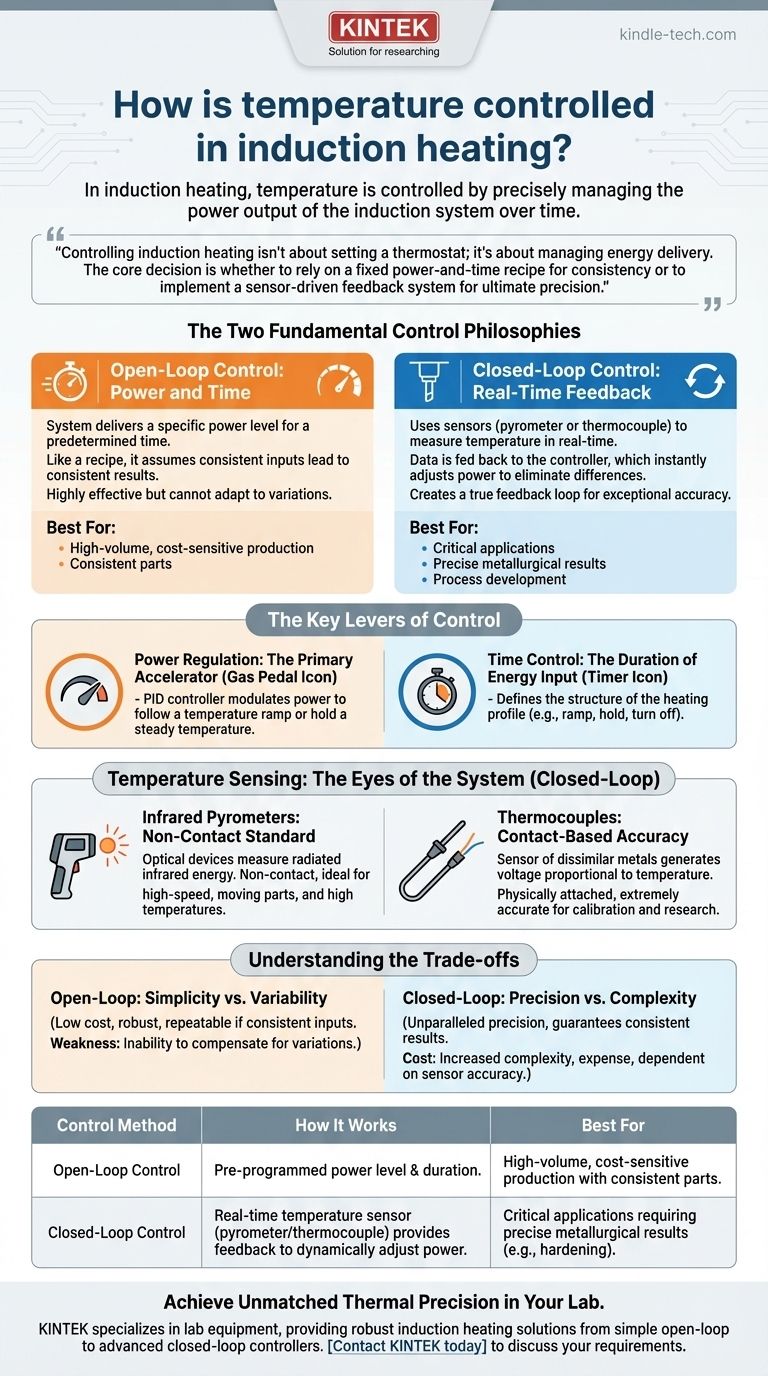
In induction heating, temperature is controlled by precisely managing the power output of the induction system over time. This is accomplished using one of two primary methods: a simple, pre-programmed schedule of power and duration (open-loop control), or a more sophisticated system that uses real-time temperature sensors to continuously adjust power and achieve a specific target (closed-loop control).
Controlling induction heating isn't about setting a thermostat; it's about managing energy delivery. The core decision is whether to rely on a fixed power-and-time recipe for consistency or to implement a sensor-driven feedback system for ultimate precision.

The Two Fundamental Control Philosophies
To achieve a target temperature, you must regulate the amount of energy the workpiece absorbs. This is done through two distinct approaches.
Open-Loop Control: Power and Time
This is the most straightforward method of control. The system is programmed to deliver a specific power level (e.g., 80% of maximum power) for a predetermined amount of time (e.g., 7.5 seconds).
This approach works like a recipe. It assumes that if you start with the same ingredients (part geometry, material, initial temperature) and apply the same process (power, time, part position), you will get the same result every time.
It is highly effective for many applications, but it cannot adapt to variations in the process.
Closed-Loop Control: Real-Time Feedback
This method uses a temperature sensor, such as a pyrometer or thermocouple, to measure the part's temperature in real-time.
This temperature data is fed back to the power supply's controller. The controller then compares the actual temperature to the desired temperature profile and instantly adjusts the power output to eliminate any difference.
