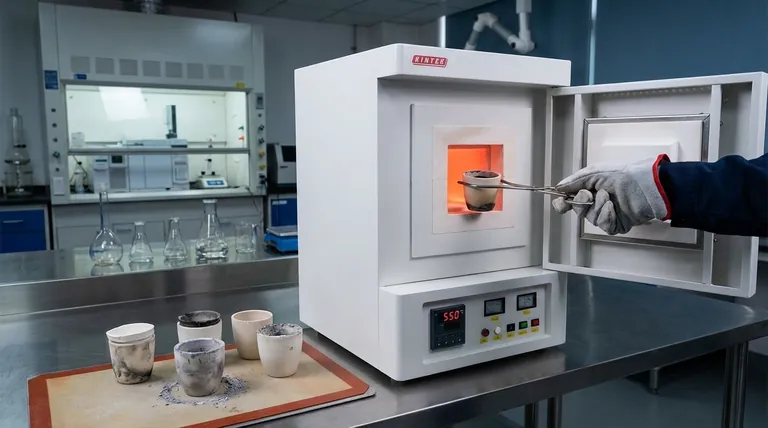
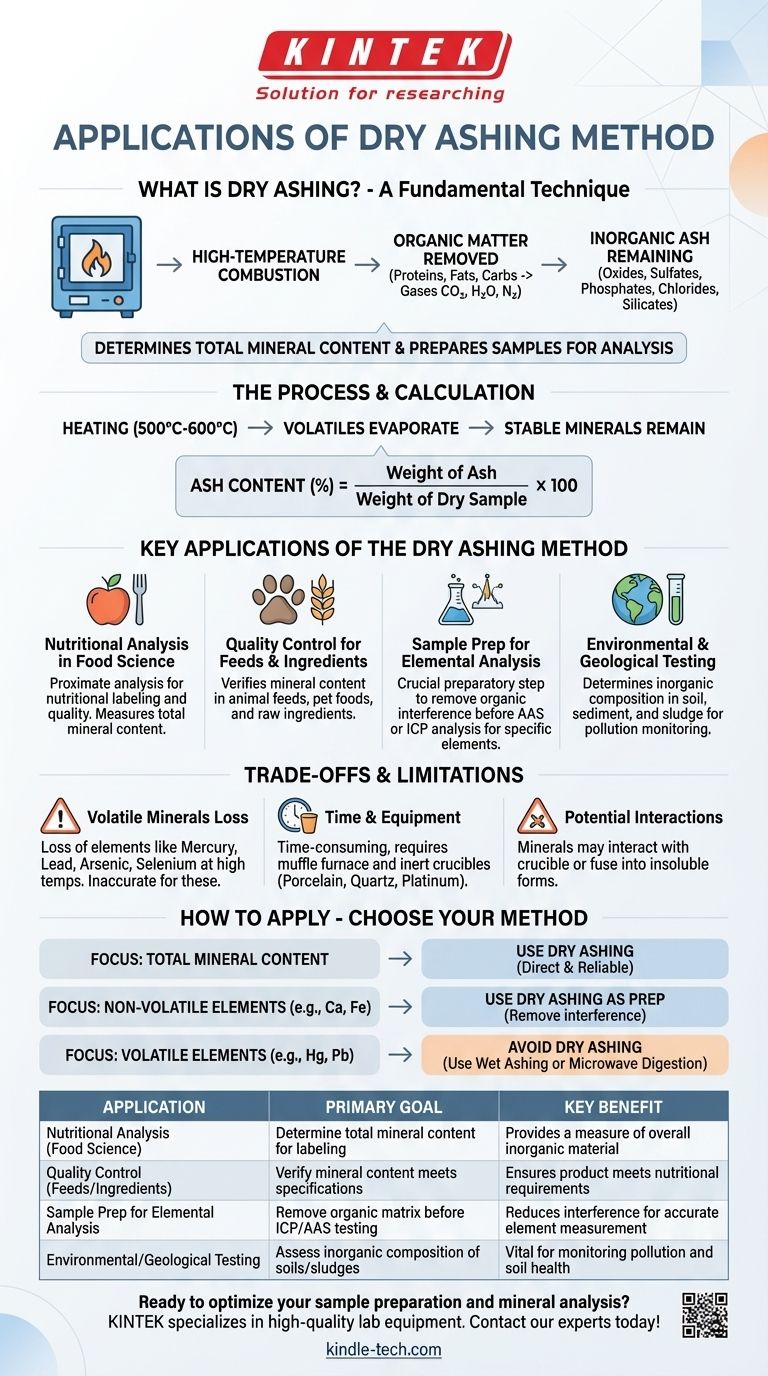
At its core, dry ashing is used to determine the total mineral content of a sample. This analytical technique involves the high-temperature combustion of organic matter, leaving behind only the inorganic, non-combustible components, collectively known as "ash." It serves as both a direct quantitative measurement and a crucial preparatory step for more detailed elemental analysis.
Dry ashing is not just about burning a sample; it's a fundamental technique for isolating the inorganic components (ash) from the organic matrix. This allows for accurate measurement of total mineral content and prepares the sample for subsequent analysis of specific elements.

