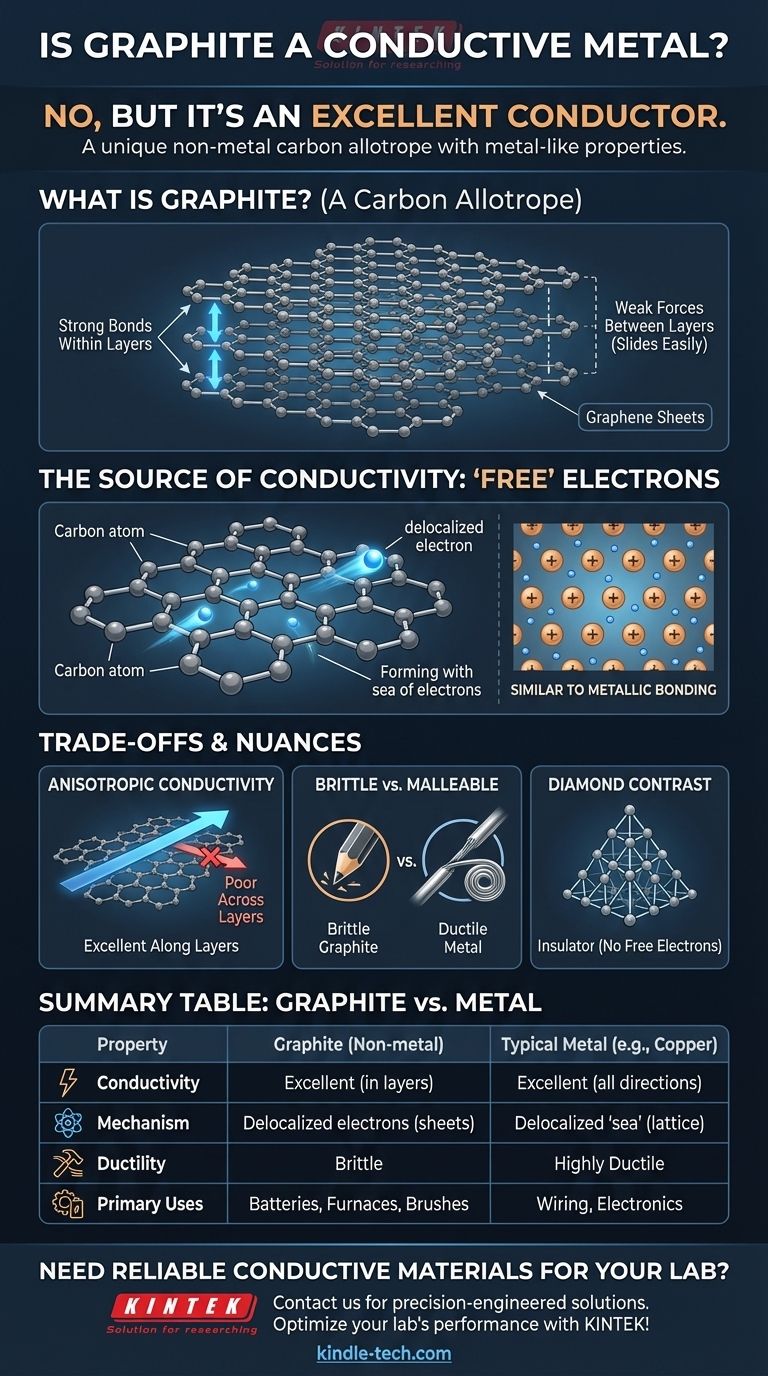
No, graphite is not a metal, but it is an excellent electrical conductor. This distinction is a source of frequent confusion, as we are often taught to associate conductivity exclusively with metallic elements. Graphite is an allotrope—a specific structural form—of the non-metal element carbon.
The core reason for this confusion is that we tend to group materials by simple categories rather than by their fundamental structure. Graphite, while a non-metal, conducts electricity because its unique layered atomic arrangement creates "free" electrons that behave almost exactly like the electrons in a true metal.
What is Graphite? A Unique Form of Carbon
Graphite's properties arise directly from its unique atomic structure. Understanding this structure is key to understanding its behavior.
Not a Metal, but an Allotrope
Elements can exist in different physical forms called allotropes. These forms have the same atoms but different structural arrangements, which gives them vastly different properties.
Graphite is an allotrope of carbon. The most famous other allotrope of carbon is diamond. Though both are pure carbon, their structures make graphite a soft conductor and diamond a hard insulator.
