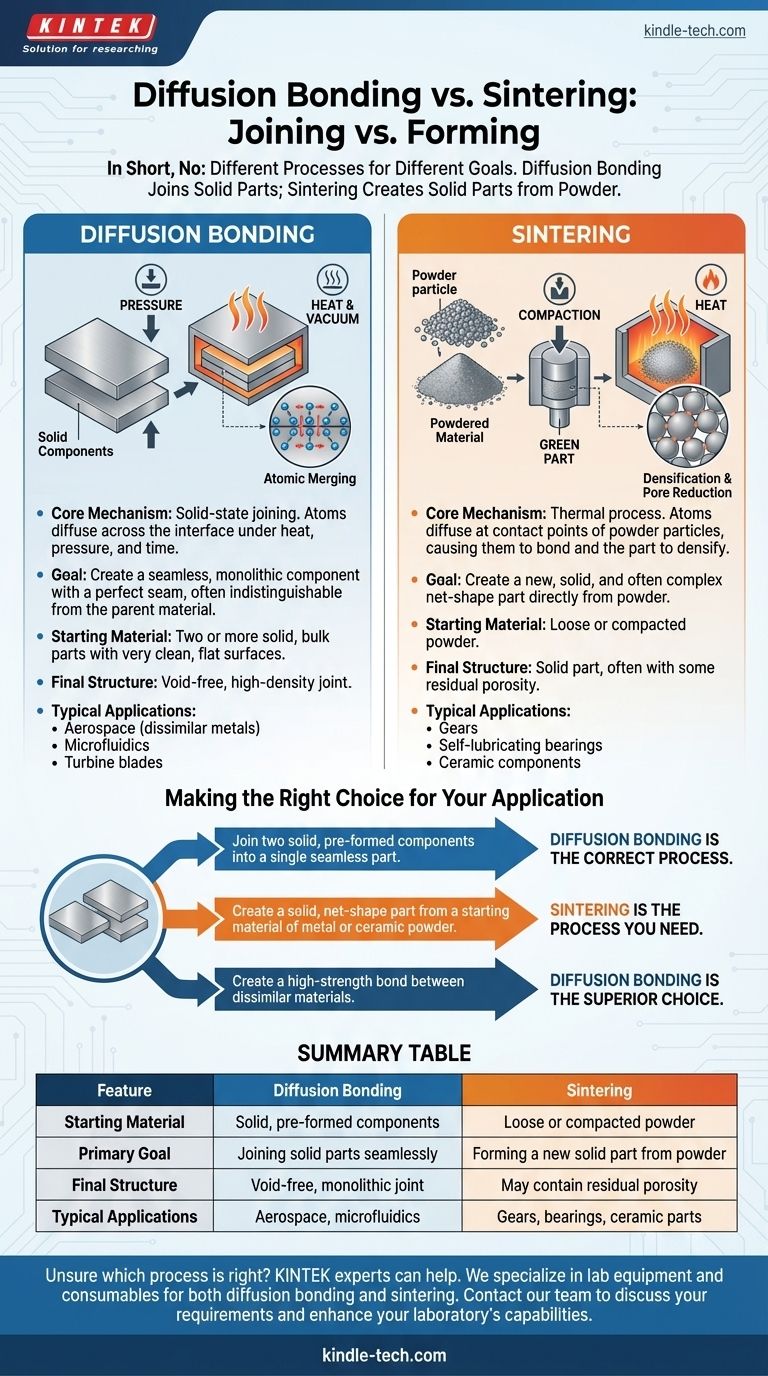
In short, no. Diffusion bonding and sintering are not the same process, although they share the foundational principles of using heat and pressure to bond materials without melting them. The critical difference lies in the starting form of the material: diffusion bonding joins solid, pre-formed components, whereas sintering creates a solid mass from a collection of powders.
The core distinction is one of purpose: diffusion bonding is a joining process used to weld solid parts together at an atomic level, while sintering is a forming process used to create a new solid part from a powdered material.
