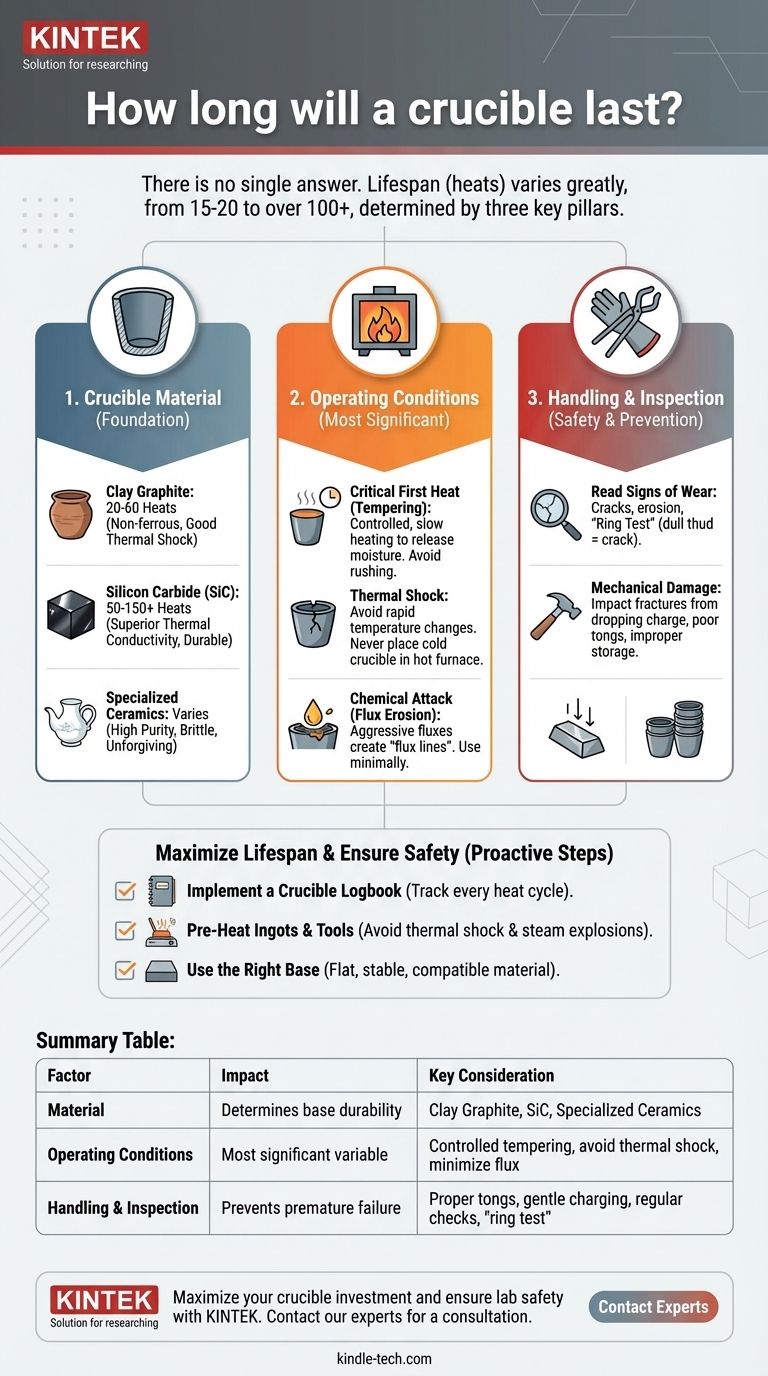
There is no single answer to how long a crucible will last. A crucible's lifespan is measured in "heats" (melting cycles) and can range from as few as 15-20 heats to well over 100. This massive variation is not due to manufacturing defects but is overwhelmingly determined by the crucible's material, the specific conditions of its use, and—most importantly—the care and handling provided by the operator.
Your crucible's lifespan is not a fixed number; it is a direct result of your process. By understanding the key failure points, you can move from asking "how long will it last?" to actively controlling how long you make it last.
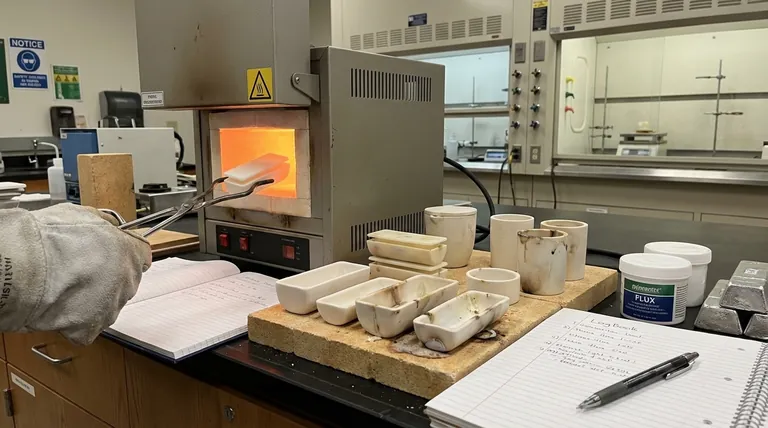

The Pillars of Crucible Longevity
A crucible's life is a battle against thermal shock, chemical attack, and mechanical stress. How well it survives depends on its composition and how you manage these forces.
Pillar 1: Crucible Material
The material a crucible is made from is the foundation of its performance. Each type has inherent strengths and weaknesses.
