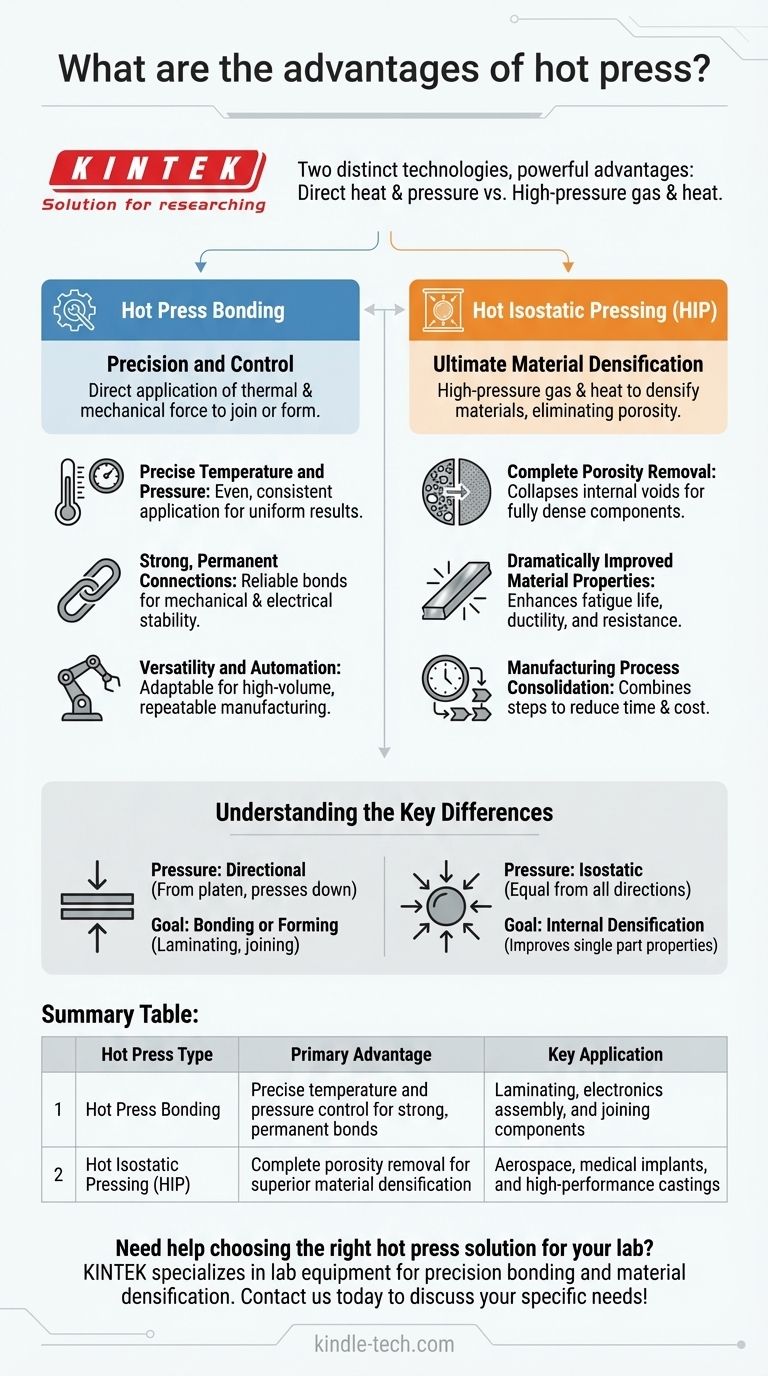
The term "hot press" refers to two distinct technologies, each with its own set of powerful advantages. A standard hot press machine uses direct heat and pressure for bonding and forming, offering exceptional precision and control. In contrast, Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) uses high-pressure gas and heat to densify materials, primarily for eliminating internal porosity in metals and ceramics to achieve superior material properties.
The core advantage of any hot press method is its ability to fundamentally alter a material's structure using controlled heat and pressure. The key is understanding whether your goal is to join materials together with precision (hot press bonding) or to densify a single part to its theoretical maximum (Hot Isostatic Pressing).

Hot Press Bonding: Precision and Control
This process involves the direct application of thermal and mechanical force, typically to join, laminate, or form materials. It is defined by its highly controllable nature.
