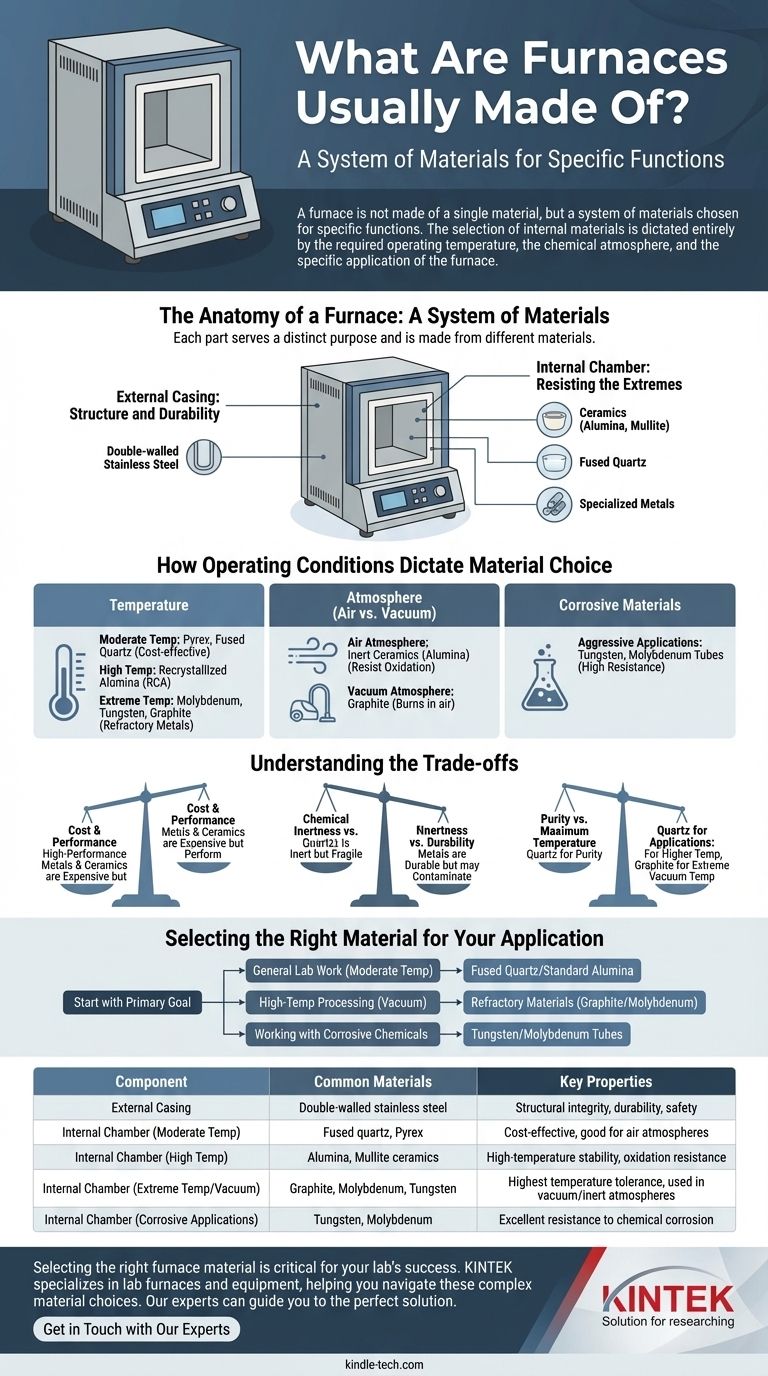
To understand what a furnace is made of, you must look at its components separately. The external body is typically built from durable metals like double-walled stainless steel for structural integrity. The critical internal components, which are directly exposed to heat and processing conditions, are made from highly specialized materials like ceramics (alumina), quartz glass, or refractory metals such as molybdenum, tungsten, and graphite.
A furnace is not made of a single material, but a system of materials chosen for specific functions. The selection of internal materials is dictated entirely by the required operating temperature, the chemical atmosphere, and the specific application of the furnace.

The Anatomy of a Furnace: A System of Materials
A furnace’s construction is best understood by separating its structural body from its functional core. Each part serves a distinct purpose and is therefore made from different materials.
The External Casing: Structure and Durability
The outer body or casing of most modern lab and industrial furnaces is made of double-walled stainless steel.
The purpose of the casing is not to withstand the peak internal temperature but to provide a robust, stable, and long-lasting structure that protects the user and houses the internal components.
The Internal Chamber: Resisting the Extremes
The internal work tube or chamber is where the material science truly matters. This is the component that must endure extreme heat, potential chemical reactions, and sometimes a hard vacuum.
