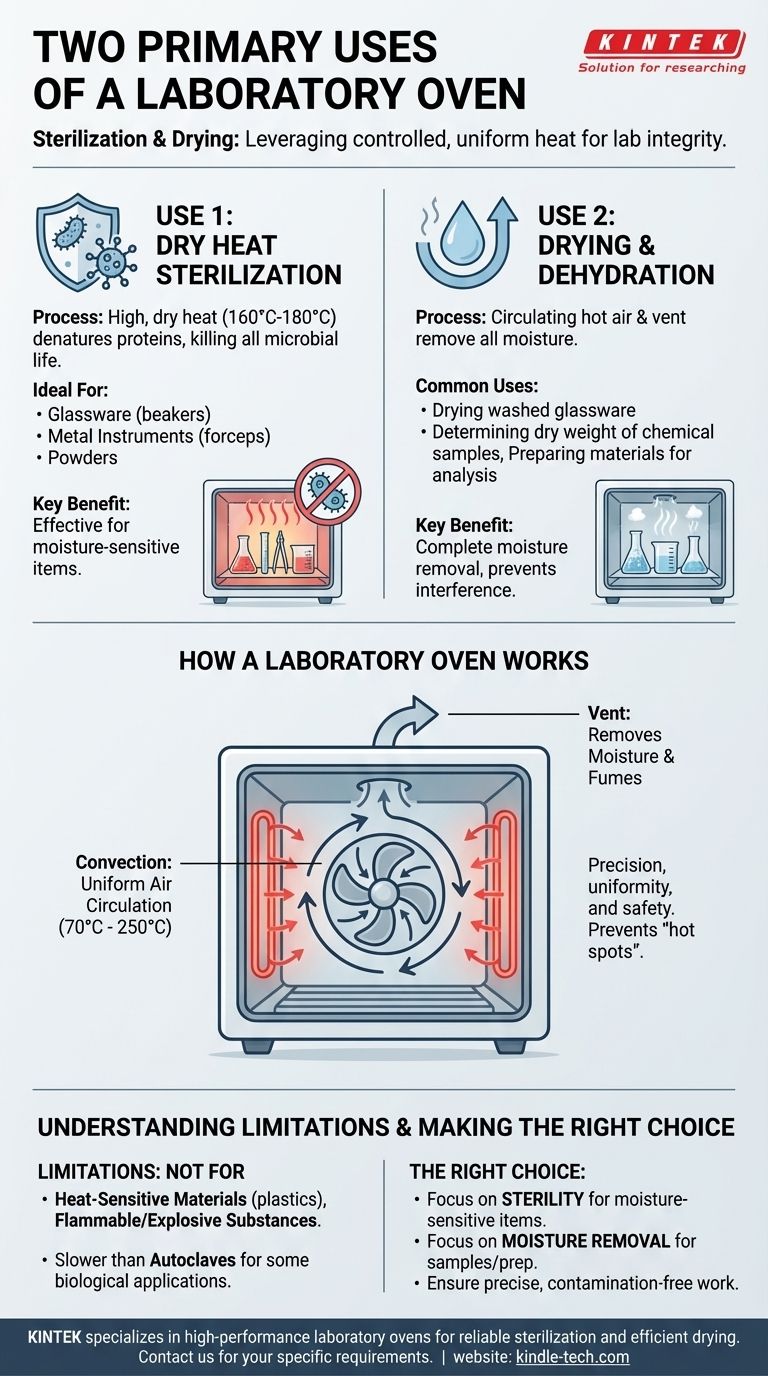
In a laboratory setting, the oven is a cornerstone for two primary functions: sterilization of equipment and the drying of samples. It leverages controlled, uniform heat to achieve these goals, making it an indispensable tool for ensuring both the integrity of experiments and the readiness of lab materials.
The core purpose of a laboratory oven is to provide a stable, high-temperature environment. This allows for the complete removal of moisture and the destruction of microorganisms without the use of direct, damaging radiant heat.