This creates a true feedback loop, allowing the system to dynamically compensate for variables and hit precise temperature targets with exceptional accuracy.
The Key Levers of Control
Regardless of the philosophy, the temperature is ultimately managed by manipulating a few key variables.
Power Regulation: The Primary Accelerator
The power supply's output is the "gas pedal" of the induction system. Increasing the power increases the strength of the magnetic field, which induces more current in the workpiece and generates heat faster.
In a closed-loop system, a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller constantly modulates this power level to precisely follow a temperature ramp or hold a steady "soak" temperature.
Time Control: The Duration of Energy Input
Time is a critical variable in every heating process. In an open-loop system, it is the primary factor, along with power, that determines the final temperature.
In a closed-loop system, time defines the structure of the heating profile. For example, a profile might be "ramp to 800°C in 4 seconds, hold at 800°C for 10 seconds, then turn off."
Frequency and Coil Design: The Foundational Parameters
The system's operating frequency and the design of the induction coil are fundamental to the process, but they are not typically used for real-time temperature control.
These parameters are selected during the initial process design phase. They determine where and how efficiently the heat is generated. Higher frequencies heat the surface (skin effect), while lower frequencies penetrate deeper into the part.
Temperature Sensing: The Eyes of the System
In a closed-loop system, the accuracy of the entire process depends on the quality of the temperature measurement.
Infrared Pyrometers: The Non-Contact Standard
Pyrometers are optical devices that measure the infrared energy radiated by a hot object to determine its temperature. They are the most common sensors for induction heating.
Their key advantage is being non-contact, making them ideal for high-speed automated lines, moving parts, and very high temperatures where contact sensors would be destroyed.
Thermocouples: Contact-Based Accuracy
A thermocouple is a sensor made of two dissimilar metals that generates a small voltage proportional to its temperature. It must be physically attached to the workpiece, often by a small tack weld.
While impractical for most production applications, thermocouples are extremely accurate and are invaluable for initial process development, scientific research, and for calibrating pyrometers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between open-loop and closed-loop control is a critical engineering decision with direct consequences for cost, complexity, and quality.
Open-Loop: Simplicity vs. Variability
An open-loop system is simple, robust, and low-cost. It is highly repeatable as long as all input conditions—such as initial part temperature, positioning in the coil, and material properties—remain perfectly consistent.
Its major weakness is its inability to compensate for process variations. A part that is slightly warmer at the start or positioned farther from the coil will reach a different final temperature, which may be unacceptable for critical applications.
Closed-Loop: Precision vs. Complexity
A closed-loop system offers unparalleled precision and guarantees a consistent result even when input variables change. It can perfectly replicate a thermal profile, ensuring repeatable metallurgical properties.
This precision comes at the cost of increased complexity and expense. The system requires sensors, sophisticated controllers, and careful setup. It is also dependent on the sensor's accuracy; a dirty pyrometer lens or incorrect emissivity setting can introduce errors.
Choosing the Right Control Strategy
Your choice between open-loop and closed-loop control depends entirely on your process requirements and end goals.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive, high-volume production where part consistency is high: An open-loop system based on power and time is often the most robust and economical solution.
- If your primary focus is metallurgical precision for critical components (like hardening or tempering): A closed-loop system using a pyrometer is non-negotiable for achieving repeatable material properties.
- If your primary focus is process development or laboratory work: A closed-loop system, often with thermocouples, is essential for gathering accurate data and establishing a reliable heating process.
By understanding these control principles, you can architect an induction heating process that delivers precise, repeatable results every cycle.
Summary Table:
| Control Method | How It Works | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Open-Loop Control | Pre-programmed power level & duration. | High-volume, cost-sensitive production with consistent parts. |
| Closed-Loop Control | Real-time temperature sensor (pyrometer/thermocouple) provides feedback to dynamically adjust power. | Critical applications requiring precise metallurgical results (e.g., hardening). |
Achieve Unmatched Thermal Precision in Your Lab
Whether you are developing a new process in a research setting or require high-volume, repeatable heating for production, selecting the right control strategy is critical. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing robust induction heating solutions tailored to your specific needs—from simple open-loop systems to advanced closed-loop controllers with precise temperature feedback.
Let our experts help you design a system that guarantees precise, repeatable results for your most critical applications. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your induction heating requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- How much electricity does an induction furnace use? Calculate Your True Energy Cost
- What is the lining material for an induction furnace? A Guide to High-Performance Refractories
- Do induction heater coils get hot? Understanding Heat Sources and Cooling Needs
- Why does an induction furnace blast? Prevent Catastrophic Steam Explosions in Your Foundry
- How does the induction furnace work? A Guide to Rapid, Clean Metal Melting
- What is the role of a high-frequency induction melting furnace in super duplex stainless steel prep? Achieve Precision
- Can you melt steel with induction? Unlock High-Purity, Efficient Metal Melting
- Can induction furnace melt iron? Unlock High-Efficiency, Clean Melting for Iron & Alloys

















