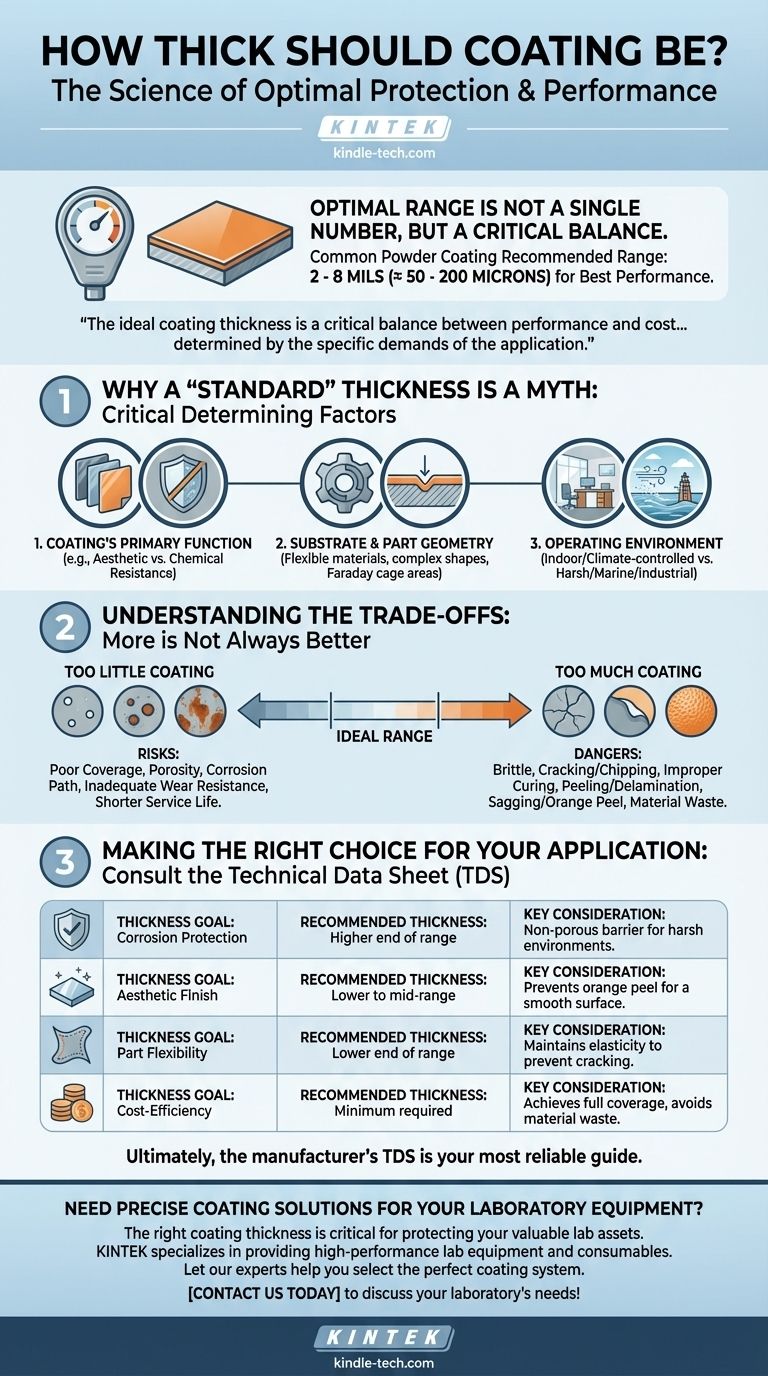
The optimal coating thickness is not a single number but a carefully chosen range dictated by the coating's purpose and the manufacturer's specifications. For many common powder coating applications, the recommended film thickness is typically between 2 to 8 mils (approximately 50 to 200 microns) to achieve the best performance.
The ideal coating thickness is a critical balance between performance and cost. It is determined not by a universal standard, but by the specific demands of the application—balancing the need for protection against the risks of mechanical failure, improper curing, and unnecessary expense.
