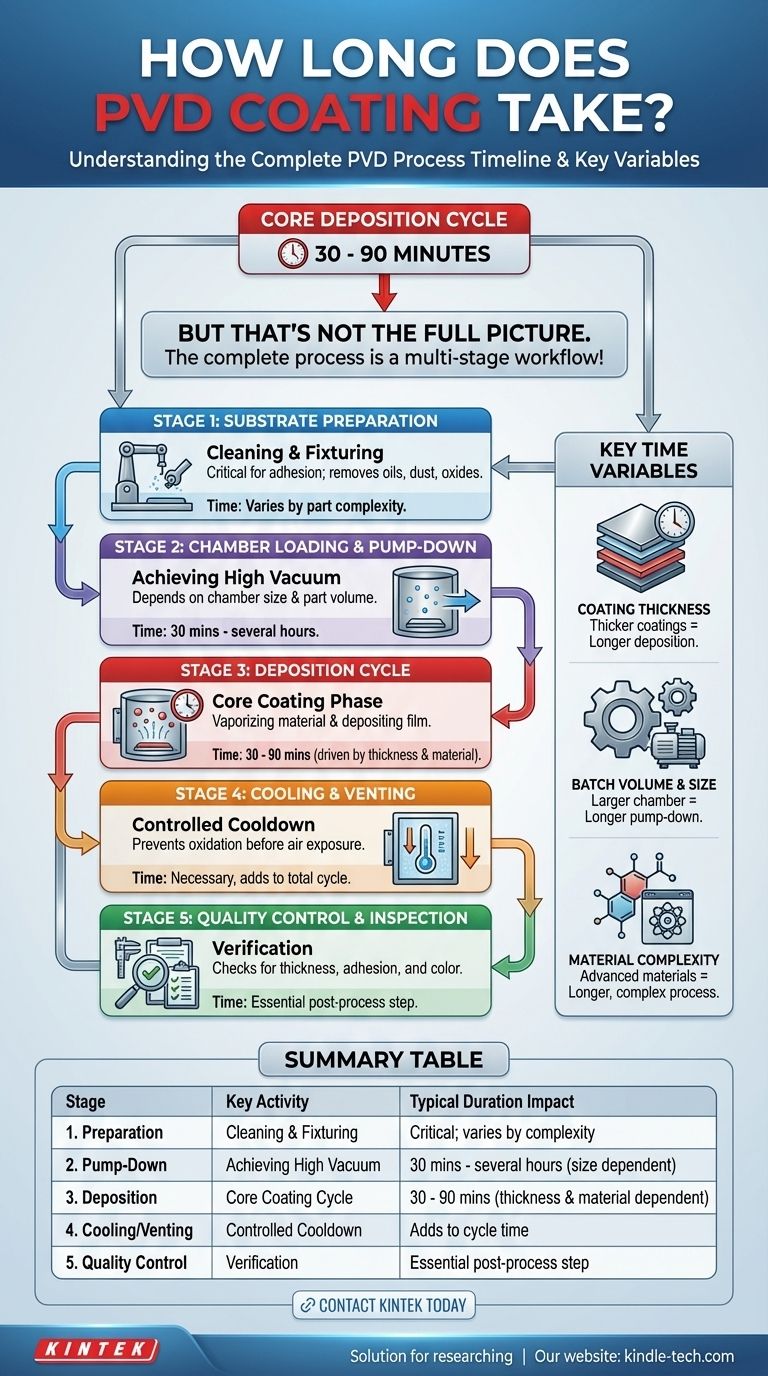
For a standard batch, the core PVD coating process that occurs inside the vacuum chamber typically takes between 30 and 90 minutes. However, this deposition time is only a fraction of the total lead time. The complete cycle, from initial part preparation to final quality inspection, is a multi-stage workflow where factors outside the chamber often dictate the overall duration.
While the vacuum deposition cycle itself is relatively short, the total process time is primarily driven by substrate preparation, chamber pump-down, desired coating thickness, and post-process quality control. Focusing only on the in-chamber time is a common oversimplification.

Deconstructing the Total PVD Timeline
To accurately estimate time, you must understand that PVD is not a single action but a sequence of critical stages. Each stage contributes to the total time required to produce a finished, coated component.
