At their core, thin film resistors offer superior precision and stability compared to their more common thick film counterparts. Their key advantages stem from the manufacturing process, where a microscopically thin, uniform layer of resistive material is deposited onto a ceramic base in a vacuum. This method allows for extremely tight tolerances, excellent performance at high frequencies, and minimal electrical noise.
The decision to use a thin film resistor is a decision for precision over power. They are the component of choice when accuracy, stability over temperature, and low-noise operation are critical design requirements, particularly in sensitive analog and high-frequency circuits.
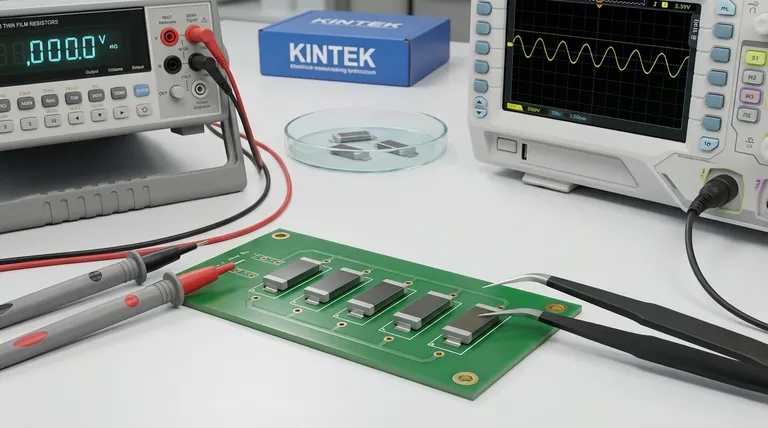
The Principle Behind Thin Film Performance
A resistor's primary job is to impede the flow of current. The way it accomplishes this determines its secondary characteristics, such as noise and stability. Thin film resistors excel because of their physical structure.
Uniform Material Deposition
Unlike thick film resistors made from a paste, thin film resistors are created using a process called Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), typically sputtering. In a vacuum chamber, individual atoms of a resistive alloy (like nickel-chromium) are sputtered onto a ceramic substrate.
This creates an extremely thin—often just a few micrometers—and highly uniform metallic film. The consistency of this film is the foundational reason for the resistor's predictable and stable electrical behavior.
Laser Trimming for Precision
After the film is deposited, a laser is often used to cut a precise pattern into it. This process, known as laser trimming, allows the manufacturer to "fine-tune" the resistance value to an exceptionally tight tolerance, often 0.1% or better.
Key Performance Advantages Explained
The manufacturing process directly translates into three major performance benefits that define where thin film resistors are used.
1. High Precision and Stability
The uniform metallic film results in a very predictable resistance value that changes very little with temperature. This is measured by the Temperature Coefficient of Resistance (TCR). Thin film resistors have a very low TCR, meaning their performance remains stable even as the device heats up or cools down.
2. Low Noise Operation
Current flowing through any resistor generates a small amount of random voltage fluctuation, known as noise. In thin film resistors, the homogenous structure of the deposited film provides a very smooth path for current. This results in significantly lower noise than thick film resistors, where current must navigate a more complex, granular path. This is critical for amplifying weak signals without distortion.
3. Excellent High-Frequency Performance
The simple, planar structure of a thin film resistor results in very low parasitic inductance and capacitance. These unwanted electrical properties can distort signals at high frequencies. The low parasitics of thin film resistors make them ideal for applications like radiofrequency (RF) circuits, wireless routers, and high-speed data processing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No component is perfect for every situation. The advantages of thin film resistors come with clear trade-offs that are important to understand.
Power Handling Limitations
The very thin resistive layer cannot dissipate a large amount of heat. Consequently, thin film resistors generally have lower power ratings than thick film or wirewound resistors of a similar size. Exceeding this rating can permanently damage the component.
Higher Cost
The vacuum deposition and laser trimming processes are more complex and costly than the screen-printing method used for thick film resistors. This makes thin film the more expensive option, reserved for applications where its performance characteristics are a necessity.
Sensitivity to Electrical Overstress
The thinness of the resistive element also makes it more susceptible to damage from electrostatic discharge (ESD) and other high-voltage surges. Careful handling during assembly and proper circuit protection are essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing between thin film and other resistor types comes down to balancing performance requirements with cost and power constraints.
- If your primary focus is precision and stability: Use thin film for applications like measurement instruments, medical devices, or audio preamplifiers where accuracy and low noise are paramount.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency performance: Thin film is the correct choice for RF circuits, communication modules, and high-speed computing where low parasitic inductance is critical.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and general use: A thick film resistor is almost always the better and more robust choice for applications like power supplies, LED drivers, and general consumer electronics where tight precision is not required.
Ultimately, selecting a thin film resistor is a deliberate engineering decision to prioritize signal integrity and precision for your most sensitive circuits.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description | Key Metric/Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| High Precision & Stability | Uniform metallic film created via PVD/sputtering. | Tight tolerances (e.g., 0.1%), low Temperature Coefficient of Resistance (TCR). |
| Low Noise Operation | Homogenous structure provides a smooth current path. | Minimal electrical noise, ideal for amplifying weak signals. |
| Excellent High-Frequency Performance | Planar structure with low parasitic inductance/capacitance. | Ideal for RF circuits, wireless, and high-speed data processing. |
| Trade-off: Power Handling | Thin layer limits heat dissipation. | Lower power rating compared to thick film/wirewound resistors. |
| Trade-off: Cost | Complex manufacturing (vacuum deposition, laser trimming). | Higher cost, reserved for performance-critical applications. |
Need Precision Components for Your Lab's Sensitive Instruments?
Thin film resistors are essential for applications where accuracy, signal integrity, and stability are non-negotiable. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including precision components for demanding R&D and testing environments.
We help you:
- Enhance Measurement Accuracy: Ensure your sensitive analog circuits and measurement instruments perform with the highest precision.
- Improve Signal Integrity: Minimize noise and distortion in critical applications like medical devices, audio equipment, and RF systems.
- Source Reliable Components: Access a curated selection of components known for their stability and performance.
Let our experts assist you in selecting the right components to optimize your laboratory's capabilities.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific lab equipment and consumable needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Beaker and Lids
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PPF and coating? Armor vs. Slick Shell for Your Car
- What is the function of PTFE reaction kettle bodies in micro-CSTR systems? Enhance Chemical Stability & Flow
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context
- Why is PTFE wire used for hanging metal specimens in biodiesel corrosion tests? Ensure Pure Experimental Results
- Why are PTFE laboratory consumables required when testing stainless steel against organic acids? Ensure Data Integrity










