At its core, induction heating technology is divided into two primary furnace designs. These are the coreless induction furnace and the channel induction furnace. While both use electromagnetic induction to melt metal with high efficiency and minimal material loss, their internal architecture and operating principles are fundamentally different, making them suitable for distinct industrial applications.
The critical distinction lies in their operational model: coreless furnaces are ideal for flexible, batch-based melting of various metals, while channel furnaces are designed for the highly efficient, continuous holding and melting of a single type of metal.

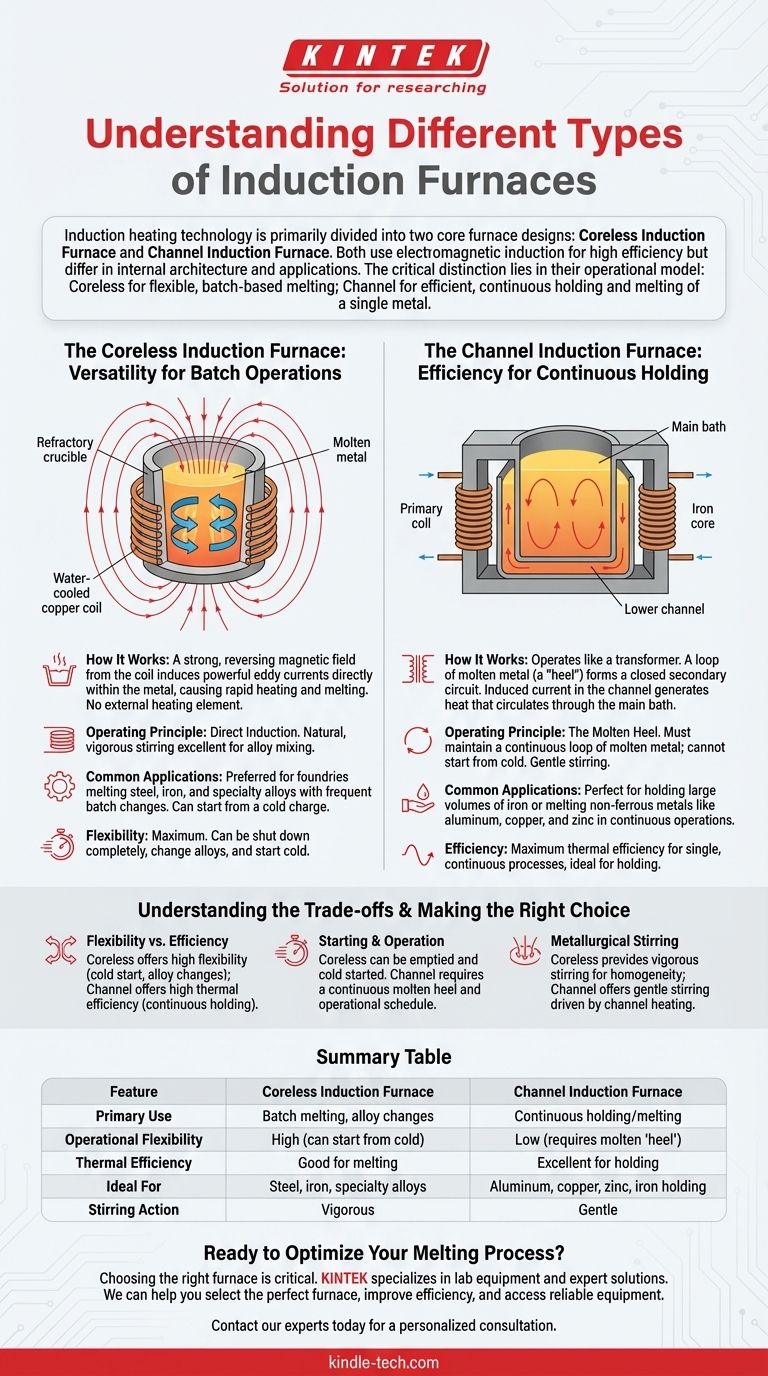
The Coreless Induction Furnace: Versatility for Batch Operations
A coreless furnace is the more conceptually straightforward of the two designs. It is essentially a refractory-lined crucible surrounded by a tightly wound, water-cooled copper coil.
