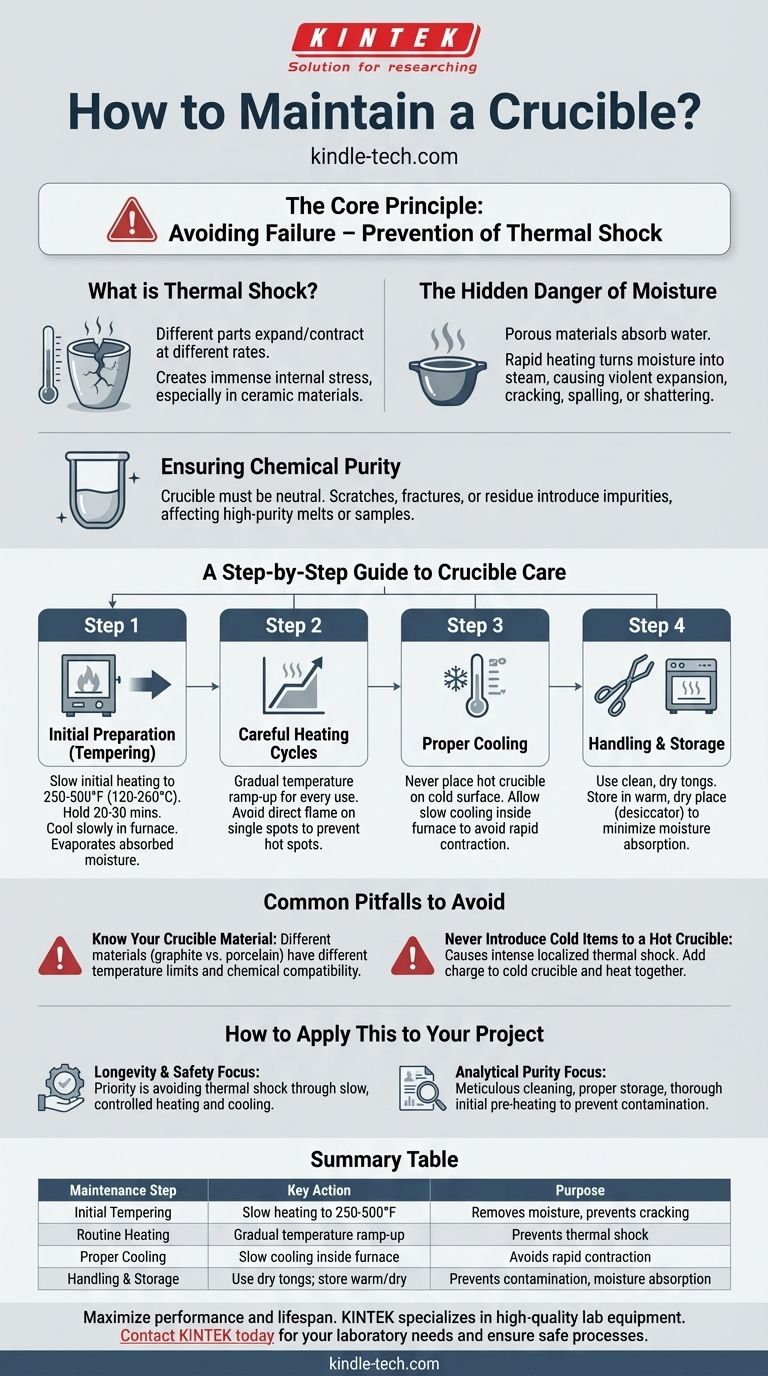
The most critical step in maintaining a new crucible is to properly temper it before its first use. This involves heating the crucible slowly and evenly to drive out any trapped moisture absorbed from the atmosphere during manufacturing and storage. This initial preparation is fundamental to preventing cracks and ensuring its longevity.
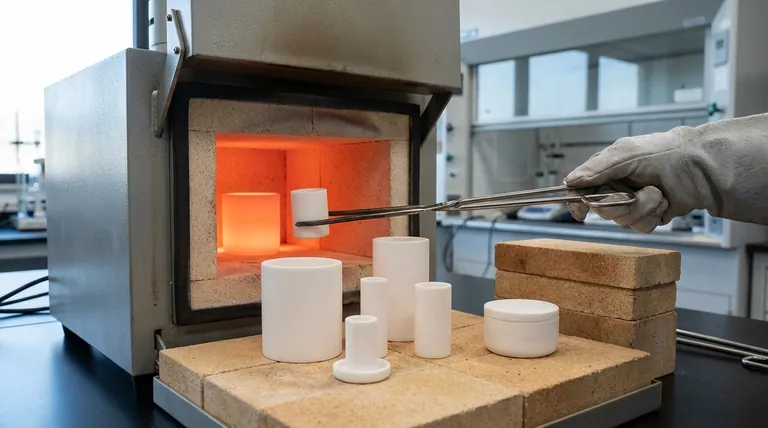
The core principle of crucible maintenance is the prevention of thermal shock. Every action, from initial tempering to routine heating and cooling cycles, is designed to minimize rapid temperature changes that can cause stress fractures and catastrophic failure.

