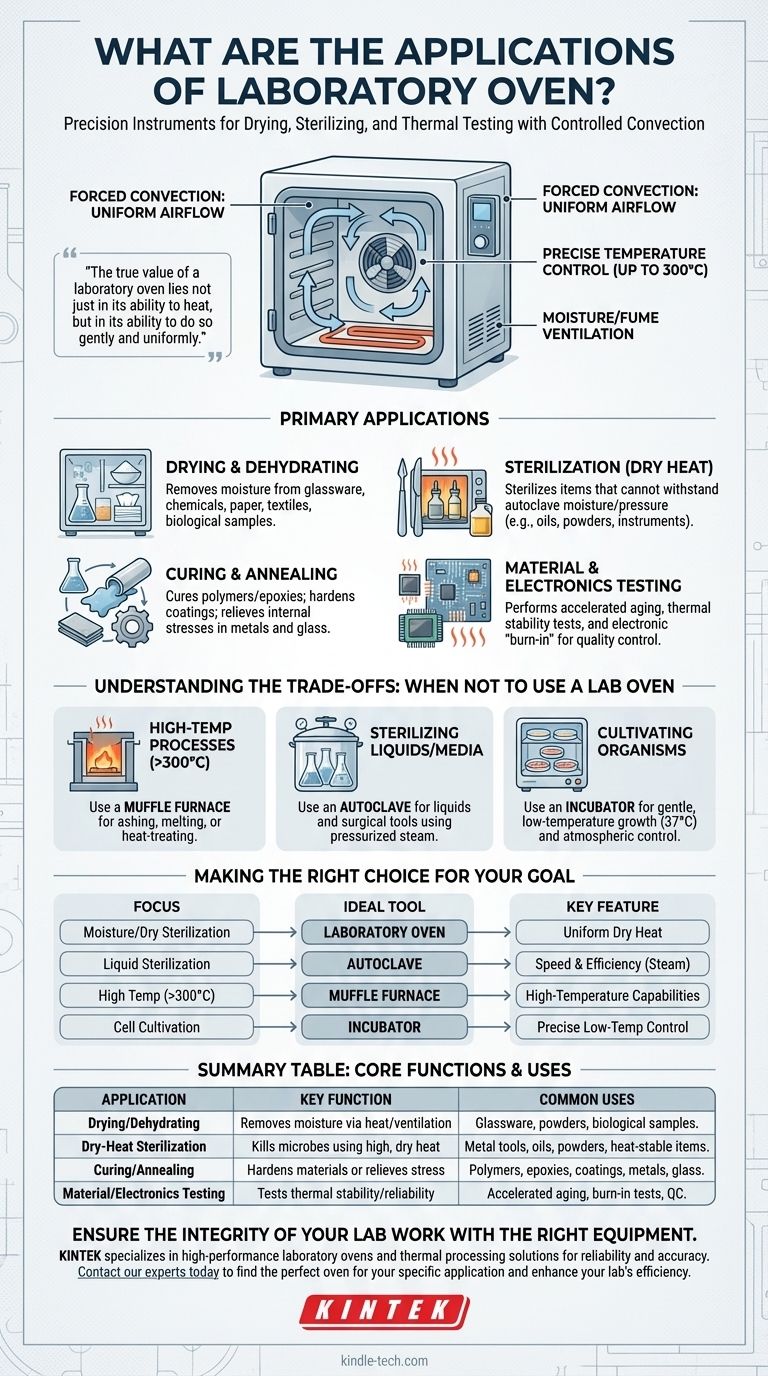
At its core, a laboratory oven is a precision instrument designed for three primary functions: drying materials, performing dry-heat sterilization, and conducting controlled thermal testing. It uses convection—the circulation of hot air—to provide a stable, uniform temperature environment, typically ranging from ambient up to 300°C, making it a foundational tool in scientific and industrial settings.
The true value of a laboratory oven lies not just in its ability to heat, but in its ability to do so gently and uniformly. Unlike a furnace or an autoclave, its purpose is to dehydrate and heat samples without the damaging effects of intense radiant energy or high-pressure steam.
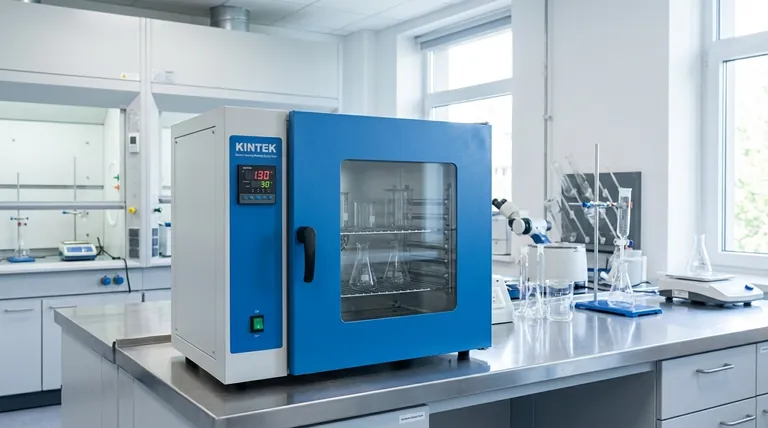

The Core Principle: How a Laboratory Oven Works
To understand its applications, you must first understand its mechanism. A laboratory oven is fundamentally a carefully controlled hot air chamber, distinct from other heating devices.
