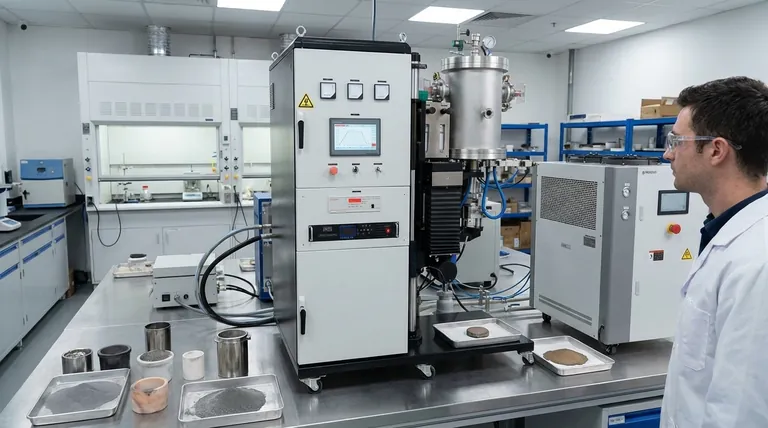
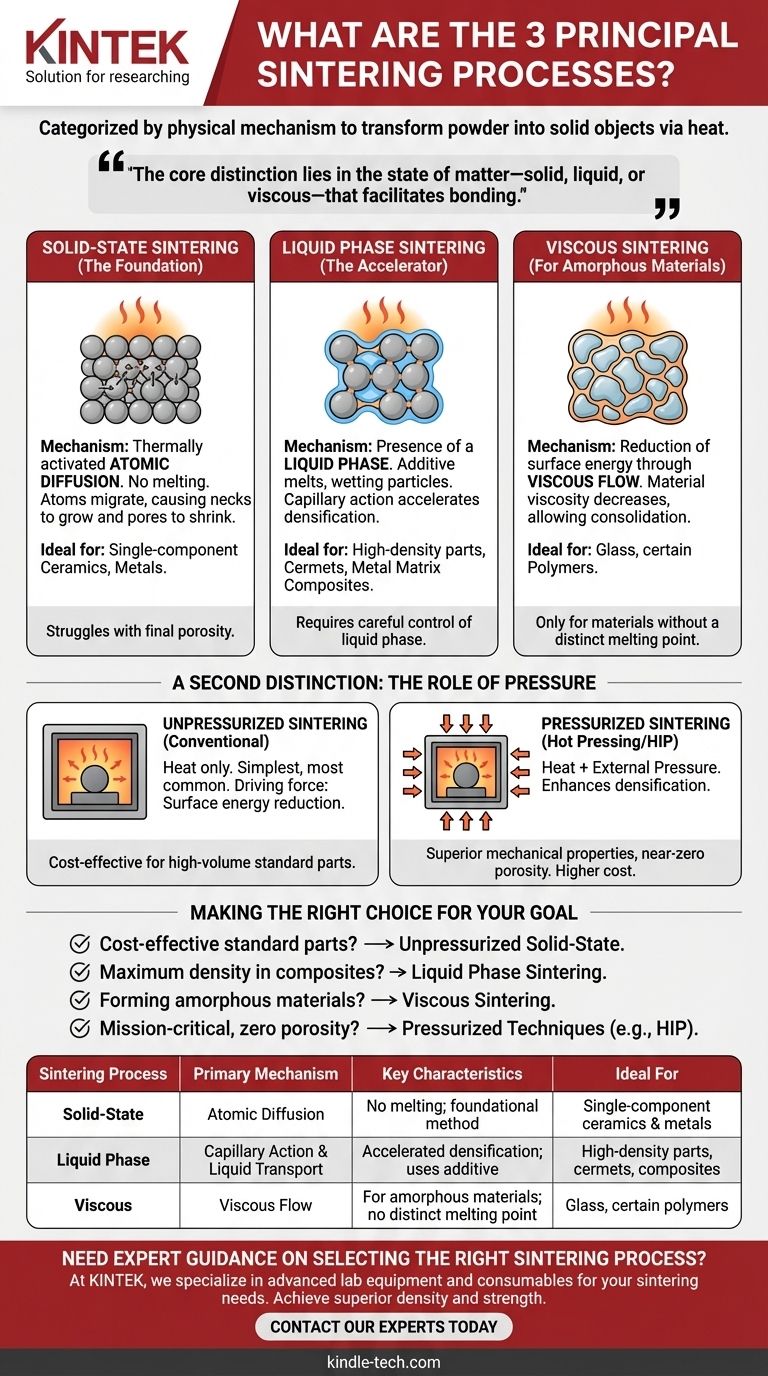
The three principal sintering processes, categorized by the physical mechanism at work, are solid-state sintering, liquid phase sintering, and viscous sintering. These methods are fundamental to powder metallurgy and ceramics, used to transform loose powder into a dense, solid object by applying heat below the material's melting point.