A Structure of Stacked Layers
Graphite is composed of countless flat sheets stacked on top of one another. Each sheet, known as graphene, is a one-atom-thick layer of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb-like hexagonal lattice.
The bonds holding the atoms together within a sheet are incredibly strong. However, the forces holding the different sheets to each other are very weak, allowing them to easily slide apart. This is why graphite is soft and flaky, forming the "lead" in pencils.
The Source of Graphite's Conductivity
The reason graphite conducts electricity lies in how its electrons are shared—or rather, not shared. This mimics the conductive mechanism of metals without graphite being a metal itself.
The Role of Carbon's Electrons
Each carbon atom has four outer electrons (valence electrons) available for bonding. In the hexagonal structure of a graphene sheet, each carbon atom forms strong covalent bonds with three neighboring atoms.
The "Free" Delocalized Electron
This leaves one of the four valence electrons unaccounted for. This fourth electron is not locked into a bond between two specific atoms. Instead, it becomes delocalized, free to move anywhere along its two-dimensional graphene sheet.
A "Sea of Electrons" in a Non-Metal
This collection of delocalized electrons forms a mobile "sea of electrons" within each layer. Since an electrical current is simply the flow of electrons, these free-moving electrons allow graphite to conduct electricity with ease.
This is fundamentally similar to metallic bonding, where a lattice of positive metal ions sits in a "sea" of shared, delocalized electrons. Graphite achieves a similar outcome using a completely different atomic structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
While graphite is a conductor, it is not a perfect substitute for metals. Its non-metallic nature comes with distinct trade-offs.
Conductivity is Not Uniform
Graphite is highly anisotropic, meaning its properties are direction-dependent. It conducts electricity extremely well along its graphene sheets, but very poorly across them. Most metals, in contrast, are isotropic and conduct electricity equally well in all directions.
Brittleness vs. Malleability
Metals are typically ductile and malleable, meaning they can be drawn into wires or hammered into new shapes without breaking. Graphite is brittle and will shatter under similar stress. You cannot form a graphite wire by stretching it.
Diamond: The Insulating Counterpart
Diamond provides the perfect contrast. In its rigid, tetrahedral lattice, each carbon atom bonds to four others, using up all four valence electrons. With no delocalized electrons, there is nothing free to move and carry a current, making diamond an excellent electrical insulator.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding these principles allows you to select the right material based on the specific properties required for a task.
- If your primary focus is flexible, omnidirectional conductivity: Metals like copper and aluminum remain the superior choice due to their ductility and isotropic nature.
- If your primary focus is a lightweight, chemically stable conductor for high temperatures: Graphite is an ideal material for applications like battery electrodes, furnace linings, and electric motor brushes.
- If your primary focus is hardness and electrical insulation: Diamond, carbon's other famous allotrope, is the solution, proving that atomic arrangement dictates everything.
Ultimately, a material's properties are defined by its atomic structure, not by the simple category we place it in.
Summary Table:
| Property | Graphite | Typical Metal (e.g., Copper) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Non-metal (Carbon Allotrope) | Metal |
| Electrical Conductivity | Excellent (within layers) | Excellent (in all directions) |
| Conduction Mechanism | Delocalized electrons in graphene sheets | Delocalized 'sea of electrons' |
| Ductility/Malleability | Brittle, cannot be drawn into wires | Highly ductile and malleable |
| Primary Use Cases | Batteries, furnace linings, motor brushes | Wiring, structural components, electronics |
Need a reliable conductive material for your lab application? Whether you're working with high-temperature furnaces, battery research, or custom electrode setups, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables ensures you get the right solution. Our team can help you select materials that match your specific conductivity, temperature, and durability requirements. Contact us today to optimize your lab's performance with precision-engineered solutions from KINTEK!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
- Carbon Graphite Plate Manufactured by Isostatic Pressing Method
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-purity graphite rod preferred as a counter electrode? Ensure Uncontaminated Electrochemical Analysis
- What is the primary function of high-purity graphite electrodes in AC leaching? Powering Efficient Metal Recovery
- What are the characteristics and applications of a graphite sheet electrode? Maximize Reaction Area for Bulk Electrolysis
- What are the properties and applications of a graphite disk electrode? Precision Tools for Electroanalysis
- What are the potential risks when using a graphite electrode in electrochemical tests? Avoid Decomposition and Contamination



















