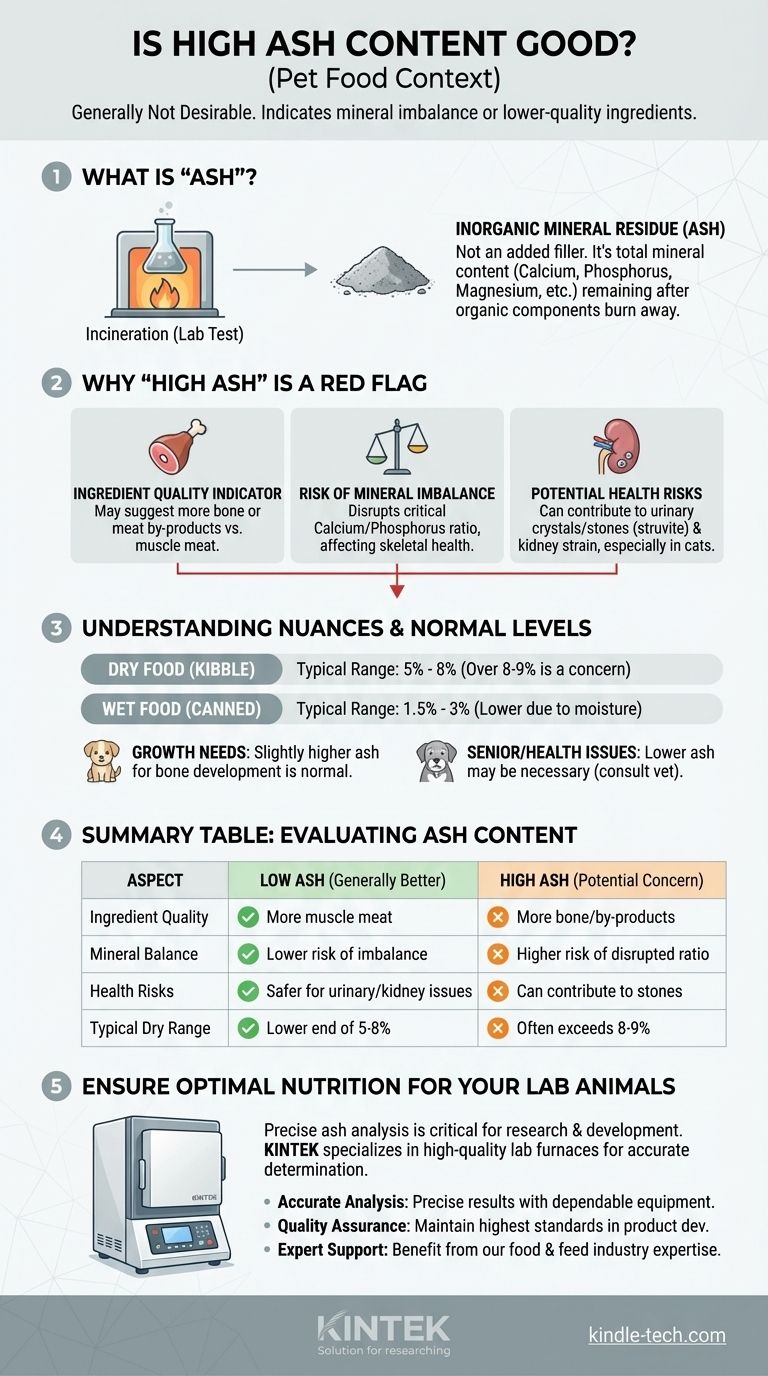
In the context of pet food, a high ash content is generally not considered a desirable quality. While it may sound like a filler ingredient, "ash" is simply the technical term for the mineral content that remains after the organic components (protein, fat, and carbohydrates) are burned away in a lab. A high level can indicate an imbalance of these minerals or the use of lower-quality ingredients.
The term "ash" on a pet food label is often misunderstood. It represents the essential minerals your pet needs for health, but an excessively high level can be a red flag for lower-quality ingredients and may pose health risks, particularly for pets with urinary or kidney conditions.
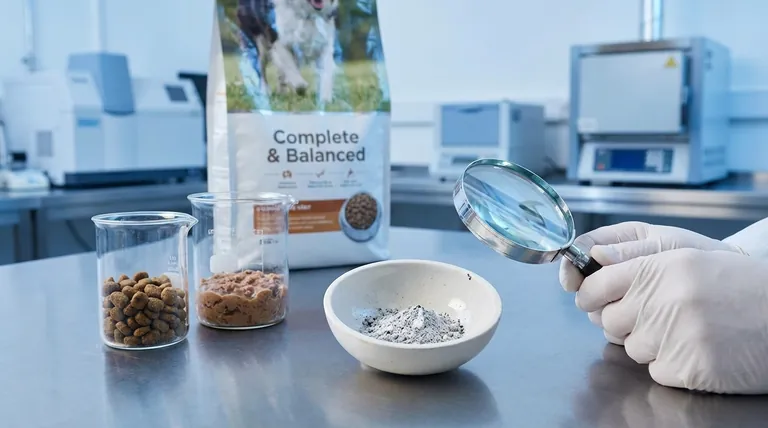

What Exactly Is "Ash" in Pet Food?
