No, compression molding and transfer molding are fundamentally different processes. While both use heat and pressure to shape material, the critical distinction lies in how the material is introduced into the mold cavity. Compression molding places the material directly into the final mold shape, whereas transfer molding heats and injects the material from a separate chamber into a closed mold.
The core difference to understand is control versus simplicity. Compression molding is a direct and simple process ideal for less complex parts, while transfer molding is an indirect process that offers greater control for intricate geometries and delicate components.

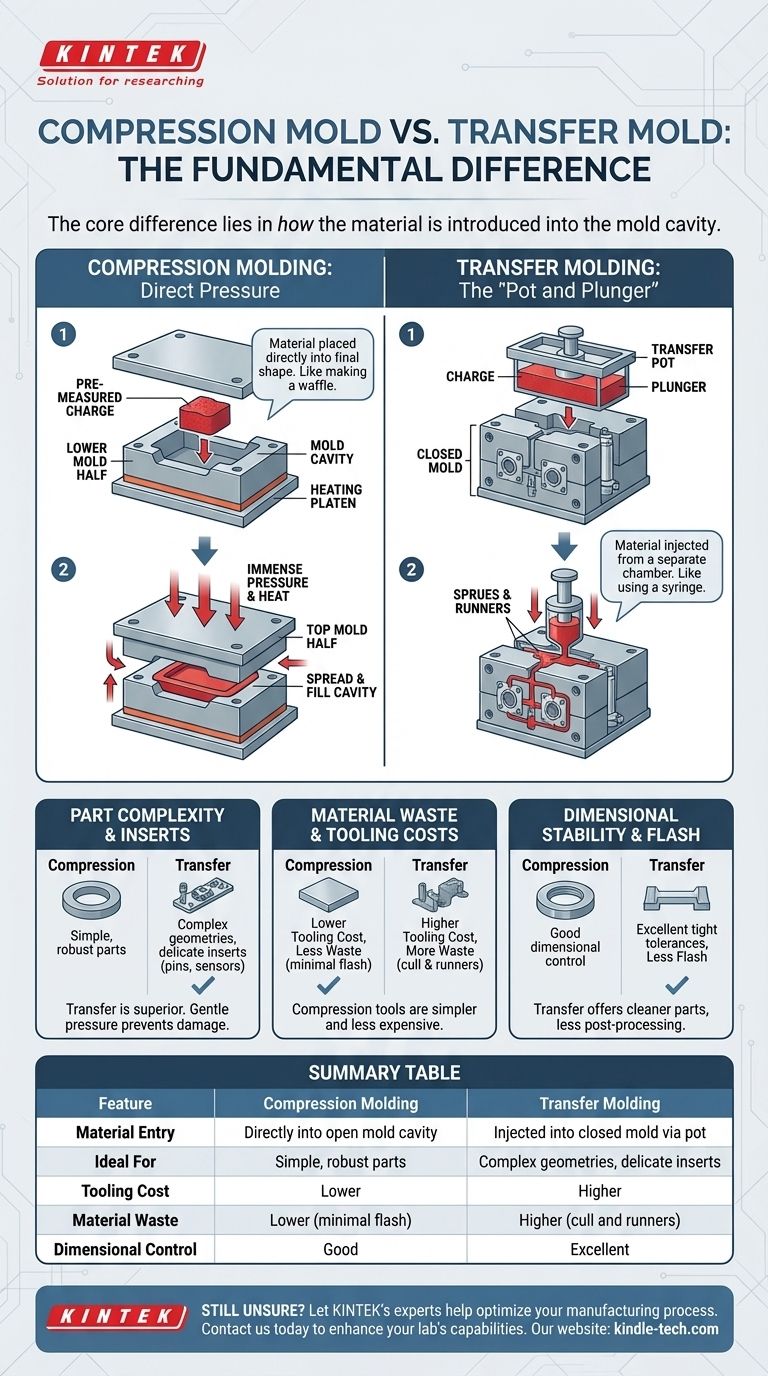
The Core Mechanics: How Material Enters the Mold
The defining difference between these two methods is the path the raw material takes before it becomes a finished part. This single distinction drives all subsequent advantages and disadvantages.