How It Works: The Crucible and Coil
When a powerful alternating current is passed through the coil, it generates a strong, reversing magnetic field. This field directly couples with the metal charge placed inside the crucible.
The Operating Principle: Direct Induction
The magnetic field induces powerful eddy currents within the metal itself, and the metal's natural electrical resistance causes it to heat up rapidly and melt. This process requires no external heating element and no physical contact with the heat source.
Common Applications
Because it can be started and stopped easily and can melt a charge from solid material, the coreless furnace is extremely versatile. It is the preferred choice for foundries melting steel, iron, and specialty alloys where different batches of material may be required.
The Channel Induction Furnace: Efficiency for Continuous Holding
The channel furnace operates more like a transformer, where the furnace's coil and iron core are the primary circuit.
How It Works: The Transformer Analogy
A loop, or "channel," of molten metal forms a closed secondary circuit through the iron core. The current induced in this molten metal loop generates intense heat, which then circulates through the main bath of the furnace via convection.
The Operating Principle: The Molten Heel
A key characteristic of a channel furnace is that it must contain a continuous loop of molten metal—known as a "heel"—to operate. It cannot be started with a cold, solid charge. This makes it ideal for holding large quantities of metal at a specific temperature for extended periods.
Common Applications
The high thermal efficiency of channel furnaces makes them perfect for holding and superheating large volumes of molten iron or melting lower-temperature non-ferrous metals like aluminum, copper, and zinc in continuous or semi-continuous operations.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these furnace types involves a clear set of operational and metallurgical trade-offs. Neither is inherently superior; they are simply engineered for different tasks.
Flexibility vs. Efficiency
The coreless furnace offers maximum flexibility. You can shut it down completely, change the alloy you're melting with each batch, and start from a cold charge.
The channel furnace offers maximum thermal efficiency for a single, continuous process. Its design is purpose-built to maintain temperature, making it more energy-efficient than a coreless furnace for holding applications.
Starting and Operation
A coreless furnace can be emptied completely between uses. A channel furnace must always maintain its molten heel, requiring a more continuous operational schedule.
Metallurgical Stirring
The electromagnetic forces in a coreless furnace create a natural, vigorous stirring action, which is excellent for mixing alloys and achieving chemical and thermal homogeneity.
Stirring in a channel furnace is gentler and is primarily driven by the heating that occurs within the channel loop itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be aligned with your specific production goal.
- If your primary focus is batch melting of diverse alloys like steel or specialty metals: The operational flexibility of the coreless furnace is the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is holding large volumes of molten metal at a constant temperature or the continuous melting of a single non-ferrous alloy: The superior energy efficiency of the channel furnace is purpose-built for this task.
- If your primary focus involves frequent shutdowns or rapid changes in production: The ability of a coreless furnace to start from cold makes it the only practical option.
Understanding this fundamental design difference is the key to selecting the right induction technology for your metallurgical process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Coreless Induction Furnace | Channel Induction Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Batch melting, alloy changes | Continuous holding/melting |
| Operational Flexibility | High (can start from cold) | Low (requires molten 'heel') |
| Thermal Efficiency | Good for melting | Excellent for holding |
| Ideal For | Steel, iron, specialty alloys | Aluminum, copper, zinc, iron holding |
| Stirring Action | Vigorous | Gentle |
Ready to Optimize Your Melting Process?
Choosing between a coreless and channel induction furnace is critical for your operation's efficiency and productivity. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert solutions for all your laboratory and metallurgical needs.
We can help you:
- Select the perfect induction furnace for your specific application.
- Improve your melting efficiency and reduce energy costs.
- Access reliable equipment and consumables for consistent results.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity



