- Clay Graphite: These are a common and cost-effective choice for melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum, brass, and bronze. They offer good resistance to thermal shock but have a moderate lifespan, often in the range of 20-60 heats under good conditions.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): SiC crucibles have superior thermal conductivity, meaning they transfer heat to the melt very efficiently. They are more durable and resistant to erosion than clay graphite, often lasting 50 to 150+ heats. They are a workhorse for aluminum, copper alloys, and precious metals.
- Zirconia, Alumina, and Pure Ceramics: These are highly specialized crucibles used for high-purity melts, reactive metals, or extremely high temperatures (e.g., platinum or steel alloys). While they can be durable under very specific, controlled conditions, they are often more brittle and far less forgiving of rough handling or thermal shock.
Pillar 2: Operating Conditions
How you use the crucible during a melt is the most significant factor in its lifespan.
- The Critical First Heat (Tempering): A new crucible contains moisture from manufacturing and storage. The first heat must be slow and controlled, allowing this moisture to escape gently. Rushing this process will cause the water to turn to steam internally, creating micro-fractures that guarantee a short life.
- Thermal Shock: Rapid temperature change is the primary enemy of any ceramic. Never place a cold crucible into a furnace already at high heat, and never set a hot crucible onto a cold, wet, or concrete surface.
- Chemical Attack from Flux: Fluxes are essential for cleaning a melt, but they are chemically aggressive. They eat away at the crucible's interior wall, creating a distinct "flux line" of erosion. Using excessive or overly aggressive flux will dramatically shorten a crucible's life.
Understanding the Risks and Failure Modes
Knowing what to look for is critical for both maximizing life and ensuring safety. A failing crucible is a serious hazard.
Reading the Signs of Wear
Regular inspection is non-negotiable. Before every use, check for:
- Cracks: Look for vertical cracks or fine, web-like "star" cracks, especially on the bottom. A crack of any kind is a signal that the crucible may be near the end of its life.
- Erosion: Note the depth of the flux line. If the wall feels significantly thinner in that area, the crucible's structural integrity is compromised.
- The "Ring Test": Gently tap the side of a cool, empty crucible with a piece of wood or metal. A sound crucible will produce a clear, high-pitched ring. A dull thud indicates an internal crack you cannot see.
Mechanical Damage: The Silent Killer
Impacts and stress from improper handling are a common cause of premature failure.
- Charging: Never drop heavy ingots or scrap directly into an empty crucible. This can cause impact fractures. Carefully lower the first pieces in, or create a cushion with smaller material.
- Tongs and Tools: Use properly fitting tongs that grip the crucible securely without pinching it. Poorly fitting tongs create stress points that can lead to cracking.
- Storage: Crucibles are fragile. Store them in a dry, warm area off the floor. Do not stack them inside one another without protective padding, as this can easily lead to chipping and cracking.
How to Maximize Crucible Lifespan
A proactive approach turns chance into predictable performance.
Implement a Crucible Logbook
For each new crucible, start a log. Record the date of its first use and make a tally mark for every heat cycle. This simple practice provides invaluable data, helping you predict replacement needs and identify which practices are extending or shortening crucible life.
Pre-Heat Ingots and Tools
Placing cold, potentially damp tools or charge material into molten metal is both a safety hazard (steam explosion) and a source of thermal shock for the crucible. Pre-heating these items on top of the furnace is a best practice.
Use the Right Base
The crucible must sit on a flat, stable base block inside the furnace that is the same material or compatible with the crucible. An uneven base creates stress points on the crucible floor, leading to cracks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational priority dictates your focus.
- If your primary focus is maximizing lifespan for cost savings: Master the slow, careful tempering of new crucibles and keep a detailed logbook for every heat.
- If your primary focus is safety and avoiding failure: Your most critical step is the pre-heat inspection—check for cracks and perform the "ring test" before every single use.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Ensure your tongs fit perfectly and that your charging method is gentle to avoid mechanical stress and premature replacement.
Ultimately, the lifespan of your crucible is a direct reflection of your skill and discipline as an operator.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Lifespan | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Crucible Material | Determines base durability & heat resistance | Clay Graphite (20-60 heats), Silicon Carbide (50-150+ heats), Specialized Ceramics (varies) |
| Operating Conditions | Most significant variable; proper use extends life | Controlled first heat (tempering), avoiding thermal shock, minimizing flux erosion |
| Handling & Inspection | Prevents premature failure from mechanical stress | Proper tongs, gentle charging, regular crack checks, and the 'ring test' |
Maximize your crucible investment and ensure lab safety with the right equipment from KINTEK.
Are you experiencing short crucible lifespans or concerned about safety risks? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables. We can help you select the ideal crucible material for your specific application and provide expert guidance on best practices for operation and handling.
Contact our experts today for a consultation to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how our solutions can enhance your process efficiency, reduce costs, and improve safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is the use of high-purity alumina crucibles necessary for NMC powders? Ensure Purity in Cathode Synthesis
- What are the functional advantages of using high-purity alumina crucibles? Achieve Precise Oxidation Data
- What role do high-purity alumina crucibles play in high-temperature steam oxidation? Ensure Data Integrity up to 1350°C
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles used for LATP? Preserve Purity and Conductivity in Sintering
- What is the function of alumina crucibles in Na3V2(PO4)2F3 synthesis? Ensure Purity in NVPF Production



