Compression Molding: Direct Pressure
In compression molding, a pre-measured amount of molding material, called the charge, is placed directly into the open, heated lower half of the mold cavity.
The top half of the mold is then closed, applying immense pressure. This action forces the material to spread and fill the entire cavity, taking its shape. It's analogous to making a waffle—you place the batter directly onto the iron and close the lid to form the final shape.
Transfer Molding: The "Pot and Plunger"
Transfer molding adds an intermediate step. The charge is not placed in the part cavity itself but in a separate chamber known as the transfer pot, located above the cavity.
The mold is closed first. Then, a plunger pressurizes the material in the pot, heating it to a liquid state and forcing it through channels (sprues and runners) into the completely closed mold cavity. This is more like using a syringe to inject liquid into a container.
Why This Difference Matters for Your Part
The choice between these methods has direct consequences on part design, material waste, and tooling costs.
Part Complexity and Inserts
Transfer molding is far superior for parts with complex geometries or delicate inserts (like metal pins or electronic sensors).
Because the mold is already closed when the material flows in, the material enters with a more consistent and gentle pressure. This prevents damage to or displacement of fragile insert components. The high, direct pressure of compression molding can easily bend pins or crack inserts.
Material Waste and Tooling Costs
Compression molding tools are generally simpler and less expensive to manufacture. The process can be highly efficient with material, as the charge can be measured to closely match the final part volume.
Transfer molding tools are more complex due to the integrated pot, plunger, and runner system, leading to higher initial tooling costs. It also inherently creates more waste, as the leftover material in the pot and runners (the "cull") is cured and must be discarded.
Dimensional Stability and Flash
Transfer molding typically offers tighter dimensional tolerances and produces less "flash" (excess material that seeps out where the mold halves meet).
Since the mold is closed and clamped before injection, there is very little opportunity for material to escape. This results in cleaner parts that require less post-processing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither process is universally better; they are simply suited for different tasks. Understanding their inherent limitations is key to making an informed decision.
The Simplicity of Compression Molding
Its primary advantage is its simplicity, which translates to lower tooling costs and faster cycle times for the right application. It is ideal for larger, simpler, and robust parts like electrical components, gaskets, and automotive panels. Its major limitation is the lack of fine control over material flow.
The Precision of Transfer Molding
Its primary advantage is the precision and control it offers, making it the go-to method for small, intricate parts and overmolding applications. The trade-offs are the higher tooling investment and the unavoidable material waste from the cull.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific requirements of your part and your production goals.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for simpler, robust parts without inserts: Compression molding is almost always the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is producing complex parts with delicate inserts or tight tolerances: Transfer molding provides the necessary control and precision.
- If your primary focus is producing very high volumes of small, detailed thermoset parts: Transfer molding's consistency and low flash often make it more efficient in the long run, despite higher tool costs.
By understanding that the key difference is how the material is delivered to the cavity, you can confidently select the manufacturing process that best aligns with your design's complexity and your project's budget.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Compression Molding | Transfer Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Material Entry | Directly into open mold cavity | Injected into closed mold via transfer pot |
| Ideal For | Simple, robust parts | Complex geometries, delicate inserts |
| Tooling Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Material Waste | Lower (minimal flash) | Higher (cull and runners) |
| Dimensional Control | Good | Excellent |
Still unsure which molding process is right for your application?
Let KINTEK's experts help you optimize your manufacturing process. We specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables to support your compression or transfer molding needs. Our team can guide you to the most efficient solution for your specific part design and production goals.
Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's capabilities and streamline your manufacturing workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Assemble Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Lab Infrared Press Mold
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Rubber Vulcanizer Vulcanizing Machine Plate Vulcanizing Press for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why are a laboratory hydraulic press and precision molds required for pressing MAX phase green bodies? - Expert Guide
- What role do high-strength graphite molds play during vacuum hot pressing? Enhance Precision in CuAlMn Composites
- How do graphite molds and hydraulic presses work together? Perfect Your FeCrAl Pre-Forming Today!
- What is the role of a laboratory hydraulic press in molecular sieve catalyst preparation? Achieve Optimal Pelleting
- What is the lifespan of a mold? It's Immortal Unless You Control Moisture



















