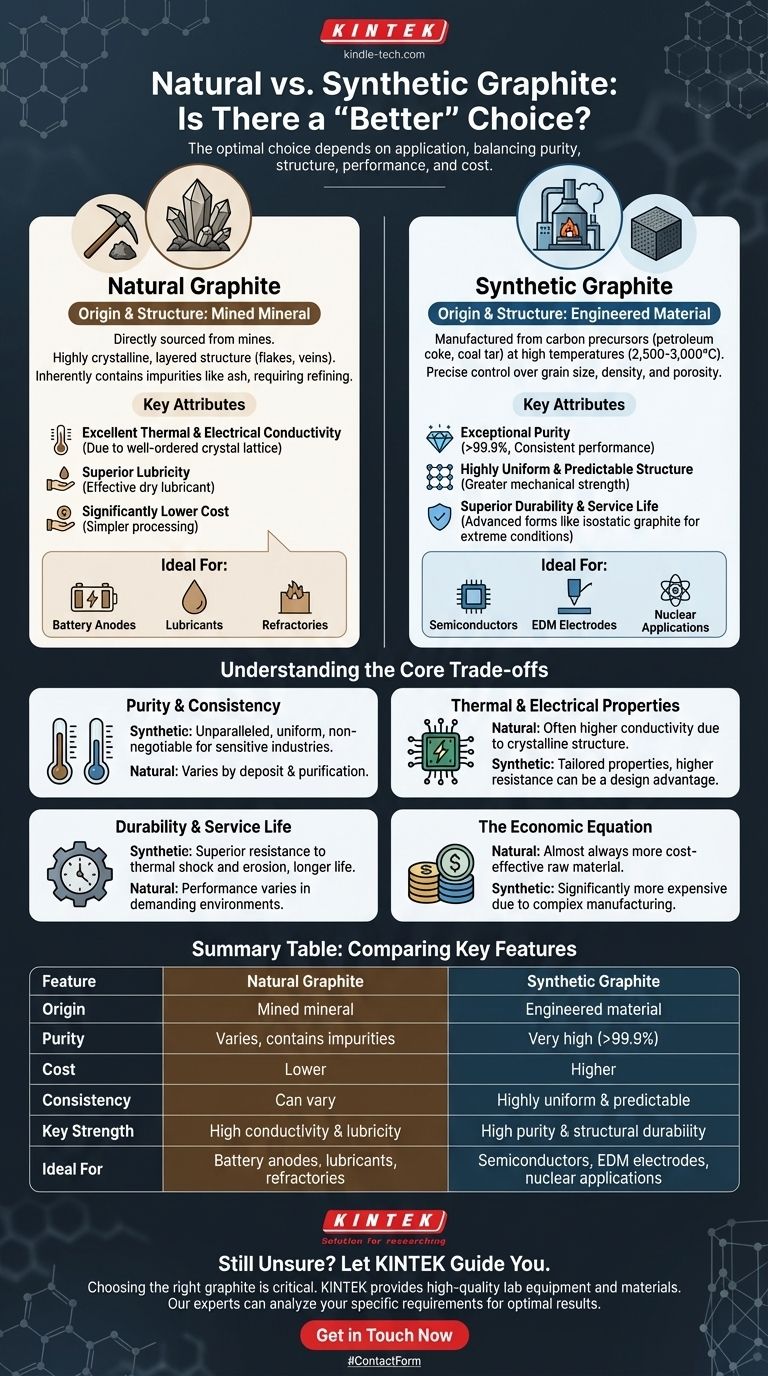
In the world of carbon materials, there is no single "better" graphite. The optimal choice between natural and synthetic graphite is dictated entirely by the specific requirements of your application, balancing factors like purity, structural uniformity, performance, and cost.
The fundamental difference lies in their origin and structure. Natural graphite is a mined mineral with a crystalline structure, making it ideal for applications requiring high conductivity and lubricity. Synthetic graphite is an engineered material with a uniform, high-purity structure designed for demanding environments where predictable performance is critical.

The Case for Natural Graphite
Origin and Structure
Natural graphite is a mineral composed of graphitic carbon that is sourced directly from mines. It is characterized by its highly crystalline, layered structure, often found in forms such as flakes, veins, or amorphous lumps.
This natural origin means it inherently contains impurities like ash, which must be removed through a refining process to meet specific performance standards.
