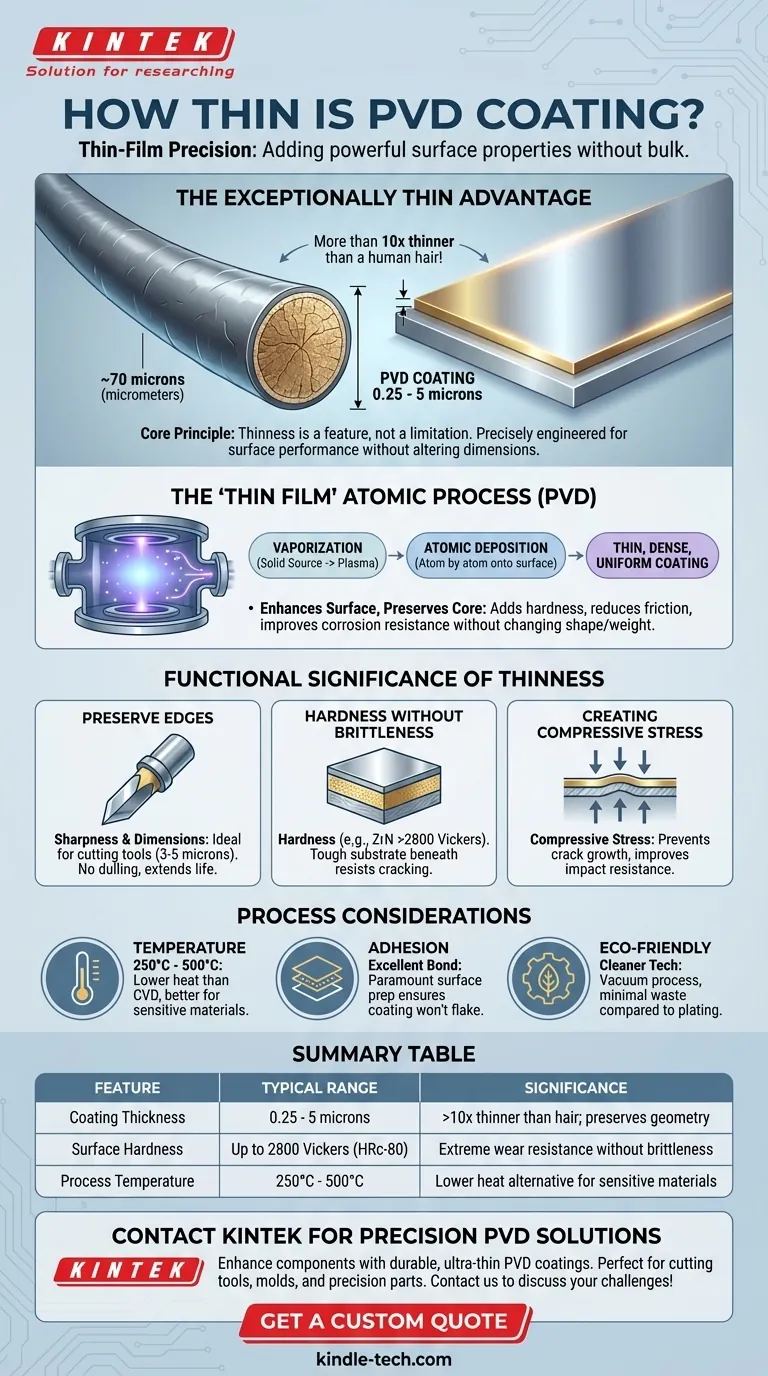
In practice, a PVD coating is exceptionally thin. The typical thickness ranges from 0.25 to 5 microns (micrometers). To put that into perspective, a human hair is approximately 70 microns thick, making a PVD coating more than 10 times thinner than a single strand of hair.
The core principle to understand is that the extreme thinness of a PVD coating is not a limitation but its defining feature. This thin-film application is precisely engineered to add powerful surface properties, like extreme hardness and wear resistance, without altering the underlying component's critical dimensions or geometry.

What is PVD and Why is it a "Thin Film" Process?
