product.
Indirect vs. Direct Heating
Most industrial furnaces rely on indirect heating. The heat source is separated from the material by a physical barrier, making conduction through that barrier a critical and often limiting step.
In direct heating, the flame or hot gases make direct contact with the material being processed. This design maximizes heat transfer from radiation and convection but can be unsuitable for sensitive products.
Applying This Knowledge to Your Goal
By understanding this balance, you can diagnose heating issues and optimize your process for a specific outcome.
- If your primary focus is uniform heating: You must optimize for strong and consistent convection using fans and intelligent gas flow design.
- If your primary focus is rapid, high-temperature processing: You need to maximize radiation from the heat source and the furnace's internal refractory walls.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: You must minimize unwanted heat loss through conduction by investing in high-quality insulation.
By mastering the interplay of these three transfer mechanisms, you gain precise control over your thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Heat Transfer Mode | How It Works | Key Application in Furnaces |
|---|---|---|
| Radiation | Transfer via electromagnetic waves. | Dominant at high temperatures; heats via glowing elements/walls. |
| Convection | Transfer via movement of hot gases. | Distributes heat evenly; enhanced by fans for forced convection. |
| Conduction | Transfer through direct molecular contact. | Delivers heat through furnace walls and into the material itself. |
Need precise thermal control for your lab processes? Understanding heat transfer is the first step to optimizing your furnace performance. At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing furnaces engineered for superior radiation, convection, and conduction management. Whether your priority is uniformity, speed, or energy efficiency, our solutions are designed to meet your specific laboratory needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your thermal processing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the mechanism of reactive sputtering? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- How to operate an electric arc furnace? Master the Cycle for Efficient Steel Production
- What function does heat treatment equipment perform in recycling Vitrimers? Transform Static Waste into Renewables
- How does laboratory drying equipment affect the performance of hydrogel carriers? Optimize Drug Loading and Release
- What is a gold sputtering target? A High-Purity Source for Precision Gold Coatings
- What are the advantages disadvantages and uses of sheet metal? The Ultimate Guide to Material Selection
- Does heat treatment increase the strength of a material? Tailor Your Material's Properties
- What is a rotary vacuum evaporator? A Guide to Gentle & Efficient Solvent Removal



















