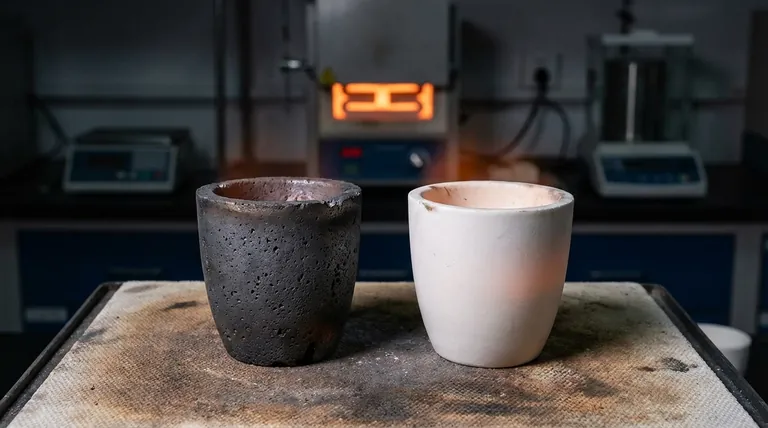
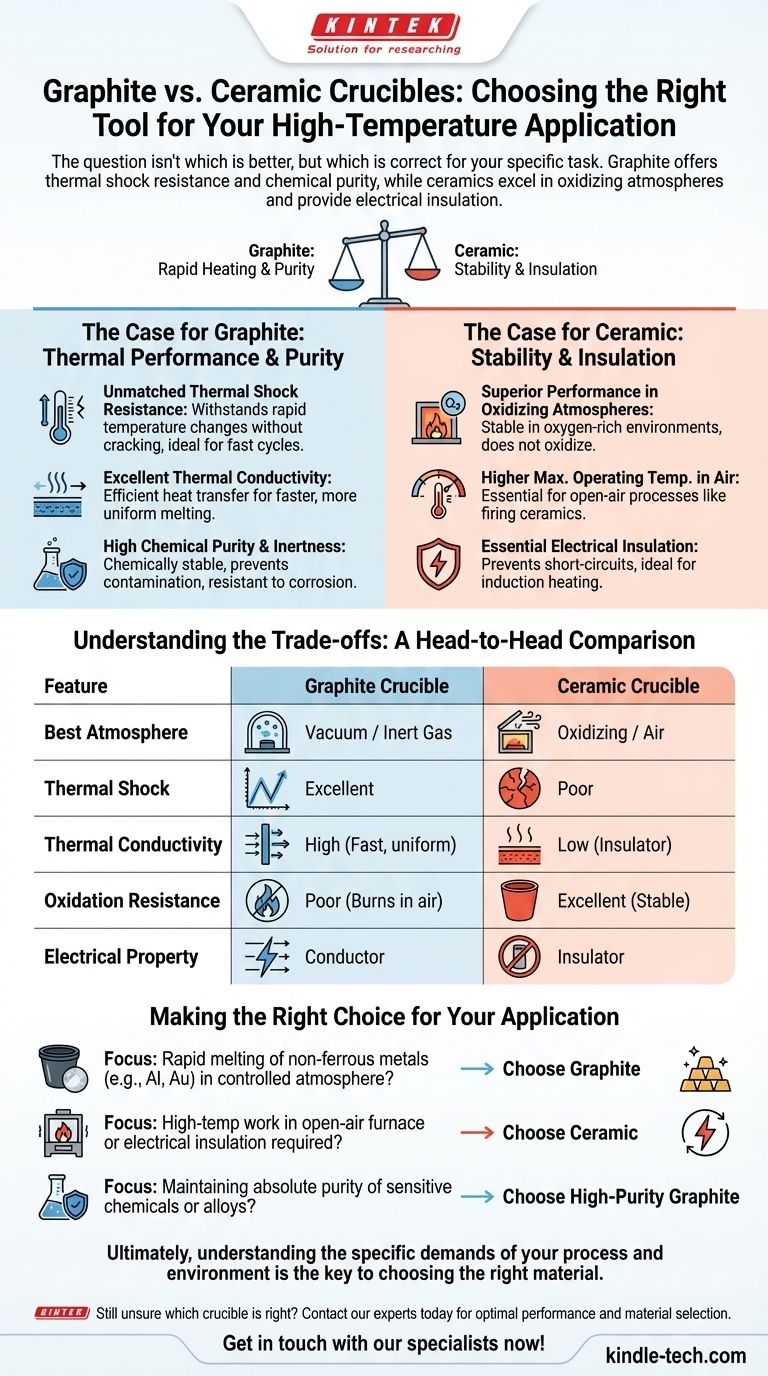
The question isn't whether graphite is better than ceramic, but which material is the correct tool for your specific high-temperature task. Graphite crucibles offer exceptional resistance to thermal shock and high chemical purity, making them ideal for rapidly heating materials. However, ceramic crucibles possess their own distinct advantages, particularly when working in oxidizing atmospheres or when electrical insulation is required.
Choosing between graphite and ceramic crucibles comes down to a primary trade-off: Graphite's unparalleled ability to handle rapid temperature changes versus ceramic's superior stability in oxygen-rich environments at extreme temperatures.

The Case for Graphite: Thermal Performance and Purity
Graphite's unique crystalline structure gives it a combination of properties that make it exceptionally well-suited for specific high-heat applications, particularly in controlled environments.
