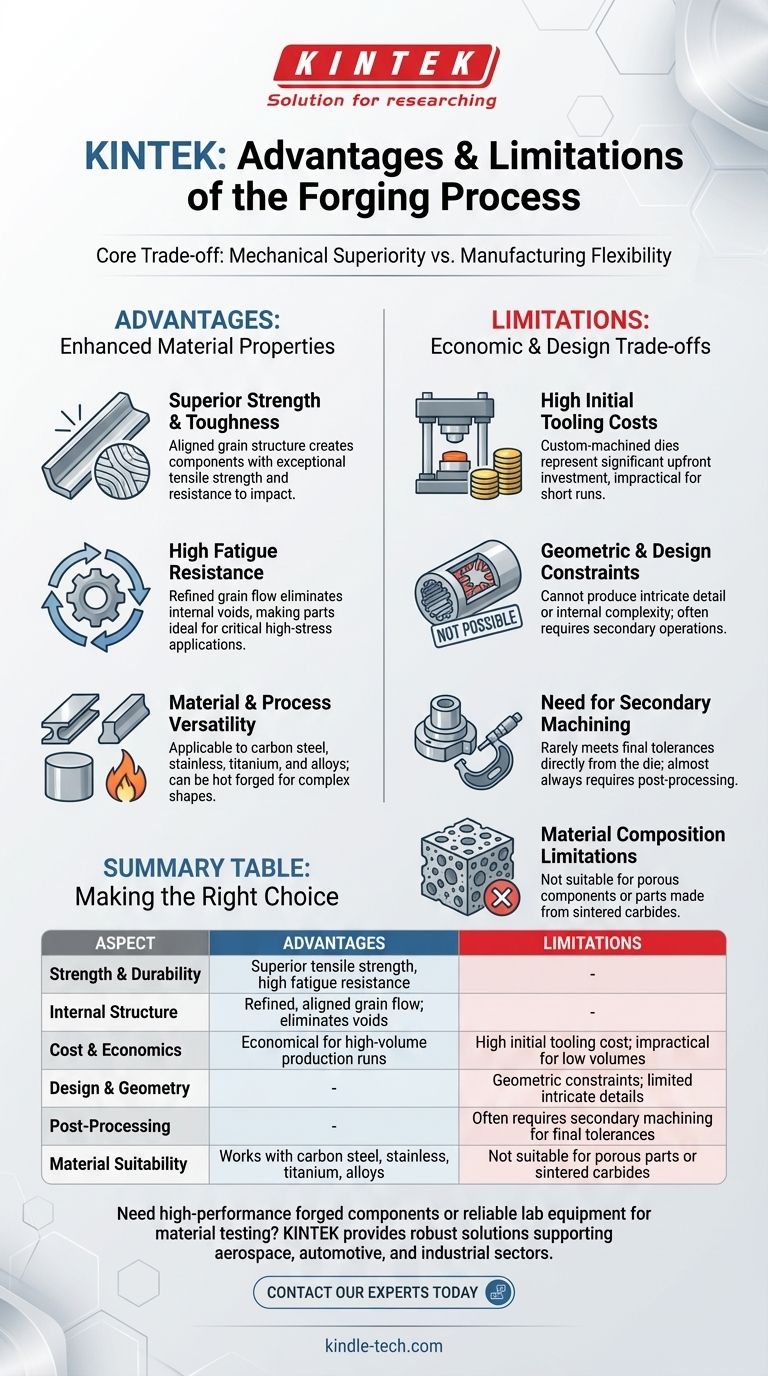
In essence, forging produces exceptionally strong and durable metal parts, but this superior performance comes with significant trade-offs. The process excels at creating components with high fatigue resistance and structural integrity by refining the metal's internal grain structure. However, it is limited by high initial tooling costs, geometric constraints, and the frequent need for secondary machining to achieve final tolerances.
The central decision point for using the forging process is a trade-off between mechanical superiority and manufacturing flexibility. Forging is the optimal choice for high-stress applications produced in large quantities, where the initial investment is justified by unparalleled strength and long-term reliability.

The Core Advantage: Enhanced Material Properties
The primary reason to choose forging is its ability to optimize the metallurgical and mechanical properties of a metal. The process uses immense compressive force to shape the material, fundamentally altering its internal structure in a way that other processes cannot replicate.
Superior Strength and Toughness
Unlike casting, where molten metal solidifies with a random grain structure, forging forces the grains to align with the shape of the part. This continuous, refined grain flow creates components with exceptional tensile strength and resistance to impact.
High Fatigue Resistance
The aligned grain structure eliminates internal voids and defects common in other methods. This structural integrity makes forged parts highly resistant to fatigue and wear from cyclic loading, making them ideal for critical components in aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery.
Material and Process Versatility
Forging can be applied to a wide range of metals, including carbon steel, stainless steel, titanium, and various alloys. The process can also be adapted, such as with hot forging, where heat is applied to allow for greater material deformation and the creation of more complex shapes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While forging creates superior parts, its advantages are not universal. The process carries specific economic and design limitations that make it unsuitable for certain applications.
High Initial Tooling Costs
The dies used to press and shape the metal are extremely hard and must be custom-machined, representing a significant upfront investment. This high initial cost makes forging economically impractical for short production runs or prototypes.
Geometric and Design Constraints
Forging cannot produce parts with the same level of intricate detail or internal complexity as casting or machining. Creating small, finely designed features often requires extensive secondary operations, which adds to the overall cost and lead time.
The Need for Secondary Machining
Due to the nature of the process, forged parts rarely meet their final dimensional specifications directly from the die. A greater need for secondary machining is almost always required to achieve tight tolerances and a precise surface finish.
Material Composition Limitations
The forging process is not suitable for all materials or structures. It cannot be used to produce porous components like self-lubricating bearings, parts made from sintered carbides, or components that require a mixture of different metals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct manufacturing process requires aligning the method's strengths with your project's primary goal. Forging is a powerful tool, but only when used in the right context.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and reliability: Forging is the unparalleled choice for critical, high-stress components where failure is not an option.
- If your primary focus is intricate design or low-volume production: Alternative methods like CNC machining or investment casting will almost certainly be more cost-effective and flexible.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency at high volume: Forging becomes highly economical for large production runs, as the initial tooling cost is distributed over thousands of strong, reliable parts.
Ultimately, choosing to forge is an investment in mechanical integrity where the application demands it.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Strength & Durability | Superior tensile strength, high fatigue resistance | - |
| Internal Structure | Refined, aligned grain flow; eliminates voids | - |
| Cost & Economics | Economical for high-volume production runs | High initial tooling cost; impractical for low volumes |
| Design & Geometry | - | Geometric constraints; limited intricate details |
| Post-Processing | - | Often requires secondary machining for final tolerances |
| Material Suitability | Works with carbon steel, stainless, titanium, alloys | Not suitable for porous parts or sintered carbides |
Need to source high-performance forged components or reliable lab equipment for material testing?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust laboratory equipment and consumables that meet the demanding standards of industries relying on forged parts. Whether you're in aerospace, automotive, or industrial machinery, our solutions support your need for quality and reliability.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help equip your lab for success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation



