It's Not an Added Ingredient
The term "Guaranteed Analysis" on a pet food bag is a measure of its components. To determine the ash content, a sample of the food is completely incinerated in a laboratory furnace.
The organic matter—proteins, fats, and carbohydrates—burns away. The inorganic residue left behind is the ash, which is the food's total mineral content.
A Proxy for Total Mineral Content
This ash is composed of vital minerals your pet needs to thrive. These include calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, zinc, iron, and other essential trace elements.
These minerals are critical for strong bones, nerve function, and overall metabolic health. A complete lack of ash would mean a severe mineral deficiency.
Where These Minerals Come From
The primary sources of minerals in most pet foods are the meat, bone, and meal ingredients. Muscle meat contains some minerals, but bone is extremely dense in calcium and phosphorus.
Therefore, foods that rely heavily on ingredients like bone meal or meat by-products (which can include a high proportion of bone) will naturally have a higher ash content than foods made with deboned muscle meat.
Why "High Ash" Is Often a Red Flag
An Indicator of Ingredient Quality
While not a perfect measure, ash content can offer a clue about the quality of the protein sources. A very high ash level may suggest the manufacturer is using a large amount of bone or lower-cost meat meals instead of higher-quality muscle meat.
Essentially, you might be paying for ground-up bone instead of more digestible and bioavailable protein.
The Risk of Mineral Imbalance
More important than the total amount of ash is the balance of specific minerals within it. The ratio of calcium to phosphorus is particularly critical for skeletal health.
An excessively high mineral content can disrupt this delicate balance, potentially causing health issues over the long term.
Potential Health Implications
For certain pets, high ash content is a significant medical concern. High levels of magnesium and phosphorus can contribute to the formation of urinary crystals and stones (struvite), a painful and dangerous condition, especially in cats.
Pets with compromised kidney function also struggle to process and excrete excess minerals, making a high-ash diet potentially harmful.
Understanding the Nuances and Trade-offs
Ash Content Isn't the Whole Story
Judging a food solely on its ash percentage is a mistake. A food with slightly higher ash from a high-quality fish meal (which includes bones) can be far superior to a low-ash food filled with corn and other grain fillers.
Always evaluate the ash content in the context of the entire ingredient list. The quality of the protein and fat sources is paramount.
What Is a "Normal" Ash Level?
For most commercial pet foods, the typical ash content provides a useful benchmark.
- Dry Food (Kibble): A typical range is between 5% and 8%. Levels exceeding 8-9% may warrant a closer look at the ingredients.
- Wet Food (Canned): Due to high moisture content, a normal range is much lower, typically 1.5% to 3%.
Foods labeled as "low ash" are often formulated for specific health conditions and may not be necessary for a healthy, active pet.
The Needs of Different Life Stages
Nutritional needs change with age. Puppies and kittens require more calcium and phosphorus for their rapidly growing skeletons.
Consequently, foods formulated for growth will naturally and appropriately have a slightly higher ash content than formulas designed for adult or senior pets.
How to Evaluate Ash Content on a Label
Choosing the right food requires looking at the bigger picture, not just one number. Use the ash percentage as one of several data points to assess overall quality.
- If you have a healthy adult dog or cat: Look for an ash content within the typical range (5-8% for dry food) and prioritize foods with high-quality, named meat sources at the top of the ingredient list.
- If you have a puppy or kitten: Expect slightly higher ash levels to support growth, but ensure the food is specifically labeled as "complete and balanced" for their life stage by AAFCO standards.
- If your pet has a history of urinary or kidney issues: Consult your veterinarian immediately, as a prescription low-ash diet is likely the safest and most effective choice.
Ultimately, viewing ash content as one clue to overall food quality, rather than a single pass/fail metric, empowers you to make the best nutritional choice for your pet.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Low Ash Content (Generally Better) | High Ash Content (Potential Concern) |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredient Quality | Indicates more muscle meat | May indicate more bone or meat by-products |
| Mineral Balance | Lower risk of mineral imbalance | Higher risk of disrupted calcium/phosphorus ratio |
| Health Risks | Safer for pets with urinary/kidney issues | Can contribute to urinary crystals and stones |
| Typical Range (Dry Food) | On the lower end of 5-8% | Often exceeds 8-9% |
Ensure Optimal Nutrition for Your Lab Animals
Just as precise mineral content is vital for pet food, accurate analysis is critical for your research and development. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including furnaces for precise ash content determination. Our reliable tools help you ensure ingredient quality and product safety.
Let us support your laboratory's needs:
- Accurate Analysis: Achieve precise results with our dependable furnaces.
- Quality Assurance: Maintain the highest standards in your product development.
- Expert Support: Benefit from our expertise in lab equipment for the food and feed industry.
Ready to enhance your analytical capabilities? Contact our team today to find the perfect solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Temperatures for Advanced Materials
- What is the temperature range of a graphite furnace? Unlock up to 3000°C for advanced materials processing.
- What is the temperature of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C
- What temperature can graphite withstand? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Potential
- Does graphite have a melting point? Unlocking the Extreme Heat Resistance of Graphite













