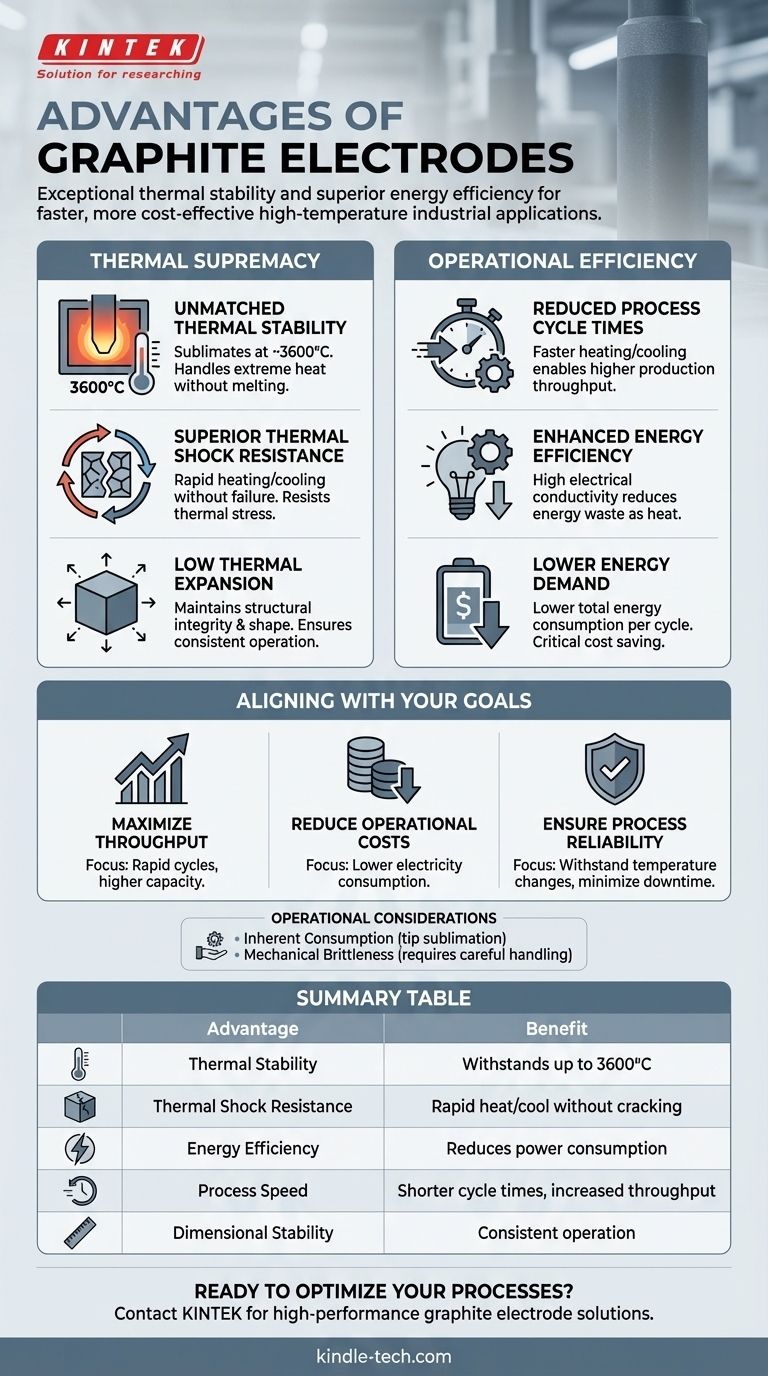
The primary advantages of graphite electrodes stem from their exceptional thermal stability and superior energy efficiency in high-temperature industrial applications. These properties allow them to handle extreme heat and conduct massive electrical currents with minimal energy loss, leading to faster and more cost-effective production cycles.
Graphite electrodes are not simply a component; they are a critical enabler of operational efficiency. Their ability to withstand extreme heat and conduct electricity with minimal energy loss directly translates to faster production cycles and lower operating costs.