Key Advantage: Precise Temperature and Pressure
Modern hot press machines utilize advanced technologies like pulse heating for rapid and precise temperature ramping.
This, combined with a rigid structure (often a four-column, three-plate design), ensures that both heat and pressure are applied evenly and consistently across the part's surface.
Key Advantage: Strong, Permanent Connections
The combination of controlled heat and pressure creates strong, reliable, and permanent bonds.
This is critical for applications requiring robust mechanical connections or stable electrical pathways, such as in electronics assembly.
Key Advantage: Versatility and Automation
These machines are highly adaptable, often featuring multiple working modes and pre-stored programs for different applications.
Advanced features like CCD vision systems allow for perfect alignment before pressing, while adjustable cylinders ensure accurate positioning, making the process ideal for high-volume, repeatable manufacturing.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP): Ultimate Material Densification
HIP is a manufacturing process that places a part inside a high-pressure vessel. The part is heated and subjected to immense, uniform pressure from an inert gas, like argon.
Key Advantage: Complete Porosity Removal
The primary benefit of HIP is the elimination of internal voids and microporosity within a material.
This is especially crucial for castings and additively manufactured (3D printed) metal parts, where porosity can lead to component failure under stress. HIP collapses these internal voids, resulting in a fully dense part.
Key Advantage: Dramatically Improved Material Properties
By creating a uniform, dense microstructure free from defects, HIP significantly enhances a material's performance.
This leads to dramatic increases in fatigue life (by 10 to 100 times), as well as improved ductility, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance, making parts suitable for the most demanding environments.
Key Advantage: Manufacturing Process Consolidation
HIP can often combine multiple manufacturing steps into one.
Processes like heat treatment, quenching, and aging can be integrated into a single HIP cycle, reducing total production time, handling, and cost.
Understanding the Key Differences
While both processes use heat and pressure, their methods and goals are fundamentally different. Confusing them can lead to selecting the wrong process for your application.
Pressure Application: Directional vs. Isostatic
A standard hot press applies directional force from a platen or tool. It presses down on a surface.
HIP applies isostatic pressure, meaning the gas pressure acts equally on the part from all directions. This is what allows it to collapse internal voids without distorting the part's external shape.
Primary Goal: Bonding vs. Densification
The goal of a hot press machine is typically to bond or form materials, such as laminating layers or attaching a flexible circuit to a PCB.
The goal of HIP is internal densification. It improves the properties of a single, already-formed part (like a casting) or consolidates metal powders into a solid block.
Material and Application
Hot press bonding is used for joining components, films, and substrates in industries like electronics and composites.
HIP is used to perfect high-performance metal and ceramic parts for critical applications in aerospace, medical implants, and energy, where material failure is not an option.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct technology requires a clear understanding of your end goal.
- If your primary focus is bonding components or laminating materials: Choose a hot press machine for its precise control over directional pressure and temperature for joining surfaces.
- If your primary focus is eliminating internal porosity in castings or 3D printed parts: Use Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) to achieve full density and superior, reliable mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is creating a solid, high-performance part from metal powder: HIP is the definitive process for turning powder into a component with properties equal to or better than forged material.
Understanding this distinction ensures you select the right tool to achieve your specific manufacturing outcome.
Summary Table:
| Hot Press Type | Primary Advantage | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Hot Press Bonding | Precise temperature and pressure control for strong, permanent bonds | Laminating, electronics assembly, and joining components |
| Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) | Complete porosity removal for superior material densification | Aerospace, medical implants, and high-performance castings |
Need help choosing the right hot press solution for your lab? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering tailored solutions for precision bonding and material densification. Whether you require a standard hot press for electronics assembly or a HIP system for high-performance parts, our expertise ensures optimal performance and reliability. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
People Also Ask
- What is the historical background of the Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) process? From Nuclear Roots to Industry Standard
- What is HIP in material processing? Achieve Near-Perfect Density for Critical Components
- What pressure is hot isostatic press? Achieve Full Density & Superior Material Performance
- What is the principle of hot isostatic pressing? Achieve 100% Density and Superior Performance
- How much energy does hot isostatic pressing consume? Unlock Net Energy Savings in Your Process



















