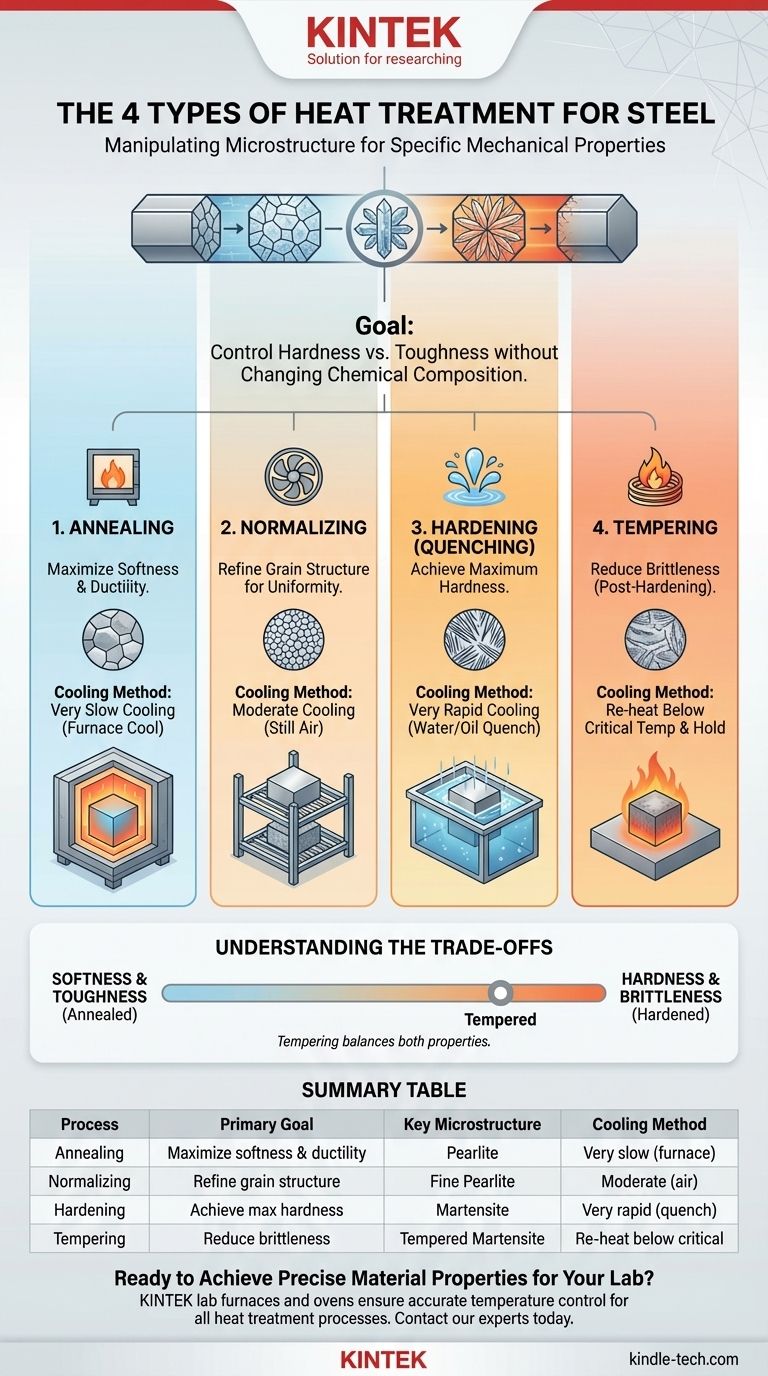
The four primary types of heat treatment for steel are annealing, normalizing, hardening, and tempering. Each process involves a specific cycle of heating and cooling designed to intentionally alter the steel's internal microstructure. The ultimate goal is to manipulate its mechanical properties—like hardness, toughness, and ductility—to suit a specific application.
The core principle to understand is that heat treatment does not change the steel's chemical composition. Instead, it rearranges its internal crystal structure to control the trade-off between strength and brittleness, tailoring the material for its intended purpose.
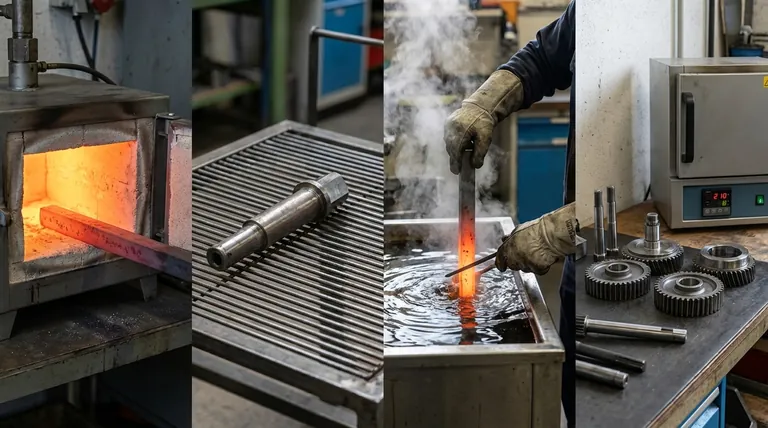

The Foundation: Why Heat Treat Steel?
To understand heat treatment, you must first understand the microstructure of steel. These processes are designed to control which crystal structures form within the material, as each structure has distinct properties.
