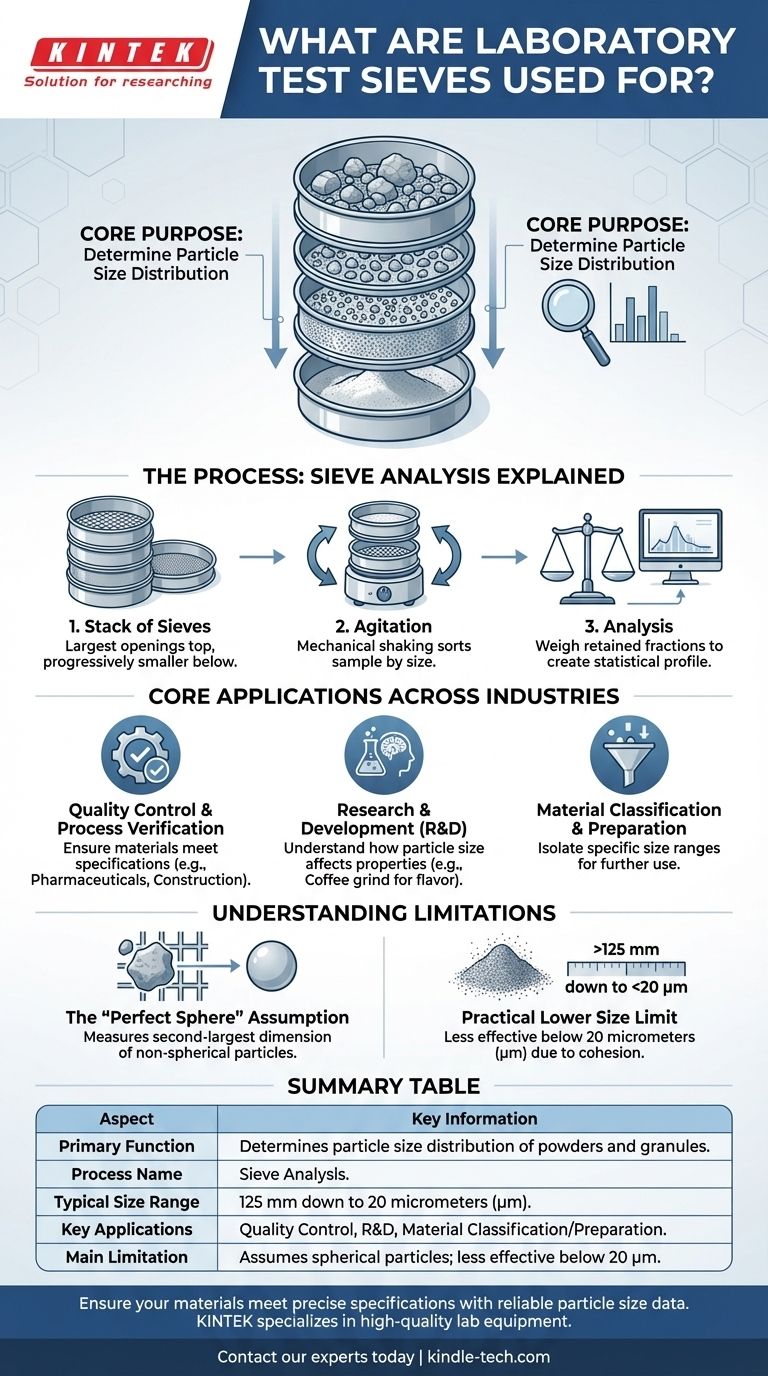
At their core, laboratory test sieves are precision instruments for physical measurement. They are used to determine the particle size distribution of powders, granules, and other bulk materials. This process, known as sieve analysis, involves passing a sample through a stack of sieves with progressively smaller mesh openings to separate the material into distinct size fractions, which are then weighed and analyzed.
The physical properties and performance of a granular material are often dictated by the size of its individual particles. Laboratory test sieves provide a standardized, reliable, and universally accepted method to measure and control this critical variable, making them an essential tool for quality control and research.

The Fundamental Goal: Understanding Particle Size
Sieve analysis is not simply about separating big particles from small ones. It is a quantitative method for characterizing the full spectrum of sizes within a given sample.
What is Particle Size Distribution?