Stage 1: Substrate Preparation and Cleaning
Before any coating can begin, the part to be coated (the substrate) must be perfectly clean. This is non-negotiable for ensuring proper coating adhesion.
This stage involves removing any oils, grease, dust, or oxides from the surface through various chemical and mechanical cleaning methods. Inadequate preparation is a primary cause of coating failure.
Stage 2: Chamber Loading and Pump-Down
Once cleaned, parts are loaded into fixtures and placed inside the PVD chamber. The chamber is then sealed, and a powerful vacuum system begins evacuating the air.
Achieving the necessary high-vacuum environment does not happen instantly. The time required for this "pump-down" phase depends on the size of the chamber and the cleanliness of the parts and internal fixtures. This step alone can take a significant amount of time.
Stage 3: The Deposition Cycle
This is the core "coating" phase and what is typically measured in the 30-90 minute timeframe. It involves heating the substrates and then using a high-energy source to vaporize a solid source material (the target).
These vaporized atoms travel through the vacuum and condense on the substrates, forming a thin, dense, and highly adherent film, atom by atom. The precise duration of this step is determined by the specific coating material and the required final thickness.
Stage 4: Cooling and Venting
After the deposition is complete, the parts must cool down within the vacuum chamber. Attempting to expose hot components to air can cause oxidation and compromise the coating's surface.
Once cooled to a safe temperature, the chamber is slowly vented with an inert gas before being brought back to atmospheric pressure, allowing the doors to be opened and the parts removed.
Stage 5: Quality Control and Inspection
The process does not end when the parts leave the chamber. Each batch typically undergoes quality control (QC) to ensure it meets specifications.
This may involve using advanced equipment like an X-ray fluorescent (XRF) machine to verify coating thickness and composition or a spectrophotometer to confirm color consistency.
Understanding the Key Time Variables
The duration of the PVD process is not fixed. It is a dynamic outcome based on several trade-offs between speed, cost, and final coating quality.
Coating Thickness vs. Deposition Time
This is the most direct relationship. A thicker coating requires more material to be vaporized and deposited onto the substrate, which directly extends the time of the deposition cycle.
Substrate Size and Batch Volume
Larger individual parts or a larger volume of parts require a bigger vacuum chamber. A larger chamber has more atmospheric gas to remove, leading to a longer pump-down time. It also requires more time to achieve uniform heating.
Coating Material and Complexity
Depositing a simple, single-element metal is often faster than creating a complex compound. Some advanced coatings require reacting the vaporized metal with specific gases (like nitrogen or oxygen) inside the chamber, which adds complexity and time to the process control steps.
Estimating Your PVD Process Time
To get a realistic estimate for your project, you must consider your primary objective. The answer changes based on whether you are optimizing for speed, quality, or production throughput.
- If your primary focus is rapid turnaround: Use standard, thinner coatings on smaller parts to minimize both pump-down and deposition cycle times.
- If your primary focus is performance and quality: Expect longer lead times to accommodate thicker coatings, complex materials, and the extensive quality control necessary to validate results.
- If your primary focus is large-scale production: The key to improving throughput is optimizing the workflow around the chamber, including pre-cleaning and batch loading strategies, as these are often bigger bottlenecks than the deposition cycle itself.
Understanding these individual stages and variables allows you to move beyond a simple time estimate and strategically plan your manufacturing process for optimal results.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Activity | Typical Duration Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Substrate Cleaning & Fixturing | Critical for adhesion; varies by part complexity |
| 2. Pump-Down | Achieving High Vacuum | 30 mins - several hours (chamber size dependent) |
| 3. Deposition | Core Coating Cycle | 30 - 90 mins (coating thickness & material dependent) |
| 4. Cooling/Venting | Controlled Cooldown | Necessary to prevent oxidation; adds to cycle time |
| 5. Quality Control | Thickness & Color Verification | Essential for quality assurance; post-process step |
Need a precise PVD coating timeline for your specific components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing lab equipment and consumables for advanced coating processes. Our expertise ensures you get accurate estimates and optimal results, whether you're prioritizing speed, quality, or high-volume production.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK can streamline your PVD coating workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















