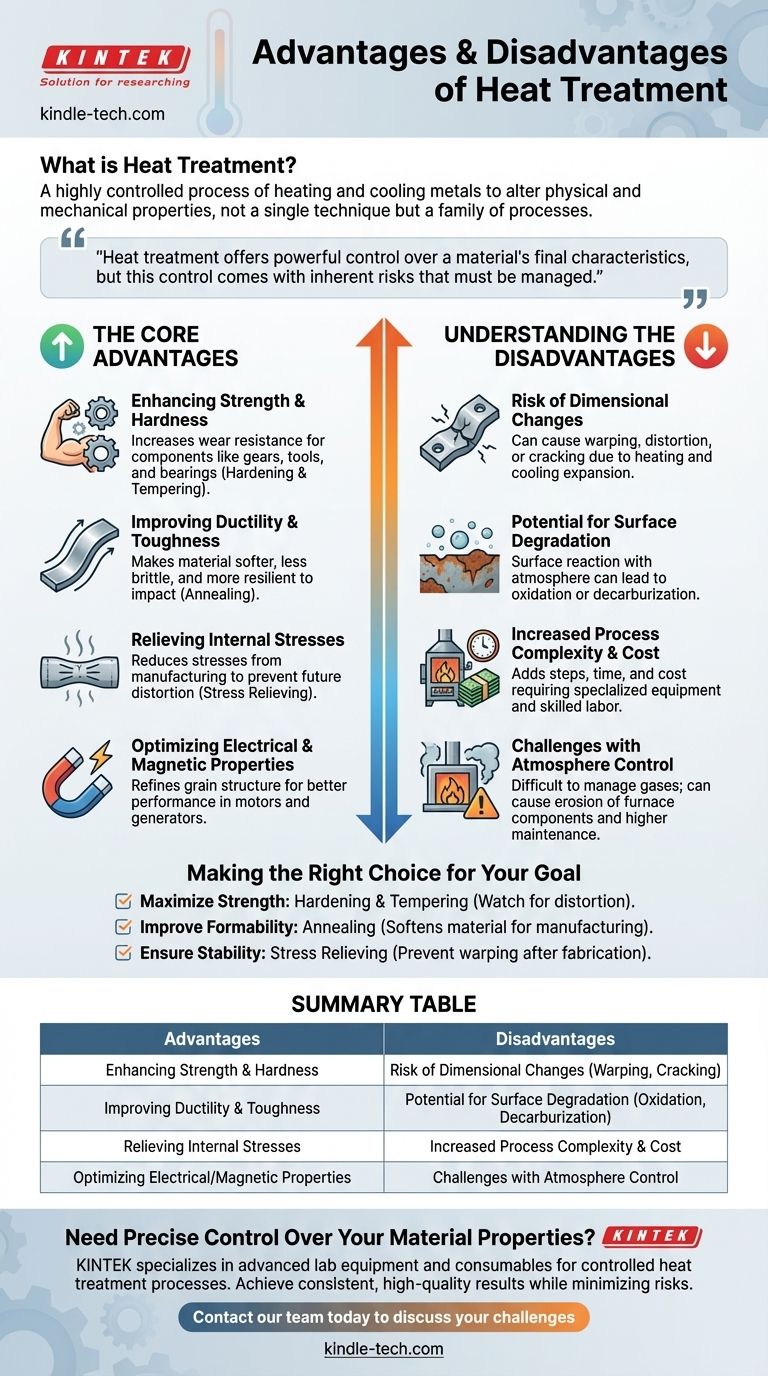
At its core, heat treatment is a highly controlled process of heating and cooling metals to intentionally alter their physical and mechanical properties. It is not one single technique but a family of processes used to make a material harder, softer, or more durable, relieve internal stresses, and improve its overall performance for a specific application.
Heat treatment is an essential manufacturing tool that offers powerful control over a material's final characteristics. However, this control comes with inherent risks, such as dimensional distortion and surface damage, which must be carefully managed to achieve the desired outcome.
