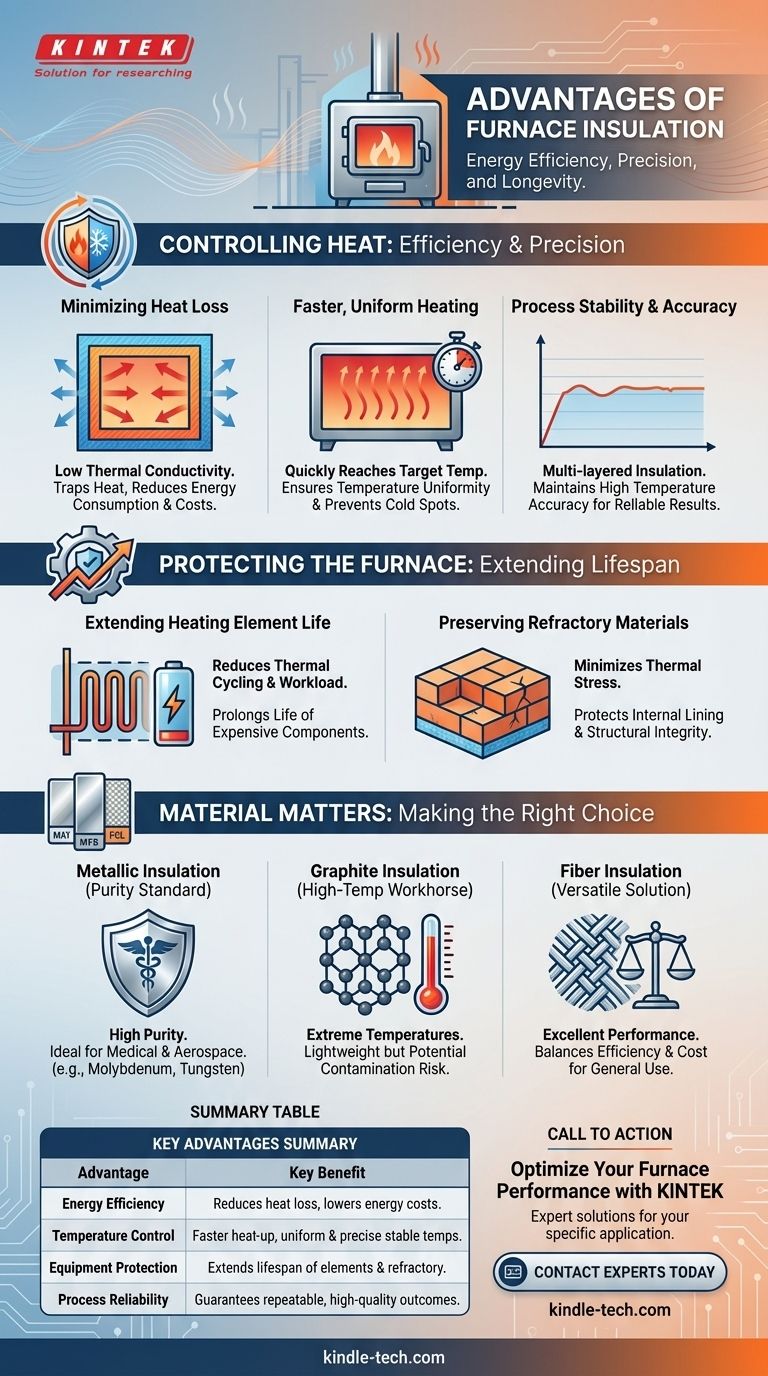
At its core, furnace insulation provides three primary advantages: it dramatically reduces energy consumption, ensures precise and stable operating temperatures, and extends the operational life of the furnace's critical components. This is achieved by minimizing heat loss to the surrounding environment, which allows the system to heat up faster and maintain its target temperature with less energy input.
Effective insulation is more than a cost-saving measure; it is the fundamental component that guarantees process reliability. It dictates the furnace's efficiency, the quality of the final product, and the long-term durability of the entire heating system.

The Fundamental Role of Insulation: Controlling Heat
High-performance furnaces are defined by their ability to generate and control heat precisely. Insulation is the technology that makes this control possible.
Minimizing Heat Loss for Energy Efficiency
The primary job of insulation is to resist the transfer of heat. Materials with low thermal conductivity are used to create a barrier between the hot interior of the furnace and the cooler exterior.