A sample of sand, flour, or chemical powder is not made of uniform particles. It is a mixture of particles of many different sizes.
Particle size distribution is the measurement of this mix. The analysis tells you what percentage of your sample falls into specific size ranges (e.g., 15% is larger than 500 microns, 40% is between 250 and 500 microns, etc.).
The Basic Sieving Principle
The process uses a stack of test sieves, each with a wire mesh of a specific, certified aperture size. The sieve with the largest openings is placed at the top, with subsequent sieves having progressively smaller openings placed below it.
A measured sample of the material is placed in the top sieve. The stack is then agitated by a mechanical sieve shaker.
Smaller particles pass through the mesh openings until they are retained by a sieve with openings too small for them to pass. This effectively sorts the sample by size.
From Separation to Analysis
After shaking is complete, the material retained on each sieve is weighed. By calculating the weight of each fraction relative to the total sample weight, you can create a statistical profile or curve of the particle size distribution. This data is the primary output of the analysis.
Core Applications Across Industries
The data from sieve analysis is critical for ensuring that materials will behave as expected. This makes it a foundational process in nearly every industry that handles solid materials.
Quality Control and Process Verification
This is the most common application. Sieve analysis is used to confirm that both raw materials and finished products meet required specifications.
In pharmaceuticals, particle size affects a drug's dissolution rate and bioavailability. In construction, the aggregate size distribution is critical for the strength and workability of concrete. Sieving ensures this consistency.
Research and Development (R&D)
When developing new products, R&D teams use sieves to understand how particle size influences material properties.
For example, they might test different grinds of coffee to see how the particle size distribution affects extraction and flavor. This allows them to define the ideal specifications for a new product.
Material Classification and Preparation
Sometimes, the goal is not just analysis but fractioning—separating a bulk material into specific size ranges. These separated fractions can then be used for further testing or as components in a specialized product.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While sieve analysis is a powerful standard, it is essential to understand its inherent assumptions and limitations to interpret results correctly.
The "Perfect Sphere" Assumption
Sieve analysis inherently assumes that all particles are perfect spheres. In reality, particles can be elongated, flat, or irregular.
An elongated particle may pass through a mesh opening that is smaller than its total length by orienting itself vertically. This means the method technically measures a particle's second-largest dimension, a crucial detail to remember when comparing results with other methods.
The Practical Lower Size Limit
Sieving is most effective for particles ranging from 125 millimeters down to about 20 micrometers (µm).
Below 20 µm, forces like static electricity and cohesion cause fine particles to clump together, preventing them from passing through the mesh. For these sub-sieve or "ultra-fine" materials, other methods like laser diffraction are required.
Procedural Sensitivity
The final results can be influenced by the test procedure itself. Factors like the duration of shaking, the amplitude of vibration, and the initial sample size must be standardized. Without a consistent procedure, results from different tests cannot be reliably compared.
Applying Sieve Analysis to Your Objective
Your approach to sieve analysis should align directly with your end goal.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control: Prioritize establishing and adhering to a standardized operating procedure (SOP) to ensure repeatable and comparable results over time.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Use sieve analysis to correlate specific particle size fractions with desired product performance characteristics, such as strength, texture, or dissolution rate.
- If your primary focus is material preparation: Use individual sieves or small stacks to cleanly isolate the specific particle size range required for subsequent experiments or production processes.
Ultimately, mastering sieve analysis is about controlling a fundamental physical property to guarantee the intended quality and performance of your material.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Information |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Determines particle size distribution of powders and granules. |
| Process Name | Sieve Analysis. |
| Typical Size Range | 125 mm down to 20 micrometers (µm). |
| Key Applications | Quality Control, R&D, Material Classification/Preparation. |
| Main Limitation | Assumes spherical particles; less effective below 20 µm. |
Ensure your materials meet precise specifications with reliable particle size data. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including precision test sieves and sieve shakers, to support your laboratory's quality control and research needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect sieving solution for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of sieve analysis? A Guide to Cost-Effective Particle Sizing
- What is the operating procedure of a sieve shaker? Master Accurate Particle Size Analysis
- What is the maximum sieving deviation permitted? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Precision Limits
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- Can sieving be used to separate a solid substance from a liquid substance? Learn the Right Technique for Your Mixture



















