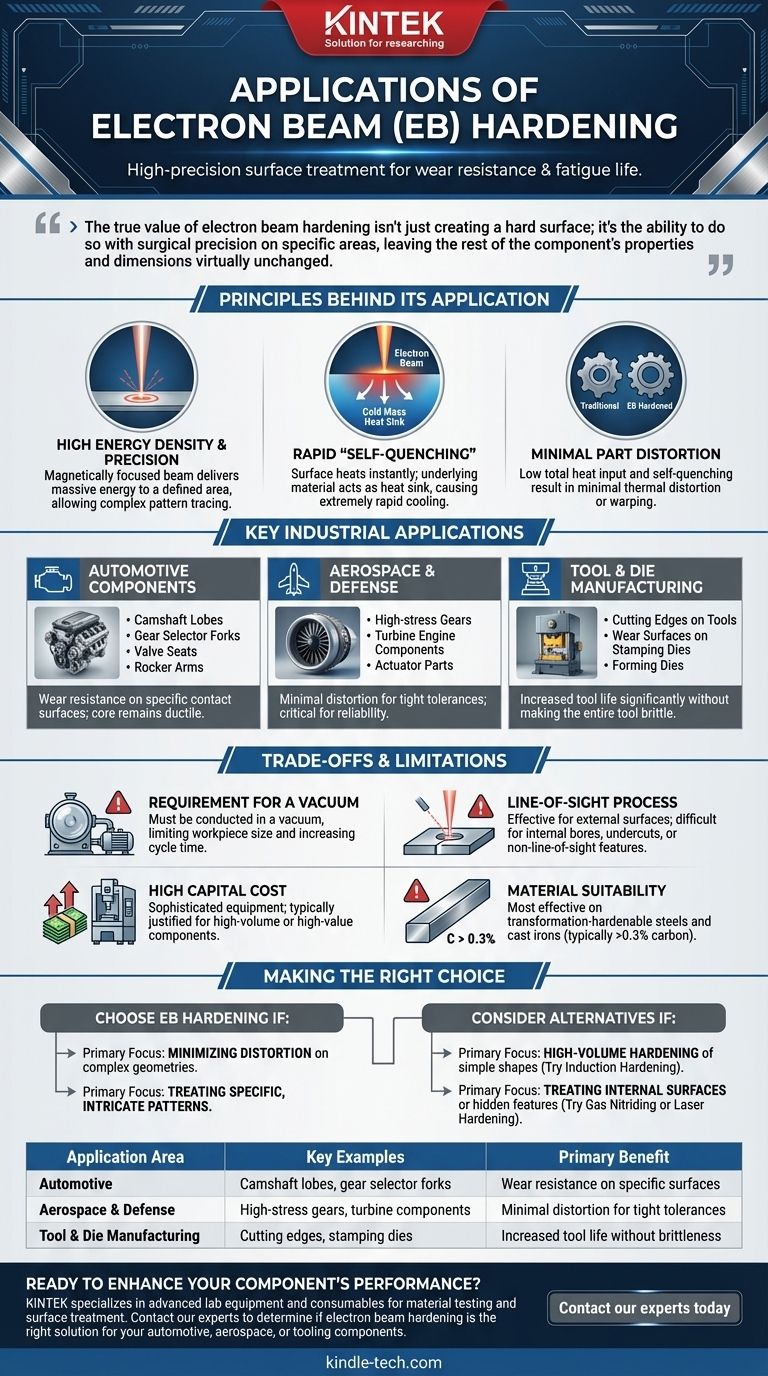
At its core, electron beam (EB) hardening is a high-precision surface treatment method used to increase the wear resistance and fatigue life of critical steel and cast iron components. It finds its primary applications in the automotive, aerospace, and tool manufacturing industries where targeted hardness is required on complex parts with minimal distortion.
The true value of electron beam hardening isn't just creating a hard surface; it's the ability to do so with surgical precision on specific areas, leaving the rest of the component's properties and dimensions virtually unchanged.

The Principles Behind Its Application
To understand where EB hardening excels, you must first grasp its fundamental advantages over conventional methods. These advantages directly dictate its ideal applications.
High Energy Density and Precision
The process uses a magnetically focused beam of high-velocity electrons to deliver a massive amount of energy to a very small, precisely defined area on the component's surface. This allows for the exact tracing of complex patterns.