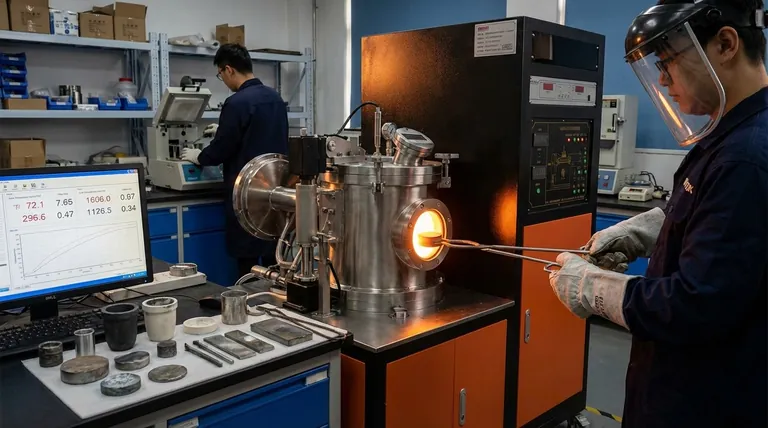

The Core Advantages: Tailoring Material Properties
The primary reason to employ heat treatment is to precisely modify a material, most often steel, to meet specific engineering requirements that cannot be achieved in its raw state.
Enhancing Strength and Hardness
Heat treatment processes like hardening and tempering can dramatically increase a material's strength and its resistance to wear and abrasion. This is critical for components like gears, tools, and bearings that must withstand significant mechanical stress.
Improving Ductility and Toughness
Conversely, processes like annealing can make a material softer and more ductile (easier to bend or shape without fracturing). This improves a material's toughness, reducing its brittleness and making it more resilient to impact.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Manufacturing processes like welding, machining, or hot forming create significant internal stresses within a material. Stress relieving, a form of heat treatment below the material's critical temperature, reduces or eliminates these stresses, preventing future distortion and increasing the part's stability.
Optimizing Electrical and Magnetic Properties
Beyond mechanical changes, certain heat treatments can also refine a material's grain structure to enhance specific electrical or magnetic properties. This is vital for components used in electric motors, transformers, and generators.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While the benefits are significant, heat treatment is a precision process where a lack of control can introduce new problems. Understanding these potential disadvantages is key to successful application.
Risk of Unwanted Dimensional Changes
The very act of heating and cooling causes materials to expand and contract. If not managed with precise control over heating and cooling rates, this can lead to warping, distortion, or cracking, rendering the part unusable.
Potential for Surface Degradation
At high temperatures, the surface of a metal can react with the atmosphere. This can result in a rough, scaled surface (oxidation) or the loss of key surface elements like carbon (decarburization), which can compromise hardness and fatigue life.
Increased Process Complexity and Cost
Heat treatment adds steps, time, and cost to the manufacturing cycle. It requires specialized furnaces, precise temperature and atmosphere controls, and skilled operators, all of which contribute to the final part's expense.
Challenges with Atmosphere Control
Using a controlled atmosphere to prevent surface degradation introduces its own set of challenges. It can be difficult to manage gas usage effectively, and the gases themselves can cause erosion of furnace components, like electric heating elements, leading to higher maintenance costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a specific heat treatment process must be driven by the final goal for the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and wear resistance: Hardening and tempering are likely the correct choice, but you must account for potential distortion.
- If your primary focus is improving machinability or formability: Annealing is the solution, as it softens the material and makes subsequent manufacturing steps easier.
- If your primary focus is ensuring stability after fabrication: Stress relieving is a critical step to prevent parts from warping over time, especially after heavy welding or machining.
Ultimately, viewing heat treatment as a strategic tool for tuning material properties is the key to unlocking its full engineering potential.
Summary Table:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Enhances Strength & Hardness | Risk of Dimensional Changes (Warping, Cracking) |
| Improves Ductility & Toughness | Potential for Surface Degradation (Oxidation, Decarburization) |
| Relieves Internal Stresses | Increased Process Complexity & Cost |
| Optimizes Electrical/Magnetic Properties | Challenges with Atmosphere Control |
Need precise control over your material properties?
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for controlled heat treatment processes. Whether you're hardening tools, annealing for formability, or stress-relieving critical components, our solutions help you achieve consistent, high-quality results while minimizing risks.
Let our expertise support your laboratory's success. Contact our team today to discuss your specific heat treatment challenges and discover the right equipment for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing



