The Core Performance Advantage: Thermal Supremacy
The defining characteristic of graphite is its ability to perform under conditions where most materials would instantly fail. This thermal resilience is the foundation of its advantages.
Unmatched Thermal Stability
Graphite has one of the highest melting points of any known material. It does not melt but sublimates at temperatures around 3600°C, making it uniquely suited for the extreme environments of electric arc and induction furnaces.
Superior Thermal Shock Resistance
The material's excellent thermo-mechanical properties allow for rapid heating and cooling without cracking or failing. This resistance to thermal shock is critical for the intense, fluctuating temperature cycles of modern metallurgical processes.
Low Thermal Expansion
Graphite expands very little when subjected to intense heat. This dimensional stability ensures the electrode maintains its structural integrity and shape, which is crucial for consistent and predictable furnace operation.
Driving Operational Efficiency
Graphite's physical properties translate directly into tangible economic and operational benefits, primarily by reducing the time and energy required for each production batch.
Reduced Process Cycle Times
Because graphite can be heated and cooled very quickly, the overall time required for each industrial process is significantly reduced. This allows for higher production throughput and greater operational capacity.
Enhanced Energy Efficiency
Graphite provides a better energy balance than comparable materials. Its high electrical conductivity means less electrical energy is wasted as heat due to resistance, lowering the overall power demand for high-temperature applications.
Lower Energy Demand
The combination of rapid heating and high conductivity results in lower total energy consumption per cycle. This is a critical cost-saving factor in energy-intensive industries like steel manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While graphite is the superior choice, it is essential to acknowledge its operational realities. No material is without its limitations.
Inherent Consumption
Graphite electrodes are consumable. At extreme temperatures, the tip of the electrode is gradually consumed through sublimation and oxidation. This consumption is an expected operational cost that must be managed.
Mechanical Brittleness
Compared to metals, graphite is a brittle material. It requires careful handling during transportation, storage, and installation to prevent cracks or complete fractures, which can lead to costly operational disruptions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection and use of graphite electrodes should be aligned with your specific operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximizing production throughput: The rapid heating and cooling capabilities of graphite are your greatest asset, enabling shorter and more frequent process cycles.
- If your primary focus is reducing operational costs: The high energy efficiency and low electrical resistance of graphite directly lower electricity consumption, a major expense in furnace operations.
- If your primary focus is process reliability: Graphite's superior thermal shock resistance ensures it can withstand extreme temperature changes without failure, minimizing the risk of unexpected downtime.
Ultimately, graphite electrodes remain the industry standard because their unique combination of thermal and electrical properties delivers a level of performance that alternative materials cannot match.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Core Benefit |
|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Withstands extreme temperatures up to 3600°C |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Rapid heating/cooling without cracking |
| Energy Efficiency | High conductivity reduces power consumption |
| Process Speed | Shorter cycle times increase throughput |
| Dimensional Stability | Low thermal expansion ensures consistent operation |
Ready to optimize your high-temperature processes? KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance graphite electrodes and other critical lab equipment and consumables. Our solutions are designed to enhance your operational efficiency, reduce energy costs, and maximize production throughput. Contact our experts today to find the perfect graphite electrode solution for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
- Glassy Carbon Electrochemical Electrode
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
People Also Ask
- What technical advantages do carbon graphite electrodes offer for electroactive biofilms? Optimize Your Bio-Research
- What are the characteristics and applications of a graphite sheet electrode? Maximize Reaction Area for Bulk Electrolysis
- How should a graphite electrode be cleaned and stored after an experiment? Ensure Reliable Electrochemical Data
- Why is a high-purity graphite rod selected as the EIS counter electrode? Ensure Data Integrity and Chemical Stability
- What are the potential risks when using a graphite electrode in electrochemical tests? Avoid Decomposition and Contamination



