Key Performance Attributes
The well-ordered crystal lattice of natural graphite gives it excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. It also possesses superior lubricity, making it an effective dry lubricant.
From a commercial standpoint, its primary advantage is a significantly lower cost compared to its synthetic counterpart, as it requires mining and purification rather than a complex manufacturing process.
The Case for Synthetic Graphite
An Engineered Material
Synthetic graphite is a manufactured product created by subjecting carbon precursors, like petroleum coke and coal tar pitch, to extremely high temperatures (2,500 to 3,000°C).
This graphitization process allows for precise engineering and control over its final properties, such as grain size, density, and porosity. This results in a material that is highly predictable and consistent from batch to batch.
Key Performance Attributes
The key advantage of synthetic graphite is its exceptional purity, which can exceed 99.9%. As noted, pure graphite performs better in terms of overall durability and consistent electrical properties.
This purity, combined with a uniform, fine-grained structure, provides greater mechanical strength. Advanced forms, like isostatic graphite, are engineered for structural applications, offering a significantly increased service life and superior performance under extreme conditions.
Understanding the Core Trade-offs
Purity and Consistency
Synthetic graphite offers unparalleled purity and structural consistency, which is non-negotiable in sensitive industries like semiconductor or nuclear applications.
Natural graphite's performance, while excellent, can vary based on the geological deposit and the intensity of the purification process.
Thermal and Electrical Properties
High-quality flake natural graphite often exhibits higher thermal and electrical conductivity than standard synthetic grades due to its near-perfect crystalline structure.
However, the properties of synthetic graphite can be tailored. For applications like heating elements or electrodes, its slightly higher electrical resistance is often a design advantage.
Durability and Service Life
The purity and uniform microstructure of synthetic graphite often translate to better performance in demanding environments. For structural components exposed to high heat or corrosive chemicals, engineered forms like isostatic graphite provide superior resistance to thermal shock and erosion, leading to a longer service life.
The Economic Equation
Natural graphite is almost always the more cost-effective raw material, making it the default choice for high-volume applications where its properties are sufficient.
The energy-intensive, multi-step manufacturing process makes synthetic graphite significantly more expensive, reserving it for applications where its unique performance characteristics justify the cost.
How to Choose the Right Graphite for Your Goal
Your application's primary demand—be it economic efficiency or absolute performance—is the deciding factor.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and high conductivity: Natural graphite is the clear choice for applications like lubricants, pencils, battery anodes, and refractory materials.
- If your primary focus is high purity and predictable performance: Synthetic graphite is essential for demanding uses such as semiconductor manufacturing, EDM electrodes, and nuclear moderators.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and service life under stress: Advanced engineered forms like isostatic graphite provide the structural integrity required for crucibles, continuous casting dies, and rocket nozzles.
Ultimately, understanding the inherent differences between these materials empowers you to select not the "best" graphite, but the right graphite for the job.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Natural Graphite | Synthetic Graphite |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Mined mineral | Engineered material |
| Purity | Varies; contains impurities | Very high (>99.9%) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Consistency | Can vary by deposit | Highly uniform & predictable |
| Key Strength | High conductivity & lubricity | High purity & structural durability |
| Ideal For | Battery anodes, lubricants, refractories | Semiconductors, EDM electrodes, nuclear applications |
Still Unsure Which Graphite Is Right for Your Project?
Choosing between natural and synthetic graphite is critical for your product's performance and cost-efficiency. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including the right graphite materials for your specific laboratory or industrial needs.
Our experts can help you analyze your application requirements—whether you need the cost-effectiveness of natural graphite or the high-purity, durable performance of synthetic graphite—to ensure optimal results.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation and let KINTEK provide the perfect material solution for your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Electrode Polishing Material for Electrochemical Experiments
People Also Ask
- Why is graphite used in furnaces? For Extreme Heat, Purity, and Efficiency
- What are the advantages of graphite furnace? Achieve High-Temperature Precision and Purity
- What are the advantages of graphite? Unlock Superior Performance in High-Temperature Processes
- Does graphite have a melting point? Unlocking the Extreme Heat Resistance of Graphite
- What are the applications of graphite material? Leveraging Extreme Heat and Precision for Industrial Processes



