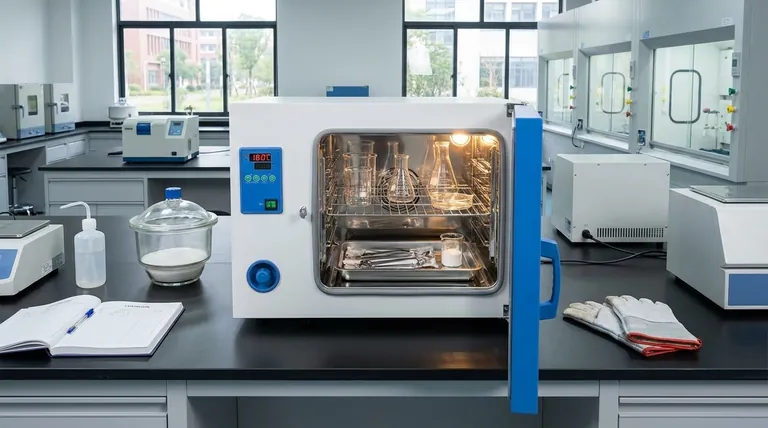

How a Laboratory Oven Achieves Its Purpose
A laboratory oven is fundamentally different from a kitchen oven. Its design is centered on precision, uniformity, and safety for scientific applications.
The Principle of Convection Heating
The key mechanism is convection. An internal fan circulates hot air throughout the chamber, ensuring every item receives a uniform temperature. This prevents "hot spots" that could damage a sample or leave parts of an instrument unsterilized.
Controlled Temperature Environment
These ovens typically operate at temperatures between 70°C and 250°C (160°F to 480°F). This range is high enough to kill most microbes and evaporate water efficiently but is generally below the combustion point of many materials.
Removal of Moisture and Fumes
A crucial feature is the vent. As water evaporates from samples or fumes are released during heating, the vent allows them to escape the chamber. This process is essential for complete drying and prevents a buildup of potentially reactive volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Deep Dive into Core Applications
While the oven has several uses, sterilization and drying are its most frequent and critical roles.
Use 1: Dry Heat Sterilization
Sterilization is the process of eliminating all forms of microbial life. The oven's high, dry heat denatures the proteins within microorganisms, effectively killing them.
This method is ideal for sterilizing materials that can withstand high temperatures but could be damaged by moisture, such as glassware (beakers, flasks), metal instruments (forceps, scalpels), and powders.
Use 2: Drying and Dehydration
The most common daily use for a lab oven is drying. The combination of circulating hot air and the vent efficiently removes all traces of moisture.
This is essential for drying washed glassware before an experiment, removing water from chemical samples to determine their dry weight, or preparing materials for further chemical analysis where moisture would interfere.
Understanding the Limitations
While versatile, a laboratory oven is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for safe and effective use.
Not for Heat-Sensitive Materials
Plastics, rubber, and many electronic components cannot withstand the high temperatures of a sterilizing oven and will melt or be destroyed.
Slower than Other Sterilization Methods
Dry heat sterilization is effective but slow, often requiring hours at a high temperature. For many biological applications, a steam sterilizer (autoclave) is significantly faster and more efficient for items that can tolerate moisture.
Not for Flammable or Explosive Materials
Standard laboratory ovens are not designed to safely heat flammable solvents or volatile substances. Doing so can lead to a dangerous buildup of fumes and create a significant fire or explosion risk. Specialized, explosion-proof ovens are required for such applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To use a laboratory oven effectively, match the tool to your specific scientific objective.
- If your primary focus is sterility for moisture-sensitive items: The oven is the correct choice for metal instruments and glassware.
- If your primary focus is complete moisture removal: The oven is the ideal tool for drying samples, powders, or preparing glassware for an experiment.
Ultimately, the laboratory oven serves as a reliable workhorse for preparing materials and ensuring your experiments start on a clean, dry, and sterile foundation.
Summary Table:
| Primary Use | Key Function | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Sterilization | Eliminates microbes via dry heat | Glassware, metal instruments, powders |
| Drying/Dehydration | Removes moisture with uniform heat | Preparing glassware, sample drying, moisture analysis |
Ensure your lab's foundational work is precise and contamination-free. KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory ovens designed for reliable sterilization and efficient drying. Our equipment provides the uniform heat and safety features your lab needs for accurate results. Contact us today to find the perfect oven for your specific laboratory requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is a forced-air drying oven required for ZnS powder? Protect Sintered Ceramics from Cracking
- How does a laboratory constant temperature drying oven contribute to the processing of synthesized Zinc Oxide precipitates?
- What is the function of a laboratory drying oven in Zr2.5Nb alloy pretreatment? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Results
- What is the primary purpose of using an electric drying oven for dense refractory bricks? Optimize Raw Material Prep
- What is the role of a laboratory drying oven in catalyst treatment? Ensure Structural Integrity & High Performance



