Rapid "Self-Quenching"
The beam heats the surface layer almost instantaneously. As soon as the beam moves on, the large, cold mass of the underlying material acts as a perfect heat sink, pulling heat away from the surface at an extremely high rate. This self-quenching effect is what creates the hardened martensitic structure.
Minimal Part Distortion
Because the heat is applied only to the surface and for a very short duration, the total heat input into the component is remarkably low. This, combined with the self-quenching, means there is very little of the thermal distortion, warping, or change in dimension common with furnace or induction hardening.
Key Industrial Applications in Detail
The unique characteristics of EB hardening make it the preferred solution for specific, demanding components.
Automotive Components
This is the largest area of application, driven by the need for high-performance, lightweight parts in mass production.
Key examples include camshaft lobes, gear selector forks, valve seats, and rocker arms. These parts require exceptional wear resistance on very specific contact surfaces while the core remains ductile and tough.
Aerospace and Defense
In this sector, performance and reliability are paramount. EB hardening is used on critical components where failure is not an option.
Applications include treating the surfaces of high-stress gears, turbine engine components, and actuator parts. The minimal distortion is critical for maintaining the tight tolerances required in aerospace engineering.
Tool and Die Manufacturing
The longevity of tools and dies depends entirely on the hardness and durability of their working surfaces.
EB hardening is used to create extremely hard cutting edges on tools or to selectively harden wear surfaces on stamping and forming dies. This increases tool life significantly without making the entire tool brittle.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No process is perfect. Objectivity requires acknowledging the constraints of electron beam hardening, which often define when not to use it.
Requirement for a Vacuum
The process must be conducted in a vacuum chamber to prevent the electrons from colliding with air molecules. This limits the size of the workpiece and can add to the cycle time for pumping down the chamber.
Line-of-Sight Process
The electron beam travels in a straight line. This means it is highly effective for treating external surfaces but cannot easily harden internal bores, undercuts, or other features that are not in its direct line-of-sight.
High Capital Cost
The equipment for electron beam hardening is sophisticated and represents a significant capital investment. Therefore, its use is typically justified for high-volume production runs or for very high-value components where the performance benefits outweigh the cost.
Material Suitability
The process is most effective on materials capable of transformation hardening, primarily steels and cast irons with sufficient carbon content (typically >0.3%). It is not suitable for non-ferrous alloys or steels that cannot be hardened by quenching.
Making the Right Choice for Your Component
Selecting a surface hardening process requires matching the technology's strengths to your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is minimizing distortion on complex geometries: EB hardening is an exceptional choice, often superior to induction or through-hardening.
- If your primary focus is treating specific, intricate patterns on a surface: The precise control of the electron beam allows for hardening patterns that other methods cannot easily replicate.
- If your primary focus is high-volume hardening of simple shapes: Traditional induction hardening may be a more cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is treating internal surfaces or hidden features: You will need to consider alternative methods like gas nitriding or laser hardening, which can access non-line-of-sight areas.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently specify electron beam hardening for applications where precision, performance, and dimensional stability are non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Examples | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Camshaft lobes, gear selector forks | Wear resistance on specific surfaces |
| Aerospace & Defense | High-stress gears, turbine components | Minimal distortion for tight tolerances |
| Tool & Die Manufacturing | Cutting edges, stamping dies | Increased tool life without brittleness |
Ready to enhance your component's performance with precision hardening?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for material testing and surface treatment. Our expertise can help you determine if electron beam hardening is the right solution for your automotive, aerospace, or tooling components, ensuring superior wear resistance and minimal distortion.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover the value we can bring to your laboratory or production process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- Why is a Solar Furnace necessary for verifying sulfuric acid decomposition components? Ensure Industrial Scale Success
- What are the methods of brazing heating? Choose the Right Method for Your Production Needs
- What products are made from sintering? High-Strength Parts for Automotive, Dental & Industrial Use
- What do the processes of calcination and sintering have in common? Key Shared Thermal Principles Explained
- What is the sintering temperature of polymers? Find Your Material's Perfect Sintering Window
- How do laboratory high-temperature heating devices work with FT-IR to evaluate lubricant antioxidants? Expert Analysis
- How is plastic waste different from other types of waste? The Hidden Threat of Microplastics
- Are electric arc furnaces efficient? Unlocking Modern Steelmaking's Power and Flexibility



















