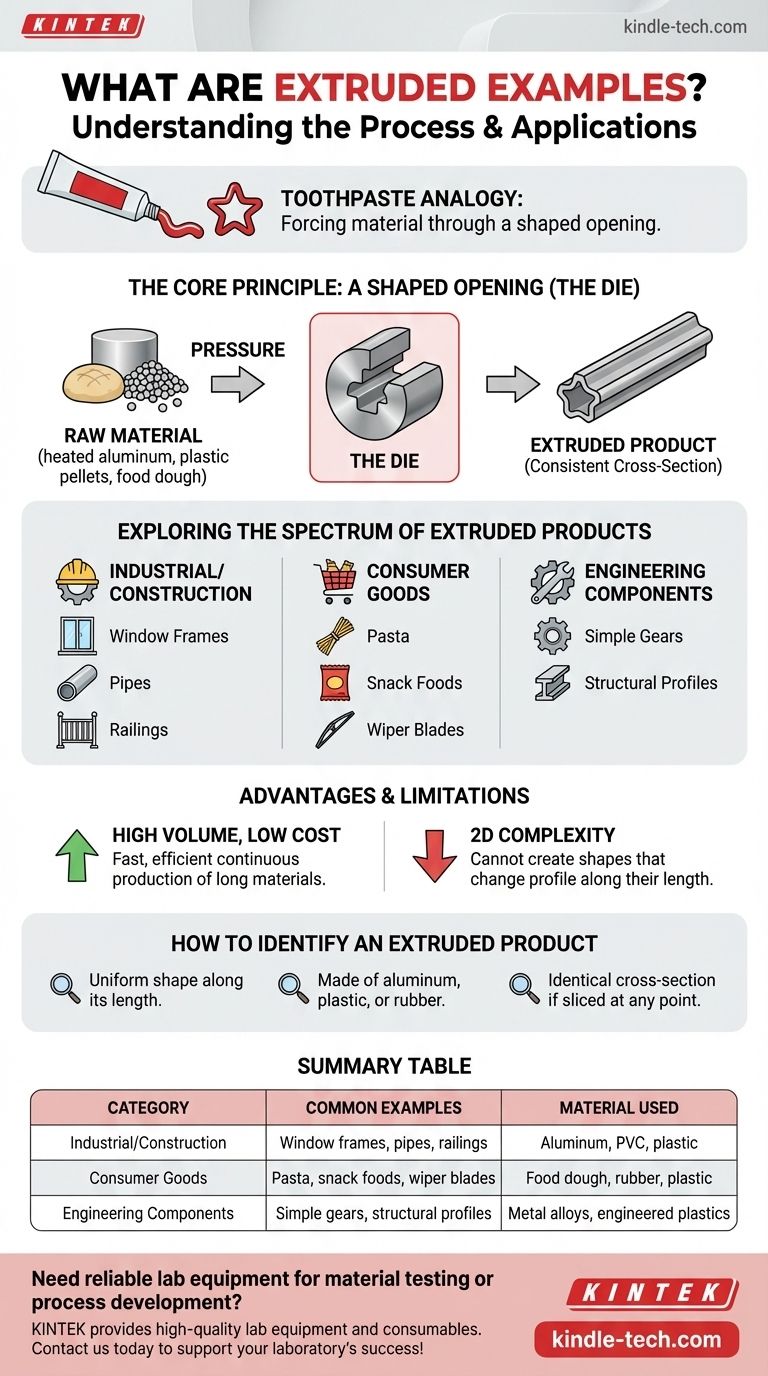
In short, extruded products are items created by forcing a material through a shaped opening called a die. Common examples include everyday objects like pasta, aluminum window frames, plastic pipes, and even many snack foods. The defining feature of all these items is their consistent cross-sectional profile.
The core concept to grasp is that extrusion is a manufacturing process designed to create objects of a fixed, continuous shape. Think of it like squeezing toothpaste from a tube—the shape of the opening determines the shape of the paste that comes out.

What Unites These Examples? The Extrusion Process
To truly understand what makes something an "extruded example," you need to look past the final product and see the manufacturing principle they all share.
The Core Principle: A Shaped Opening
The heart of the extrusion process is the die. This is a hardened tool with a specific cutout.
A raw material, such as heated aluminum, plastic pellets, or food dough, is pushed with immense pressure through this die. The material emerges on the other side as a long, continuous piece that perfectly matches the shape of the die's opening.
The Result: A Consistent Cross-Section
This process means that every extruded object has a uniform profile along its entire length.
If you were to slice through a plastic pipe, an aluminum railing, or a piece of spaghetti at any point, the cross-section would look identical. This consistency is the hallmark of extrusion.
Exploring the Spectrum of Extruded Products
The versatility of this process is evident in the vast range of products it creates, from industrial components to common household goods.
Industrial and Construction Materials
Many foundational materials in construction are extruded. This includes aluminum cans, PVC pipes, and the complex profiles of window panes and shower stalls. The process is ideal for creating long, strong, and uniform structural pieces.
Everyday Consumer Goods
You interact with extruded products daily. All forms of pasta, from spaghetti to fusilli, are extruded. Many puffed snack foods get their shape this way, as do rubber windshield wipers and plastic railings.
Advanced Engineering Components
Extrusion is also precise enough to create complex mechanical parts. While not as common for intricate shapes, certain types of gears with a consistent tooth profile can be extruded efficiently before being cut to length.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Extrusion
Like any manufacturing method, extrusion has clear advantages and limitations that determine its use.
The Key Advantage: High Volume, Low Cost
Once the initial die is created, the extrusion process is incredibly fast and efficient. It allows for the continuous production of thousands of feet of material with minimal labor, making it extremely cost-effective for high-volume manufacturing.
The Primary Limitation: Two-Dimensional Complexity
The defining strength of extrusion—its consistent cross-section—is also its main constraint. The process cannot create shapes that change their profile along their length. For example, you can extrude a simple pipe, but you cannot extrude a complex object like a bottle with a narrowing neck.
How to Identify an Extruded Product
By understanding the core principles, you can easily spot extruded items in the world around you.
- If you see a long object with a uniform shape: It is very likely an extruded product, especially if it's made of aluminum, plastic, or rubber.
- If you are designing a part with a constant profile: Consider extrusion as a highly efficient and cost-effective manufacturing method for your project.
- If you are trying to understand how something was made: Look at its cross-section. If that shape is the same from end to end, you are almost certainly looking at an example of extrusion.
Recognizing the principle of extrusion allows you to see the simple, efficient engineering behind countless objects you use every day.
Summary Table:
| Product Category | Common Examples | Material Used |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial/Construction | Window frames, pipes, railings | Aluminum, PVC, plastic |
| Consumer Goods | Pasta, snack foods, wiper blades | Food dough, rubber, plastic |
| Engineering Components | Simple gears, structural profiles | Metal alloys, engineered plastics |
Need reliable lab equipment for material testing or process development? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your research and manufacturing needs. Whether you're developing new extruded products or optimizing your production process, our solutions help you achieve precise, consistent results. Contact us today to learn how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Lab Rubber Calendering Machine
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- Single Punch Manual Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is the process of calendering? A Guide to High-Volume Plastic Film Production
- What are the ingredients used in rubber compounding? A Guide to the Essential Formula
- How does a grinding mill work? A Guide to Crushing, Grinding, and Pulverizing
- What is the difference between grinding and pulverizing? Achieve the Perfect Particle Size for Your Application
- What is a calendering machine? Transform Material Surfaces with Precision