Convection Heating for Uniformity
A fan actively circulates air within the insulated chamber. This process, known as forced convection, ensures that every item inside the oven experiences the same temperature, eliminating "hot spots" that could damage or destroy sensitive samples.
Precise Temperature Control
A digital controller and sensor work together to maintain the set temperature with a high degree of accuracy. This stability is critical for experiments where slight temperature deviations could invalidate the results.
Moisture and Fume Removal
Nearly all lab ovens feature an adjustable vent. This port allows moisture vapor and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released from the sample during heating to escape, which is essential for effective drying and curing.
Primary Applications in Detail
The oven's design directly enables its core applications across research, quality control, and manufacturing.
Drying and Dehydrating
This is the most common application. The combination of gentle heat and ventilation makes it ideal for removing moisture from laboratory glassware, chemical powders, paper, textiles, and biological tissue samples prior to analysis.
Sterilization (Dry Heat)
A lab oven performs dry-heat sterilization, a process used for materials that cannot withstand the moisture and pressure of an autoclave. This includes items like oils, powders, metal instruments, and certain types of glassware that might be damaged by steam.
Curing and Annealing
In materials science and manufacturing, ovens are used to cure polymers, epoxies, and coatings, causing a chemical reaction that hardens the material. They are also used for annealing, a process of heating and slow cooling to relieve internal stresses in metals and glass.
Material and Electronics Testing
Ovens are critical for quality control. They are used to perform accelerated aging tests, determine the thermal stability of components, and "burn-in" electronic parts to detect early failures in a controlled environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When NOT to Use a Lab Oven
Knowing a tool's limitations is as important as knowing its strengths. Choosing the wrong device can ruin samples and produce invalid data.
For High-Temperature Processes (>300°C)
If your application involves ashing samples, melting metals, or heat-treating ceramics, you need a muffle furnace. Furnaces are designed to reach much higher temperatures (often over 1000°C) and use intense radiant heat.
For Sterilizing Liquids or Media
While an oven can sterilize, an autoclave is far more efficient for liquids, culture media, and most surgical instruments. An autoclave uses high-pressure steam to sterilize in minutes, whereas a dry-heat oven requires much longer exposure times (hours) at higher temperatures.
For Cultivating Living Organisms
To grow cell cultures or microbes, you must use an incubator. An incubator provides gentle, low-temperature heating (typically 37°C) and often controls humidity and gas levels (like CO2). An oven's dehydrating environment is designed to kill organisms, not sustain them.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal equipment is fundamental to reliable and repeatable results. Use this guide to make a clear decision.
- If your primary focus is removing moisture or sterilizing heat-stable, non-liquid items: The laboratory oven is your ideal tool for its uniform, dry heat.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing liquids, surgical tools, or culture media: You need an autoclave for its speed and efficiency using pressurized steam.
- If your primary focus is processing materials above 300°C (e.g., ashing or creating alloys): You must use a muffle furnace for its high-temperature capabilities.
- If your primary focus is growing and maintaining cell cultures or bacteria: You require a dedicated incubator for its precise low-temperature and atmospheric control.
Choosing the right tool for the task is the first step toward ensuring the integrity of your work.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Drying/Dehydrating | Removes moisture via heat and ventilation | Glassware, powders, biological samples |
| Dry-Heat Sterilization | Kills microbes using high, dry heat | Metal tools, oils, powders, heat-stable items |
| Curing/Annealing | Hardens materials or relieves internal stress | Polymers, epoxies, coatings, metals, glass |
| Material/Electronics Testing | Tests thermal stability and component reliability | Accelerated aging, burn-in tests, quality control |
Ensure the integrity of your lab work with the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory ovens and a full range of thermal processing equipment. Whether your needs involve precise drying, sterilization, or material testing, our solutions are designed for reliability and accuracy. Contact our experts today to find the perfect oven for your specific application and enhance your lab's efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- 50L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 30L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 20L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a laboratory drying oven in catalyst treatment? Ensure Structural Integrity & High Performance
- What role does a laboratory drying oven play in the processing and chemical analysis of aluminum dross?
- What is the role of a blast drying oven in COF synthesis? Driving High-Crystallinity Solvothermal Reactions
- Why is a laboratory-grade forced air drying oven required for alloy chip moisture analysis? Ensure Data Precision
- Why is a forced-air drying oven required for ZnS powder? Protect Sintered Ceramics from Cracking



















