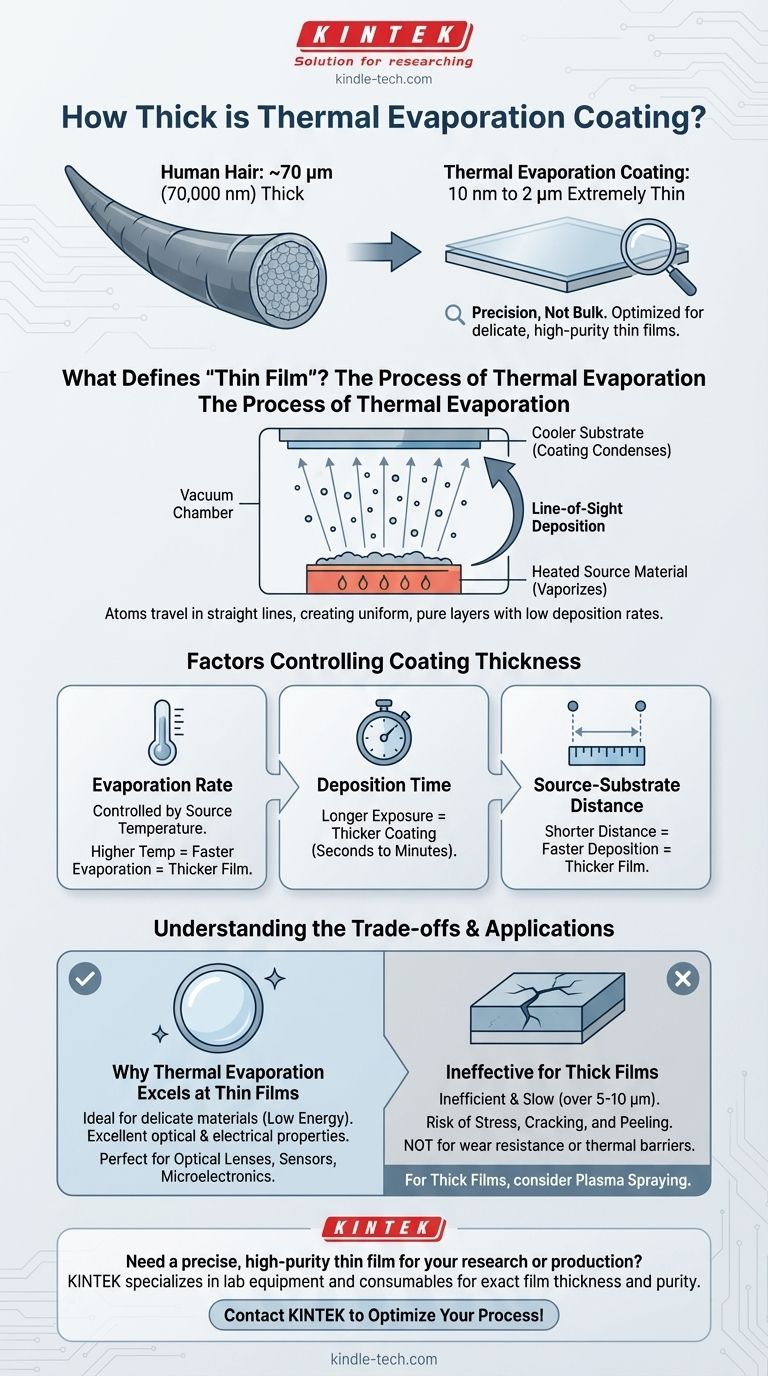
In short, thermal evaporation coatings are extremely thin. This physical vapor deposition (PVD) process is designed for precision, typically creating films ranging from a few nanometers (nm) to a few micrometers (µm) thick. The technique's strength lies in its ability to produce highly uniform and pure layers, not in building substantial thickness.
The core principle to understand is that thermal evaporation is a technique fundamentally optimized for creating delicate, high-purity thin films with precise control. It is not a method for producing thick, bulky, or structural coatings.

What Defines "Thin Film" in Thermal Evaporation?
Thermal evaporation operates by heating a source material in a vacuum until it vaporizes. This vapor then travels and condenses onto a cooler substrate, forming the coating. The nature of this process dictates the resulting film's characteristics.
The Typical Thickness Range
The vast majority of applications for thermal evaporation involve coatings between 10 nanometers and 2 micrometers. To put this in perspective, a human hair is about 70 micrometers thick. This process operates on a scale thousands of times smaller.
The Principle of Line-of-Sight Deposition
In the high vacuum of the chamber, evaporated atoms travel in a straight line from the source to the substrate. This line-of-sight travel allows for the creation of very uniform layers but also means the deposition rate is relatively low and gentle.
Precision and Control
The primary advantage of this method is control. By carefully managing the source temperature and deposition time, engineers can achieve highly repeatable films with specific thicknesses, which is critical for applications like optical lenses and electronic components.
Factors That Control Coating Thickness
Achieving a specific thickness is not arbitrary; it is a direct result of several key process parameters that can be precisely manipulated.
Evaporation Rate
The temperature of the source material directly controls how quickly it evaporates. A higher temperature leads to a higher evaporation rate, which deposits a thicker film in the same amount of time.
Deposition Time
This is the most straightforward control factor. The longer the substrate is exposed to the material vapor, the thicker the resulting coating will be. For very thin films, this time can be a matter of seconds.
Source-to-Substrate Distance
The geometry of the deposition chamber is critical. As the vapor expands from the source, its density decreases. Placing the substrate closer to the source will result in a faster deposition rate and a thicker film.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing thermal evaporation is a decision based on specific technical requirements. Its strengths in producing thin films are also its limitations for other applications.
Why Thermal Evaporation Excels at Thin Films
This process is ideal for delicate applications because it imparts very little energy to the substrate. It's a "gentle" coating method perfect for materials sensitive to damage from more energetic processes like sputtering. This results in very pure films with excellent optical or electrical properties.
The Limitation for Thick Films
Attempting to build thick coatings (e.g., over 5-10 micrometers) with thermal evaporation is inefficient and often ineffective. The process is very slow compared to other methods, and internal stresses can build up in the film, causing it to crack or peel away from the substrate.
When a Different Method is Needed
For applications requiring thick films for wear resistance or thermal barriers, other techniques are necessary. For instance, a related PVD process called plasma spraying introduces material as a powder into a hot plasma flame, allowing for the rapid creation of very thick films.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The suitability of thermal evaporation is entirely dependent on your end goal. The central question is not how thick the coating can be, but what properties the final surface needs to have.
- If your primary focus is optical coatings, sensors, or microelectronics: Thermal evaporation is the ideal choice for its precision and ability to create high-purity films in the nanometer-to-micrometer range.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance, corrosion protection, or thermal barriers: You require a robust, thick-film process like plasma spraying or other thermal spray technologies.
Ultimately, the power of thermal evaporation lies not in its ability to build bulk, but in its precision to construct functional surfaces layer by layer.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Typical Range/Characteristic | Key Impact on Thickness |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness Range | 10 nanometers (nm) to 2 micrometers (µm) | Defines the process's primary application scope. |
| Evaporation Rate | Controlled by source temperature | Higher rate = thicker film for a given time. |
| Deposition Time | Seconds to minutes | Longer time = thicker coating. |
| Source-Substrate Distance | Varies with chamber geometry | Shorter distance = faster deposition = thicker film. |
Need a precise, high-purity thin film for your research or production?
Thermal evaporation is ideal for creating delicate coatings for optical lenses, electronic components, and sensors. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables to achieve the exact film thickness and purity your application demands.
Let our experts help you optimize your deposition process. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods



















