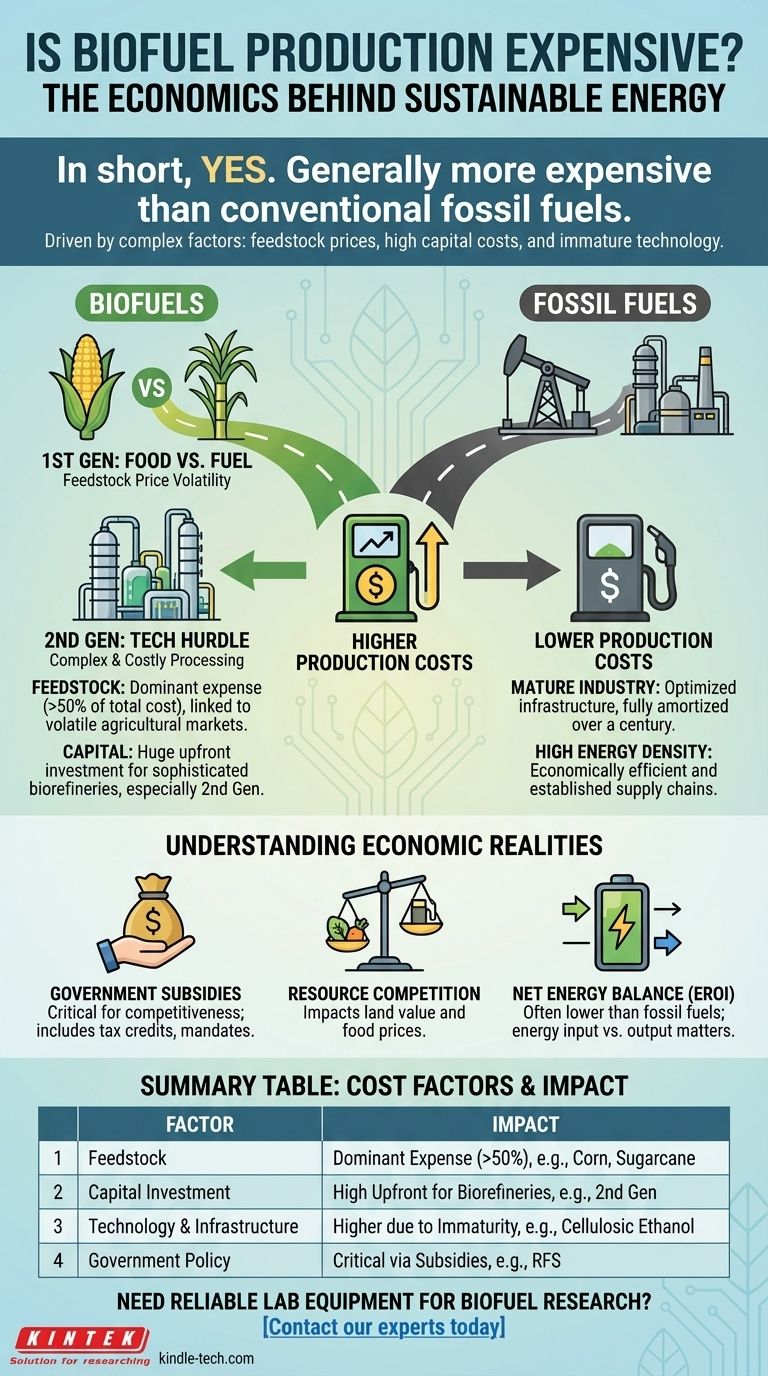
In short, yes. Biofuel production is generally more expensive than conventional fossil fuel production, often significantly so. This cost difference arises from complex factors including the price of raw materials (feedstock), the high capital investment required for processing facilities, and the relative immaturity of the technology and its supporting infrastructure.
The core issue is that biofuels must compete with a fossil fuel industry that has been optimized for over a century. While the price of biofuels can vary dramatically based on the type of feedstock and government policy, they consistently face an uphill battle to match the low cost and high energy density of gasoline and diesel on a purely economic basis.

The Key Drivers of Biofuel Cost
To understand the economics, we must first recognize that "biofuel" is not a single product. The costs are entirely dependent on the source material and the technology used to convert it into fuel.
First-Generation: The Food vs. Fuel Dilemma
First-generation biofuels are derived from food crops. The most common examples are corn ethanol in the United States and sugarcane ethanol in Brazil.