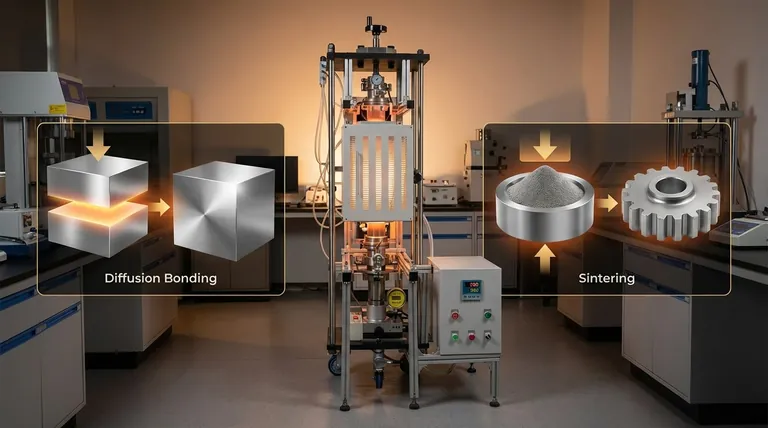
What is Diffusion Bonding? The Science of Atomic Merging
Diffusion bonding is a highly precise solid-state joining method. It creates a bond between two components that is often indistinguishable from the parent materials themselves.
The Core Mechanism
The process involves bringing two very clean, flat surfaces into contact under high pressure and temperature in a vacuum or inert atmosphere. The heat provides the energy for atoms at the interface to vibrate and move across the boundary, "diffusing" into the opposite piece and forming a single, continuous grain structure.
Key Parameters
Success depends on three factors: temperature, pressure, and time. The temperature is kept below the material's melting point, while the pressure is just enough to ensure intimate contact without causing large-scale deformation.
The Goal: A Perfect Seam
The objective is to eliminate the original interface between two solid parts, creating a monolithic component. It is a true metallurgical weld, created without any filler material.
What is Sintering? Building from the Ground Up
Sintering is a cornerstone of powder metallurgy and ceramics manufacturing. It is a thermal process that transforms a compacted powder into a dense, solid object.
The Core Mechanism
Sintering begins with a "green part," which is a loosely held-together shape made of compressed powder. When heated, atoms diffuse across the contact points of adjacent particles. This atomic transport causes the necks between particles to grow, reducing the empty space (porosity) and densifying the component.
The Role of Porosity
A key characteristic of sintering is the reduction of porosity. While the goal is often to achieve near-full density, some level of residual porosity can remain, which affects the final mechanical properties of the part.
The Goal: A Net-Shape Part
The objective of sintering is to create a new, solid, and often complex shape directly from powder. This can be more economical than machining the same shape from a solid block of material.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Distinctions
Choosing between these processes requires understanding their fundamentally different applications and limitations.
Starting Material
Diffusion bonding begins with two or more solid, bulk parts with precisely prepared surfaces. Sintering begins with a mass of loose or compacted powder.
Final Structure
Diffusion bonding produces a component with a nearly imperceptible, void-free joint, maintaining the high density of the original materials. A sintered part is formed from countless individual bonds and may contain some level of residual porosity.
Common Applications
You will see diffusion bonding used for high-performance applications like joining dissimilar or refractory metals in aerospace, creating microfluidic channels, and manufacturing turbine blades. Sintering is used for mass production of items like self-lubricating bearings, automotive gears, and ceramic components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision depends entirely on your starting point and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is to join two solid, pre-formed components into a single seamless part: Diffusion bonding is the correct process.
- If your primary focus is to create a solid, net-shape part from a starting material of metal or ceramic powder: Sintering is the process you need.
- If your primary focus is creating a high-strength bond between dissimilar materials that cannot be conventionally welded: Diffusion bonding is the superior choice.
Ultimately, mastering these techniques begins with recognizing whether your task is to join existing structures or to form a new one entirely.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Diffusion Bonding | Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Starting Material | Solid, pre-formed components | Loose or compacted powder |
| Primary Goal | Joining solid parts seamlessly | Forming a new solid part from powder |
| Final Structure | Void-free, monolithic joint | May contain residual porosity |
| Typical Applications | Aerospace components, microfluidics | Gears, bearings, ceramic parts |
Unsure which process is right for your application? The experts at KINTEK can help. We specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for both diffusion bonding and sintering processes. Whether you are joining high-performance alloys or forming complex components from powder, our solutions ensure optimal results. Contact our team today to discuss your specific requirements and enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is precise pressure control essential during ZnS vacuum hot pressing? Achieve Peak Optical Clarity and Density
- What role does the Laboratory Vacuum Hot Press Furnace play in the production of ZnS ceramics? Unlock Optical Excellence
- How does a vacuum hot press furnace achieve the densification of ZrB2–SiC–TaC? Unlock Ultra-High Ceramic Density
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 96%+ Density for (WC + B4C)p/6063Al Composites
- What is the role of a vacuum hot press furnace in TiC-steel composites? Achieve 99% Density with Precision



