Manipulating the Microstructure
At its core, steel is an alloy of iron and carbon. The way these atoms arrange themselves determines the steel's behavior. Heating steel above a critical temperature (typically 723-910°C or ~1333-1670°F) transforms its structure into a state called austenite, which can dissolve carbon.
The final structure depends entirely on how it is cooled from this austenitic state. A slow cool produces soft structures, while a rapid cool traps the carbon atoms and creates a very hard structure.
The Critical Role of Cooling Rate
The speed of cooling is the most important variable in heat treatment.
- Very Slow Cooling (e.g., inside a furnace) allows atoms to rearrange into soft, stable structures.
- Moderate Cooling (e.g., in air) creates a more refined and slightly harder structure.
- Rapid Cooling (e.g., quenching in water or oil) freezes the atoms in a highly stressed, hard, and brittle state.
The Four Core Processes Explained
Each of the four main heat treatments uses a different cooling rate to achieve a specific outcome.
Annealing: Maximizing Softness and Ductility
The primary goal of annealing is to make steel as soft, ductile, and easily machinable as possible. It also serves to relieve internal stresses from prior work.
The process involves heating the steel well into the austenite region and then cooling it as slowly as possible, often by simply turning the furnace off and letting it cool overnight. This results in a coarse microstructure known as pearlite, which is ideal for subsequent machining or forming operations.
Normalizing: Refining Grain Structure
Normalizing is used to create a more uniform and fine-grained microstructure. This results in steel that is stronger and harder than annealed steel but not so hard that it is difficult to work with.
The process involves heating to the austenitic range and then cooling it in still air. This faster cooling rate produces a finer, more uniform pearlite structure, which improves strength and toughness over the annealed state.
Hardening (Quenching): Achieving Maximum Hardness
The goal of hardening, also known as quenching, is to make steel as hard and wear-resistant as possible.
This is achieved by heating the steel to form austenite and then cooling it extremely rapidly by submerging it in a quench medium like water, oil, or brine. This rapid cooling traps the carbon atoms, forming a hard, brittle, and highly stressed microstructure called martensite.
Tempering: Reducing Brittleness
A part that has been hardened is often too brittle for practical use. Tempering is a secondary process that is always performed after hardening to increase toughness.
The hardened part is re-heated to a temperature below the critical point (e.g., 200-650°C or 400-1200°F). This allows some of the trapped atoms in the martensite structure to rearrange slightly, relieving internal stress and sacrificing some hardness to gain a significant amount of toughness. The higher the tempering temperature, the softer but tougher the final part becomes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heat treatment process is always an exercise in balancing competing properties. There is no single "best" treatment, only the most appropriate one for the application.
The Hardness vs. Toughness Dilemma
This is the most fundamental trade-off. Hardness is the resistance to scratching and indentation, while toughness is the ability to absorb impact without fracturing.
- A fully hardened (quenched) steel has maximum hardness but is extremely brittle, like glass.
- An annealed steel has maximum toughness and ductility but very low hardness.
- A hardened and tempered steel provides the best balance of both properties, making it suitable for tools, springs, and structural components.
Internal Stress and Warping
Rapid cooling during hardening introduces immense internal stress into a part. This stress can cause the component to warp, distort, or even crack during or after the quenching process. Slower processes like annealing are specifically used to remove these stresses.
The Impact of Carbon Content
These heat treatments are most effective on medium and high-carbon steels (those with >0.3% carbon). Low-carbon steels lack sufficient carbon to form the hard martensite structure, so they cannot be significantly hardened through quenching and tempering alone.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right process requires a clear understanding of your final objective for the steel component.
- If your primary focus is maximum machinability and formability: Annealing is the correct process to prepare the raw material for manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is refining grain structure for uniform properties: Normalizing provides a good baseline of strength and uniformity before further processing or use.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: You must use hardening (quenching), but it is almost always followed by tempering.
- If your primary focus is creating a tough, durable part that can withstand impact: The combination of hardening followed by tempering is essential to achieve the required toughness.
By understanding these four processes, you can precisely control the final properties of steel to meet any engineering demand.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Key Microstructure | Cooling Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Maximize softness & ductility | Pearlite | Very slow (furnace cool) |
| Normalizing | Refine grain structure | Fine Pearlite | Moderate (air cool) |
| Hardening (Quenching) | Achieve maximum hardness | Martensite | Very rapid (water/oil quench) |
| Tempering | Reduce brittleness (post-hardening) | Tempered Martensite | Re-heat & hold below critical temp |
Ready to Achieve Precise Material Properties for Your Lab?
Understanding the theory is the first step. Applying it with the right equipment is what delivers results. KINTEK specializes in the precise lab furnaces and ovens needed to execute these critical heat treatment processes—from annealing to tempering—with accuracy and repeatability.
Whether you are developing new materials, testing components, or ensuring quality control, our equipment helps you control the microstructure of your steel samples to achieve the exact balance of hardness, toughness, and ductility your research demands.
Let's discuss your application needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect thermal processing solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the four types of heat treating processes? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening, and Tempering
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering
- What are the five basic heat treatment processes of metals? Master Annealing, Hardening & More



