Common materials for these chambers include ceramics (like alumina or mullite), fused quartz, and specialized metals.
How Operating Conditions Dictate Material Choice
The specific material used for a furnace's internal chamber is a direct consequence of the process it is designed to run. The three most critical factors are temperature, atmosphere, and the substance being heated.
The Role of Temperature
Temperature is the primary limiting factor. Materials are chosen based on their ability to remain stable at the desired operating temperature.
For moderate temperatures, Pyrex or fused quartz are common and cost-effective choices for work tubes.
For high-temperature applications, recrystallized alumina (RCA) ceramic is a standard. For the most extreme temperatures found in vacuum furnaces, refractory materials like molybdenum, tungsten, and graphite are used for heating elements and hearths.
The Impact of Atmosphere (Air vs. Vacuum)
The chemical environment inside the furnace is just as important as temperature. An air atmosphere contains about 21% oxygen, which is highly reactive at high temperatures.
In an air-filled furnace, materials must resist oxidation. This is why inert ceramics like alumina are so prevalent.
In a vacuum furnace, the absence of oxygen allows for the use of materials like graphite, which would simply burn away in the presence of air at high temperatures.
Handling Corrosive Materials
If the process involves chemically corrosive substances, standard materials may degrade or contaminate the sample.
For these aggressive applications, highly resistant metal tubes made of tungsten or molybdenum are required to ensure the integrity of both the furnace and the process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace material is an exercise in balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" material, only the most appropriate one for a given task.
Cost vs. Performance
High-performance materials come at a premium. Refractory metals like tungsten and high-purity ceramics are significantly more expensive than standard quartz or lower-grade alumina. This cost is justified by their ability to perform under extreme conditions where other materials would fail.
Chemical Inertness vs. Durability
Quartz glass offers exceptional purity and is highly inert, making it ideal for sensitive processes. However, it is more fragile than ceramic or metal alternatives. Metals like stainless steel or Inconel offer excellent durability but may not be suitable for processes where metallic contamination is a concern.
Purity vs. Maximum Temperature
While quartz is excellent for purity, it has a lower maximum operating temperature than alumina. Alumina, in turn, cannot handle the extreme temperatures that molybdenum or graphite can in a vacuum environment. The choice often comes down to the highest temperature your process requires.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Application
Your choice of furnace material should be guided by your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is general lab work at moderate temperatures: A furnace with a fused quartz or standard alumina work tube offers the best balance of performance and cost.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing in a vacuum: You need a furnace built with refractory materials, using graphite or molybdenum for heating elements and internal structures.
- If your primary focus is working with corrosive chemicals: You must use specialized tubes made from tungsten or molybdenum to prevent chemical degradation and ensure process integrity.
Ultimately, the right furnace material is the one that remains stable and non-reactive under your specific process conditions.
Summary Table:
| Component | Common Materials | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| External Casing | Double-walled stainless steel | Structural integrity, durability, safety |
| Internal Chamber (Moderate Temp) | Fused quartz, Pyrex | Cost-effective, good for air atmospheres |
| Internal Chamber (High Temp) | Alumina, Mullite ceramics | High-temperature stability, oxidation resistance |
| Internal Chamber (Extreme Temp/Vacuum) | Graphite, Molybdenum, Tungsten | Highest temperature tolerance, used in vacuum/inert atmospheres |
| Internal Chamber (Corrosive Applications) | Tungsten, Molybdenum | Excellent resistance to chemical corrosion |
Selecting the right furnace material is critical for your lab's success. The optimal choice depends entirely on your specific operating temperature, chemical atmosphere, and application requirements.
KINTEK specializes in lab furnaces and equipment, helping you navigate these complex material choices to ensure safety, performance, and process integrity. Our experts can guide you to the perfect solution for your high-temperature processing needs.
Contact us today to discuss your application and find the ideal furnace for your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the function of alumina milling jars in the preparation of SiC/B4C composite powders? Ensure High-Purity Mixing
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of refractory materials? Balancing Heat Resistance with Cost & Durability
- Why are stirring or homogenizing devices essential in phase inversion? Achieve Perfect Photocatalytic Membrane Dispersion
- Why are cemented carbide balls selected as the grinding media? Optimize Graphene-Reinforced Alumina Ceramics
- What is the purpose of using adjustable high-temperature fixtures? Ensure Stable Material Interfaces up to 1000°C
- What is the purpose of the compression chamber in a vacuum pump? The Heart of Vacuum Generation
- Why is it helpful to reduce pressure inside the rotavap? Gentle Solvent Removal for Heat-Sensitive Compounds
- What are the temperature and pressure limitations for using the sample holder? Essential Guide for Lab Safety



