Why a Single "Standard" Thickness is a Myth
Simply asking for a single number overlooks the critical factors that determine a coating's success. The correct thickness is a function of the coating's job, the surface it's on, and the environment it will face.
The Coating's Primary Function
The reason for the coating is the most important factor. A coating designed for aesthetics has very different requirements than one designed for chemical resistance.
For example, a thin decorative coating provides color and gloss, while a thick anti-corrosion coating must create an impermeable barrier to moisture and oxygen.
The Substrate and Part Geometry
The material being coated matters. A flexible substrate may require a thinner, more elastic coating to prevent cracking, while a rigid steel beam can support a thicker, harder film.
Complex shapes with sharp edges (Faraday cage areas) are notoriously difficult to coat evenly. They often require specific techniques to ensure minimum thickness is achieved on the edges without building up excessively in the corners.
The Operating Environment
The service environment dictates the level of protection needed. A part used indoors in a climate-controlled office requires a much less robust coating than equipment operating on a marine vessel exposed to salt spray.
Harsh industrial environments involving chemicals, abrasion, or UV exposure demand thicker and more specialized coating systems to prevent premature failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Coating Thickness
More is not always better. Both insufficient and excessive coating thickness can lead to catastrophic failure, just for different reasons. This is the most common point of failure in coating applications.
The Risks of Too Little Coating
Applying a coating too thinly is a direct path to failure. The most common issues are poor coverage and porosity.
This leaves microscopic pinholes in the film, giving corrosion a direct path to the substrate. It also results in inadequate wear resistance and a shorter service life.
The Dangers of Too Much Coating
Excessive film thickness is just as problematic. An overly thick coating can become brittle and is prone to cracking or chipping upon impact or thermal cycling.
It can also lead to improper curing, where the surface skins over while the material underneath remains soft. This results in poor adhesion and a high likelihood of the coating peeling or delaminating from the substrate.
Furthermore, thick coats can sag, run, or create an "orange peel" texture, ruining the aesthetic finish. Finally, it represents a significant waste of material and money.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Always begin by consulting the technical data sheet (TDS) for the specific coating product you are using. The manufacturer provides the optimal range; your job is to decide where to aim within that range based on your goal.
- If your primary focus is corrosion protection in a harsh environment: Aim for the higher end of the manufacturer's recommended range to ensure a non-porous, protective barrier.
- If your primary focus is a high-quality aesthetic finish: A thinner, more controlled application within the recommended range is often better to avoid orange peel and ensure a smooth surface.
- If your primary focus is part flexibility: Stay toward the lower end of the recommended thickness to maintain the coating's elasticity and prevent cracking.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for a non-critical application: Apply the minimum thickness required to achieve full coverage and the desired appearance, avoiding costly overuse.
Ultimately, the manufacturer's technical data sheet is your most reliable guide to achieving a coating that performs exactly as intended.
Summary Table:
| Thickness Goal | Recommended Thickness | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Protection | Higher end of range | Ensures a non-porous barrier for harsh environments. |
| Aesthetic Finish | Lower to mid-range | Prevents orange peel texture for a smooth surface. |
| Part Flexibility | Lower end of range | Maintains coating elasticity to prevent cracking. |
| Cost-Efficiency | Minimum required | Achieves full coverage while avoiding material waste. |
Need precise coating solutions for your laboratory equipment? The right coating thickness is critical for protecting your valuable lab assets from corrosion, wear, and chemical exposure. KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, ensuring durability and reliability for your specific application. Let our experts help you select the perfect coating system to enhance performance and longevity. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is tablet pressing in pharmaceutical industry? The Core Process for Producing Solid Oral Dosage Forms
- What is a punch tablet press? Precision Tableting for R&D and Small Batches
- What are the different parts of a single punch tablet machine? The Core Components Explained
- What are the different pill presses? Choose the Right Machine for Your Lab or Production Scale
- What are the two classifications of press machines? Single Punch vs. Rotary Presses Explained


