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a sophisticated coating process conducted in a high-vacuum chamber. Its "thin-film" nature is a direct result of how the coating is applied, which is fundamental to its advantages.
The Atomic Deposition Method
PVD works by vaporizing a solid source material into a plasma of atoms or molecules. These particles are then deposited, one atom at a time, onto the surface of the target object. This atomic-level control is what allows for the creation of an extremely thin, dense, and uniform coating.
The Goal: Enhance the Surface, Preserve the Core
The primary goal of PVD is not to add bulk but to impart new characteristics to the substrate's surface. By adding a layer that is only a few microns thick, you can dramatically increase hardness, reduce friction, or improve corrosion resistance without changing the part's shape, weight, or fit.
The Functional Significance of PVD's Thickness
The specific thickness of a PVD coating is chosen to maximize performance. A coating that is too thin may not offer sufficient durability, while one that is too thick can become brittle or negatively affect the part's function.
Preserving Critical Edges and Tolerances
For components like cutting tools, blades, and precision molds, maintaining sharpness and exact dimensions is non-negotiable. PVD coatings, often in the 3 to 5 micron range, are thin enough to protect the edge without dulling it. This reduces cutting forces and heat generation, extending tool life significantly.
Hardness Without Brittleness
PVD adds a ceramic layer with immense surface hardness. For example, a Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) coating can have a hardness of over 2800 Vickers (HRc-80). Because this hard layer is so thin and well-adhered, it benefits from the toughness of the more flexible substrate material beneath it, resisting cracks and chipping.
Creating Compressive Stress
The PVD process and subsequent cooling often create compressive stress within the thin coating. This internal stress works to hold microscopic cracks closed, preventing them from growing and causing the coating to fail. This is especially valuable in high-impact applications like milling.
Understanding the Process Considerations
While PVD is highly versatile, its application involves key parameters that ensure the thin film performs as intended. Understanding these factors is crucial for success.
Temperature Control
PVD is a physical process conducted at elevated temperatures, typically ranging from 250°C to 500°C. While this is significantly lower than alternative methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), it is still a critical factor to consider for heat-sensitive substrate materials.
The Critical Role of Adhesion
For an ultra-thin layer to be effective, its bond to the substrate must be exceptionally strong. Proper surface preparation and cleaning before the coating process are paramount. PVD is known for creating coatings with excellent adhesion that will not flake or peel under stress.
An Environmentally Responsible Choice
Compared to traditional coating methods like electroplating, which often involve hazardous chemicals, PVD is a more environmentally friendly process. It is performed in a vacuum and produces minimal waste, making it a cleaner technology.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The thinness of a PVD coating is a strategic advantage. By understanding this, you can determine if it's the correct solution for your specific engineering challenge.
- If your primary focus is maintaining sharp edges or precise tolerances: The ultra-thin nature of PVD is a key benefit, protecting the part without altering its geometry.
- If your primary focus is extreme surface hardness and wear resistance: PVD delivers a robust ceramic layer that dramatically improves durability without adding significant bulk.
- If your primary focus is working with temperature-sensitive substrates: PVD's relatively low application temperature makes it a superior choice over higher-heat coating processes.
Ultimately, understanding that PVD's thinness is a deliberate and engineered feature empowers you to leverage its unique advantages for superior material performance.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Typical Range | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Thickness | 0.25 - 5 microns | >10x thinner than a human hair; preserves part geometry |
| Surface Hardness | Up to 2800 Vickers (HRc-80) | Extreme wear resistance without brittleness |
| Process Temperature | 250°C - 500°C | Lower heat alternative to CVD for sensitive materials |
Ready to enhance your components with a durable, ultra-thin PVD coating?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab equipment and consumables, including advanced PVD coating solutions. Our coatings are engineered to provide extreme surface hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion protection while maintaining your part's critical dimensions and sharp edges—perfect for cutting tools, molds, and precision components.
Contact us today to discuss how our PVD coating expertise can solve your specific material performance challenges. Let's improve your product's durability and efficiency together!
Get a Custom Quote for Your PVD Coating Needs
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition



