Their primary cost driver is the price of the agricultural feedstock itself. This links the price of fuel directly to global food markets, creating volatility and economic tension.
Second-Generation: The Technology Hurdle
Second-generation biofuels are made from non-food sources, such as switchgrass, wood chips, or agricultural waste. This is often called cellulosic ethanol.
While this approach solves the "food vs. fuel" problem, it introduces a new, significant expense: complex and costly processing. Breaking down tough cellulose into fermentable sugars requires advanced enzymes and intensive pre-treatment, which drives up both capital and operational costs.
Feedstock: The Dominant Expense
For any biofuel, the raw material is the single largest component of its final cost, often accounting for over half of the total production expense.
When corn prices rise due to a bad harvest or increased demand for animal feed, the cost of producing corn ethanol rises in lockstep. This makes long-term price stability a major challenge.
Capital Costs: Building the Biorefinery
Biorefineries are sophisticated, expensive facilities. The capital investment required to build a new plant, especially for more advanced second-generation fuels, can be enormous.
These high upfront costs must be recouped over the life of the plant, adding a significant amount to the price of every gallon produced. This stands in contrast to the fully mature and amortized infrastructure of the petroleum industry.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Economic Realities
A simple price comparison at the pump doesn't tell the whole story. The true economic viability of biofuels is heavily influenced by policy and external factors that are not always obvious.
The Critical Role of Government Subsidies
In nearly every market, biofuels are not cost-competitive with gasoline or diesel without significant government intervention.
Tax credits, blending mandates (like the U.S. Renewable Fuel Standard), and direct subsidies are often necessary to close the price gap and make biofuels a viable product for consumers and an attractive investment for producers.
Competition for Land and Resources
Growing crops for fuel competes directly with growing crops for food. This can increase land value and drive up the price of staple food products.
Furthermore, the agricultural inputs required—water, fertilizer, and energy for farm equipment—represent another layer of cost that must be factored into the final price of the fuel.
Net Energy Balance
A crucial, and often debated, economic factor is the Energy Return on Investment (EROI). This measures how much energy is produced for every unit of energy put into the production process.
If it takes nearly one gallon of fossil fuel equivalent to produce one gallon of biofuel, the economic (and environmental) benefit is severely diminished. While most modern biofuels have a positive EROI, it is often much lower than that of conventional oil and gas.
Making an Informed Decision on Biofuels
The "right" way to view the cost of biofuels depends entirely on your primary goal. Different objectives lead to different conclusions about whether the price is justified.
- If your primary focus is pure economic competitiveness: Most biofuels currently struggle to compete with fossil fuels on price alone without subsidies.
- If your primary focus is energy security and independence: The premium price for domestically produced biofuels may be considered a worthwhile investment to reduce reliance on foreign oil.
- If your primary focus is long-term environmental sustainability: Second-generation biofuels, despite their higher initial costs, represent a more sustainable path by avoiding competition with food supplies.
Ultimately, the cost of biofuels is a strategic calculation that balances direct production expenses against national policy goals and the long-term costs of environmental impact.
Summary Table:
| Cost Factor | Impact on Biofuel Price | Key Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Feedstock | Dominant expense (often >50%) | Corn, sugarcane, agricultural waste |
| Capital Investment | High upfront costs for biorefineries | Second-generation processing facilities |
| Technology & Infrastructure | Higher due to relative immaturity | Cellulosic ethanol enzymes |
| Government Policy | Critical for competitiveness via subsidies/tax credits | Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) |
| Energy Return on Investment (EROI) | Lower than fossil fuels, affecting net energy balance | Varies by feedstock and process |
Need reliable lab equipment to optimize your biofuel research or production? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored for biofuel development—from feedstock analysis to process optimization. Contact our experts today to enhance your lab's efficiency and accelerate your sustainable energy projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Research and Development
People Also Ask
- How does a high-pressure reactor demonstrate its value in accelerated aging? Predict Catalyst Durability Fast
- What role does an autoclave play in simulating PWR conditions? Advanced Material Validation for Nuclear Safety
- Why are high-pressure autoclaves essential for preparing bio-based polyamide curing agents from dimeric acid?
- What is the contribution of a hydrothermal reactor to graded pore construction? Precision Templates for TAS
- What is the role of high-pressure reactors in the study of alloy oxidation? Essential Tools for Supercritical Research



