Unmatched Thermal Shock Resistance
Graphite can withstand extremely rapid changes in temperature without cracking. Its structure effectively dissipates thermal stress.
This makes it ideal for applications requiring fast heating and cooling cycles, or as the references note, for use in "emergency or cold conditions" where pre-heating isn't feasible.
Excellent Thermal Conductivity
Graphite transfers heat with remarkable efficiency. This leads to faster melt times and more uniform heating of the material inside the crucible.
For processes like melting non-ferrous metals, this high conductivity translates directly to reduced energy costs and increased throughput.
High Chemical Purity and Inertness
High-purity graphite is chemically stable and will not contaminate the materials being heated. It is highly resistant to corrosion from both acids and alkali solutions.
This inertness is critical when working with sensitive alloys or precious metals where even minor impurities can compromise the final product's quality.
The Case for Ceramic: Stability and Insulation
While graphite excels in thermal performance, it has a critical vulnerability that makes ceramic the superior, and often only, choice for a different set of applications.
Superior Performance in Oxidizing Atmospheres
Graphite's primary weakness is its reaction to oxygen at high temperatures. In an open-air furnace, graphite will literally burn away, a process known as oxidation.
Ceramic materials, such as alumina or zirconia, are already oxides. They are perfectly stable in oxygen-rich environments, making them the standard for any high-temperature work conducted outside of a vacuum or inert atmosphere.
Higher Maximum Operating Temperatures in Air
Because they do not oxidize, many technical ceramics can operate at higher sustained temperatures in an open atmosphere than graphite can.
This makes them essential for processes like firing ceramics, certain glass work, or metallurgical assays that require extreme heat in the presence of air.
Essential Electrical Insulation
Graphite is an electrical conductor. This can be a major problem in processes like induction heating, where the crucible itself would heat up and potentially short-circuit the system.
Ceramics are excellent electrical insulators. This property is non-negotiable in applications where the crucible must remain electrically isolated from the heating source or the material being melted.
Understanding the Trade-offs: A Head-to-Head Comparison
The best choice becomes clear when you directly compare the materials based on the demands of your specific operating environment.
Factor 1: Operating Atmosphere
- Graphite: Requires a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere at high temperatures to prevent rapid degradation from oxidation.
- Ceramic: The default choice for any work in an open-air or oxygen-rich furnace.
Factor 2: Thermal Shock
- Graphite: The clear winner. It can be heated and cooled quickly without risk of fracture.
- Ceramic: Inherently brittle and must be heated and cooled slowly and carefully to prevent cracking.
Factor 3: Heat Transfer
- Graphite: Excellent thermal conductor, allowing for fast and even heating.
- Ceramic: Acts more as an insulator, heating more slowly and retaining heat longer.
Factor 4: Mechanical Properties
- Graphite: A relatively soft material that is easy to machine into precise shapes but can be chipped or broken if handled roughly.
- Ceramic: Extremely hard and resistant to scratches but very brittle, making it susceptible to shattering from physical impact.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct crucible, align the material's core strengths with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is rapidly melting non-ferrous metals (like aluminum or gold) in a controlled atmosphere: Graphite is the superior choice due to its high thermal conductivity and thermal shock resistance.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature work in an open-air furnace or if electrical insulation is required: A ceramic crucible is the correct and necessary tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is maintaining absolute purity of a sensitive chemical or alloy: High-purity graphite offers exceptional chemical inertness and stability, preventing contamination of your material.
Ultimately, understanding the specific demands of your process and environment is the key to choosing the right material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Graphite Crucible | Ceramic Crucible |
|---|---|---|
| Best Atmosphere | Vacuum / Inert Gas | Oxidizing / Air |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent (Rapid heating/cooling) | Poor (Requires slow heating/cooling) |
| Thermal Conductivity | High (Fast, uniform heating) | Low (Acts as an insulator) |
| Oxidation Resistance | Poor (Burns in air at high temp) | Excellent (Stable in oxygen) |
| Electrical Property | Conductor | Insulator |
| Ideal For | Rapid melting of non-ferrous metals | High-temperature work in air, electrical insulation |
Still unsure which crucible is right for your specific process?
KINTEK specializes in providing the right lab equipment and consumables for your unique needs. Our experts can help you select the ideal graphite or ceramic crucible based on your application's temperature, atmosphere, and material requirements.
Contact us today to ensure optimal performance, prevent material contamination, and extend the life of your equipment. Get in touch with our specialists now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using high-purity alumina crucibles? Achieve Accurate Al2TiO5 Crystallization Kinetics Results
- Why use MgO crucibles for sintering LLZTO ceramic pellets? Ensure Purity and High Ionic Conductivity
- What is the application of crucible? A Guide to High-Temperature Melting and Analysis
- How are laboratory constant-temperature drying ovens and ceramic crucibles utilized in biomass quantification?
- What is used for making crucible for casting metals? Choose the Right Material for Your Furnace
- What is the best crucible for high temperatures? Match Your Material and Atmosphere for Success
- What are the advantages of a crucible furnace? Achieve Precision Melting for Labs & Small-Scale Production
- How do MgO crucibles and sacrificial powders help LATP sintering? Ensure Purity and Prevent Adhesion



