The Fundamental Principle: What Is Dry Ashing?
Dry ashing is a process of thermal decomposition. By understanding what happens inside the furnace, you can better grasp its applications and limitations.
Removing the Organic Matrix
The primary goal of dry ashing is to completely oxidize and remove the organic material in a sample, such as proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. This is achieved by heating the sample in a muffle furnace in the presence of air (oxygen).
The organic matter is converted into gases like carbon dioxide, water vapor, and nitrogen, which are then vented away.
The Chemical Transformation
During heating, typically between 500°C and 600°C, the sample undergoes significant changes. Water and other volatile materials evaporate first.
The remaining minerals are transformed into more thermally stable forms, such as oxides, sulfates, phosphates, chlorides, and silicates. The resulting greyish-white powder is the ash.
Calculating Ash Content
The total ash content is a simple but powerful metric. It is calculated as the weight of the ash divided by the initial dry weight of the sample, providing a percentage of the total inorganic material.
Ash Content (%) = (Weight of Ash / Weight of Dry Sample) x 100
Key Applications of the Dry Ashing Method
The ability to isolate and quantify mineral content makes dry ashing a standard procedure in a wide range of scientific and industrial fields.
Nutritional Analysis in Food Science
Determining the ash content is a fundamental part of the proximate analysis of food. This figure provides a measure of the total amount of minerals, a critical parameter for nutritional labeling and ensuring food quality.
Quality Control for Feeds and Ingredients
In the agricultural sector, dry ashing is used to verify the mineral content of animal feeds, pet foods, and raw ingredients. This ensures that the product meets the specified nutritional requirements for animal health and growth.
Sample Preparation for Elemental Analysis
Perhaps the most common application is as a preparatory step for elemental analysis. The organic matrix of a sample can interfere with techniques used to measure specific elements.
By first reducing the sample to ash, analysts can then dissolve this ash in acid and use techniques like Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) or Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) to precisely quantify individual minerals like calcium, magnesium, iron, and potassium.
Environmental and Geological Testing
Dry ashing is applied to soil, sediment, and sludge samples to determine their inorganic composition. This information is vital for assessing soil health, monitoring pollution, and conducting geological surveys.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While widely used, dry ashing is not suitable for every situation. Understanding its limitations is key to generating accurate results.
The Problem of Volatile Minerals
The biggest drawback is the loss of volatile elements at high temperatures. Certain minerals and metals, such as mercury, lead, arsenic, and selenium, can vaporize and be lost during combustion.
This leads to an inaccurate and artificially low measurement of those specific elements. If your analysis is focused on these volatile compounds, dry ashing is the wrong choice.
Time and Equipment Requirements
The process can be time-consuming, often requiring several hours or even overnight heating in a muffle furnace to ensure complete combustion.
Additionally, the process requires inert crucibles made of materials like porcelain, quartz, or platinum to avoid contaminating the sample.
Potential for Interactions
At high temperatures, some minerals can interact with the crucible material or even fuse into insoluble forms, making them difficult to dissolve for subsequent elemental analysis.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice of method should be dictated entirely by your analytical goal.
- If your primary focus is determining total mineral content: Dry ashing is a direct, reliable, and widely accepted method for measuring the overall ash percentage in a food, feed, or organic sample.
- If your primary focus is analyzing for specific, non-volatile elements (e.g., calcium, iron): Use dry ashing as an effective first step to remove organic interference before dissolving the ash for analysis by methods like ICP or AAS.
- If your primary focus is measuring volatile elements like mercury or lead: Avoid dry ashing entirely, as high temperatures will cause sample loss; you must consider a lower-temperature method like wet ashing or microwave digestion.
Ultimately, knowing when to use dry ashing is as important as knowing how to perform it.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Goal | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Nutritional Analysis (Food Science) | Determine total mineral content for labeling | Provides a measure of overall inorganic material |
| Quality Control (Feeds/Ingredients) | Verify mineral content meets specifications | Ensures product meets nutritional requirements |
| Sample Prep for Elemental Analysis | Remove organic matrix before ICP/AAS testing | Reduces interference for accurate element measurement |
| Environmental/Geological Testing | Assess inorganic composition of soils/sludges | Vital for monitoring pollution and soil health |
Ready to optimize your sample preparation and mineral analysis? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including muffle furnaces and consumables essential for reliable dry ashing. Our expertise ensures you get accurate results for your food, feed, or environmental testing needs. Contact our experts today to discuss the right equipment for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the yield of biochar in slow pyrolysis? Maximize Your Output Up to 30%
- What are the uses of muffle furnace in pharmaceutical industry? Essential for Drug Purity & Safety
- How do you run a muffle furnace? Master the Step-by-Step Process for Safe, Precise Results
- What is a muffle furnace used for in a lab? Achieve Clean, High-Temperature Processing
- How is a muffle furnace used for sample digestion? A Guide to Dry Ashing for Accurate Analysis



