By trapping heat inside the chamber, the furnace does not have to work as hard to maintain its setpoint. This directly translates to lower energy consumption and reduced operational costs. Poor insulation, conversely, leads to constant heat bleed and wasted energy.
Achieving Faster, More Uniform Heating
Because high-grade insulation keeps thermal energy contained, the furnace can reach its target temperature more quickly.
This efficiency also promotes temperature uniformity throughout the heating chamber. It prevents "cold spots" by ensuring that heat is distributed evenly, which is critical for processes where every part of the material being treated must experience the same temperature.
Ensuring Process Stability and Accuracy
For sensitive applications, temperature accuracy is non-negotiable. Multi-layered or double-walled insulation designs create an exceptionally stable thermal environment.
This stability allows the furnace controller to maintain high-temperature accuracies with minimal fluctuation, ensuring the material being processed receives the exact thermal treatment required for a repeatable, high-quality outcome.
How Insulation Protects the Furnace Itself
Insulation doesn't just benefit the process; it is a crucial element that protects the long-term health of the furnace hardware.
Extending the Life of Heating Elements
Heating elements degrade faster when they must cycle on and off frequently or run at maximum output to compensate for heat loss.
By maintaining a stable internal temperature, good insulation reduces the workload on these elements. This leads to fewer and less extreme temperature cycles, significantly extending the lifespan of these expensive components.
Preserving Refractory Materials
The internal lining of a furnace, often made of refractory bricks or ceramics, is also subject to thermal stress. Insulation helps protect this lining from extreme temperature gradients between the hot face and the cold face.
This reduces the risk of cracking and degradation, preserving the structural integrity of the furnace chamber for a longer period.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Insulation Material Matters
The type of insulation used is as important as its presence. The choice involves critical trade-offs between purity, temperature capability, and cost.
Metallic Insulation: The Purity Standard
Constructed from materials like molybdenum, tungsten, or stainless steel, metallic insulation is favored in industries where contamination is unacceptable.
It offers exceptionally high purity and a clean operating environment, making it the standard for applications in the medical, aerospace, and advanced materials sectors.
Graphite Insulation: The High-Temperature Workhorse
Graphite insulation is lightweight and can operate at extremely high temperatures, often exceeding the capabilities of metallic options.
However, its primary drawback is the potential for contamination. Graphite can absorb vapors from the process and may release micro-particles, making it unsuitable for applications requiring absolute purity.
Fiber Insulation: The Versatile Solution
Materials like alumina multi-fiber represent a common and effective type of insulation. This material is packed to a significant thickness, often in multiple layers.
Fiber insulation provides excellent thermal performance for a wide range of general-purpose furnace applications, offering a strong balance between efficiency and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The ideal insulation is determined entirely by your process goals.
- If your primary focus is process purity (e.g., medical device manufacturing, aerospace components): Metallic insulation is the only choice to avoid product contamination.
- If your primary focus is achieving extreme temperatures on a budget: Graphite insulation is a strong contender, provided you can manage its potential contamination risks.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose efficiency and reliability: A high-grade, multi-layer fiber insulation system offers the best balance of performance and value.
Ultimately, viewing insulation not as a simple feature but as the foundation of your thermal process is the key to achieving reliable and cost-effective results.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces heat loss, lowering energy consumption and operational costs. |
| Temperature Control | Ensures faster heat-up, uniform heating, and precise, stable temperatures. |
| Equipment Protection | Extends the lifespan of heating elements and refractory materials. |
| Process Reliability | Guarantees repeatable, high-quality outcomes for sensitive applications. |
Ready to optimize your furnace's performance with the right insulation?
The correct insulation is critical for your lab's efficiency, cost-control, and process reliability. KINTEK specializes in lab furnaces and equipment, providing expert solutions tailored to your specific application—whether you require high-purity metallic, high-temperature graphite, or versatile fiber insulation.
Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and ensure your thermal processes are built on a foundation of maximum efficiency and durability. Get in touch via our contact form to get started.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Does sintering use diffusion? The Atomic Mechanism for Building Stronger Materials
- What is the sintering time? A Critical Process Variable for Material Density and Strength
- What is sintering reaction? Transform Powders into Dense Solids Without Melting
- Why is high-temperature vacuum heat treatment critical for Cr-Ni steel? Optimize Strength & Surface Integrity
- Why would you braze instead of solder? For Superior Joint Strength and High-Temperature Performance



