The core distinction between sintering processes lies in the state of matter—solid, liquid, or viscous—that facilitates the bonding of particles. This choice is dictated by the material itself and the desired final properties, such as density and strength.

The Core Mechanisms of Sintering
To select the right approach, you must first understand how each fundamental process works to consolidate material and reduce porosity.
Solid-State Sintering (The Foundation)
This is the most common form of sintering, occurring entirely in the solid state without any melting.
The process is driven by thermally activated diffusion. At high temperatures, atoms migrate across the contact points between particles, causing the necks between them to grow and the pores (voids) to shrink.
This method is foundational for a wide range of materials, particularly single-component ceramics and metals.
Liquid Phase Sintering (The Accelerator)
This process involves the presence of a small amount of a liquid phase at the sintering temperature.
Typically, a secondary material with a lower melting point is mixed with the primary powder. When heated, this additive melts, creating a liquid that wets the solid particles. This liquid phase accelerates densification by pulling particles together through capillary action and providing a fast path for material transport.
Liquid phase sintering is essential for producing high-density parts, cermets, and many metal matrix composites.
Viscous Sintering (For Amorphous Materials)
This mechanism applies specifically to amorphous materials like glass or certain polymers, which do not have a distinct melting point.
Instead of atomic diffusion, the driving force is the reduction of surface energy through viscous flow. As the material is heated, its viscosity decreases, allowing it to slowly flow and consolidate, eliminating the pores between the initial particles.
A Second Distinction: The Role of Pressure
Beyond the physical mechanism, processes are also categorized by the external conditions applied, primarily the use of pressure.
Unpressurized Sintering
Also known as conventional sintering, this involves heating the compacted powder in a furnace without applying any external mechanical pressure.
This is the simplest and most widely used industrial method. The driving forces for densification are entirely based on reducing the material's surface energy through one of the core mechanisms described above.
Pressurized Sintering
In this category, external pressure is applied simultaneously with heat to force the powder particles together.
Techniques like hot pressing or hot isostatic pressing (HIP) dramatically enhance the driving force for densification. This allows for sintering at lower temperatures or for shorter times, often resulting in components with superior mechanical properties and near-zero porosity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of sintering process is a balance between material compatibility, desired performance, and cost.
Simplicity vs. Final Density
Solid-state sintering is relatively simple but can struggle to eliminate the very last fractions of porosity. Liquid phase sintering achieves higher density more easily but requires careful control of the liquid phase to prevent distortion or unwanted chemical reactions.
Cost vs. Performance
Unpressurized sintering requires less complex equipment and is more cost-effective for high-volume production. Pressurized techniques produce exceptionally high-performance parts but come with significantly higher equipment and processing costs.
Material Compatibility Is Key
The material dictates the process. Crystalline metals and ceramics rely on solid-state or liquid phase sintering. Amorphous glasses can only be consolidated via viscous sintering. The choice is not arbitrary; it's governed by the physics of the material itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific requirements will determine the optimal sintering strategy.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of standard ceramic or metal parts: Unpressurized solid-state sintering is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density in a composite material: Liquid phase sintering is the most effective method for accelerating densification and bonding.
- If your primary focus is forming parts from amorphous materials like glass: Viscous sintering is the only mechanism that applies.
- If your primary focus is producing mission-critical components with near-zero porosity: Pressurized techniques like hot isostatic pressing are required to achieve the highest performance.
Ultimately, understanding these fundamental principles empowers you to move beyond simple definitions and make informed decisions based on your specific engineering goals.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Process | Primary Mechanism | Key Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid-State Sintering | Atomic Diffusion | No melting; foundational method | Single-component ceramics & metals |
| Liquid Phase Sintering | Capillary Action & Liquid Transport | Accelerated densification; uses additive | High-density parts, cermets, composites |
| Viscous Sintering | Viscous Flow | For amorphous materials; no distinct melting point | Glass, certain polymers |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right sintering process for your materials?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your sintering needs. Whether you're working with ceramics, metals, or composites, our solutions help you achieve superior density and strength in your components.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your research and production goals with precision and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
People Also Ask
- Why is a high vacuum environment necessary in sintering equipment for TiAl alloys? Ensure High-Purity Metal Bonding
- What is sintering reaction? Transform Powders into Dense Solids Without Melting
- Does sintering use diffusion? The Atomic Mechanism for Building Stronger Materials
- Why must green bodies produced via binder jetting undergo treatment in a vacuum sintering furnace?
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost



