The Core Principle: Avoiding Failure
Proper maintenance is not about a single action but a consistent methodology. The two primary failure modes you are working to prevent are physical fracture from thermal shock and chemical contamination from a compromised surface.
What is Thermal Shock?
Thermal shock occurs when different parts of a material expand or contract at different rates due to rapid temperature changes. This creates immense internal stress.
Crucibles, especially those made of ceramic materials, are strong under compression but brittle under tension. A sudden temperature change can easily cause a stress fracture, ruining the crucible and your sample.
The Hidden Danger of Moisture
The "tempering" process described in laboratory procedures is fundamentally about moisture removal. Porous crucible materials absorb water from the air.
If you heat a crucible too quickly, this trapped moisture turns to steam, expanding violently. This expansion can cause the crucible to crack, spall, or even shatter, posing a significant safety risk.
Ensuring Chemical Purity
A crucible must be a neutral vessel that does not react with or contaminate the materials it holds. Scratches, micro-fractures, or residual material from previous uses can introduce impurities.
Proper care ensures the crucible's internal surface remains smooth and non-reactive, preserving the integrity of your high-purity melts or analytical samples.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Crucible Care
Follow these steps throughout the life of your crucible to maximize its performance and lifespan.
Step 1: Initial Preparation (Tempering)
For a brand-new crucible, a slow initial heating cycle is mandatory. Place the empty crucible in a cool furnace and gradually raise the temperature to around 250-500°F (120-260°C).
Hold it at this temperature for at least 20-30 minutes to ensure all absorbed moisture has evaporated. Afterward, allow it to cool down slowly inside the furnace.
Step 2: Careful Heating Cycles
The principle of slow heating applies to every use, not just the first. Always ramp up the temperature gradually to allow the entire crucible to heat evenly. Avoid direct flame impingement on a single spot, as this creates a "hot spot" that is a primary cause of stress fractures.
Step 3: Proper Cooling
Never remove a glowing hot crucible and place it on a cold surface, such as a steel table or stone countertop. The rapid heat transfer will almost certainly cause it to crack.
Allow the crucible to cool as slowly as possible, ideally by leaving it inside the furnace as it cools down.
Step 4: Handling and Storage
Always use clean, dry tongs to handle a crucible to avoid introducing moisture or contaminants. When not in use, store your crucibles in a warm, dry place, like a drying oven or desiccator, to minimize moisture absorption.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding the limitations of your equipment is as important as knowing the procedure.
Know Your Crucible's Material
Different materials have different properties. A graphite crucible has excellent thermal shock resistance but can be consumed in an oxidizing atmosphere. A porcelain crucible has excellent chemical resistance but is highly susceptible to thermal shock.
Always operate within the manufacturer's specified temperature limits and understand the chemical compatibility of your crucible material with the substance you are heating.
Never Introduce Cold Items to a Hot Crucible
Adding cold or room-temperature materials to a hot crucible creates an intense, localized thermal shock. Always add your charge material to the crucible while it is cold and heat them up together.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your maintenance strategy should align with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is longevity and safety: Your absolute priority is avoiding thermal shock through slow, controlled heating and cooling for every single cycle.
- If your primary focus is analytical purity: Meticulous cleaning, proper storage in a dry environment, and a thorough initial pre-heating are critical to prevent sample contamination.
Treating your crucible with deliberate care transforms it from a simple consumable into a reliable and safe scientific instrument.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Tempering | Slow heating to 250-500°F (120-260°C) | Removes moisture to prevent cracking |
| Routine Heating | Gradual temperature ramp-up | Prevents thermal shock and stress fractures |
| Proper Cooling | Slow cooling inside the furnace | Avoids rapid contraction and cracking |
| Handling & Storage | Use dry tongs; store in a warm, dry place | Prevents contamination and moisture absorption |
Maximize the performance and lifespan of your lab equipment. Proper crucible care is essential for safety and accurate results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including crucibles designed for durability and chemical resistance. Let our experts help you select the right tools and provide guidance on best practices. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory needs and ensure your processes run smoothly and safely.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
People Also Ask
- What role do alumina crucibles play in synthesizing lithium salt precursors like Li3BO3? Ensure High-Purity Synthesis
- What are the advantages of using a Glassy Carbon Crucible for fluoride salts? Ensure Purity up to 1000°C
- What materials can be used as a crucible? Select the Right Material for Your High-Temperature Application
- What are the advantages of using a nickel crucible? Ensure Safety and Purity in Lithium Smelting
- Do crucibles break easily? Understanding Thermal Shock and Proper Handling
- What are the technical advantages of using alumina crucibles in aluminization? Ensure High-Purity Coating Results
- Why use high-purity alumina crucibles for lithium cathode sintering? Ensure Purity & Prevent Chemical Contamination
- What is the use of crucible furnace? Unlock Versatile Melting for Metals & Materials



















