At their core, mechanical presses are used for high-speed, high-volume manufacturing operations like metal stamping, blanking, and coining. They are the workhorses of industries that require rapid and repeatable production of identical parts, such as automotive body panels, appliance casings, and electronic components.
The defining characteristic of a mechanical press is its ability to deliver a quick, powerful stroke with immense consistency. This makes it the ideal choice for mass production where speed and repetition are more critical than raw, sustained force.
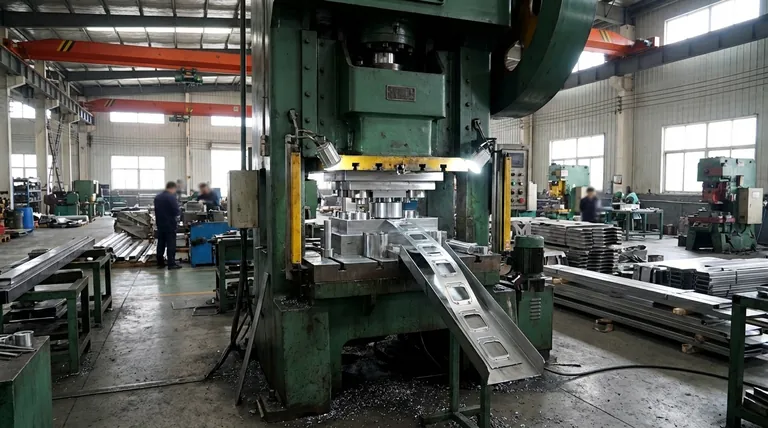

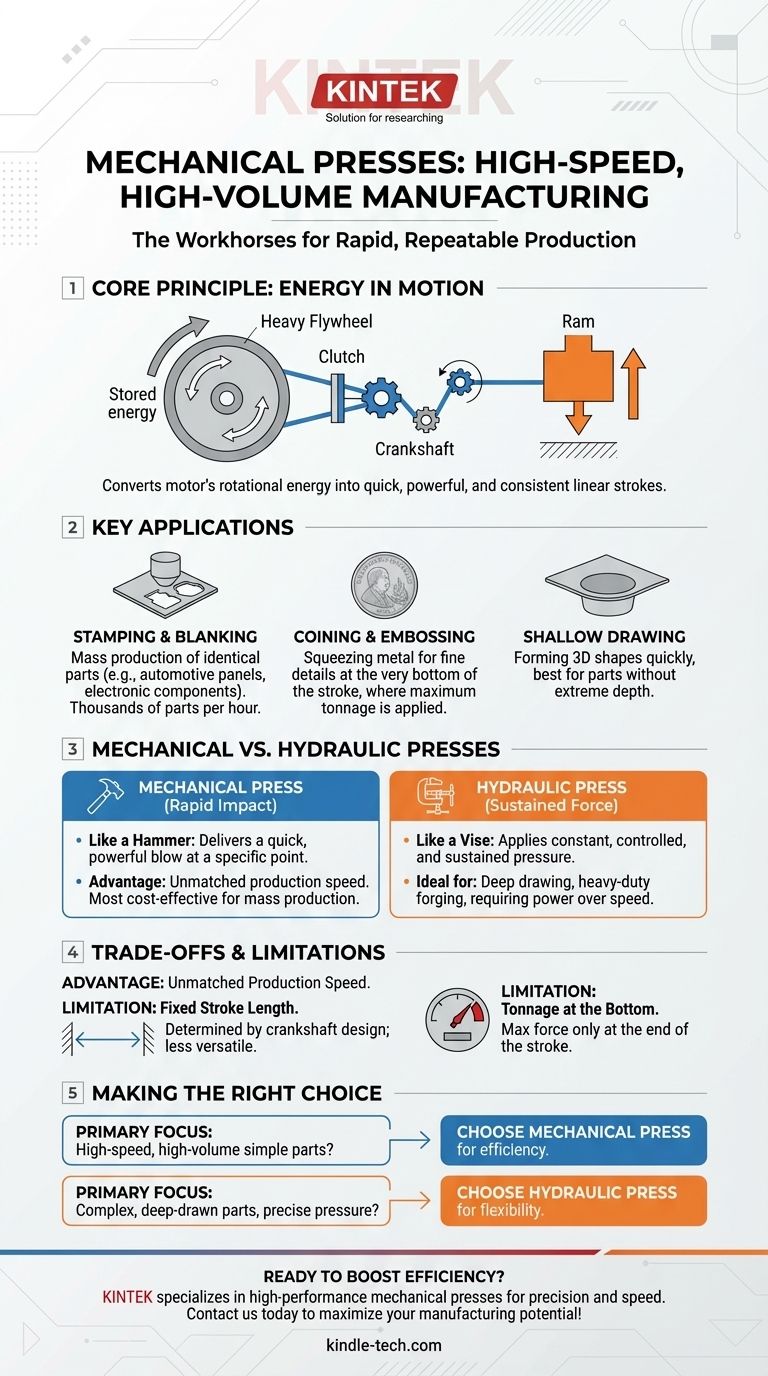
The Core Principle: Energy in Motion
A mechanical press functions by converting the rotational energy of a motor into linear motion. This is typically achieved with a large, heavy flywheel that stores energy, which is then transferred through a clutch and crankshaft to drive a ram up and down.
High-Volume Stamping and Blanking
This is the most common application. Stamping uses a die to shape or cut a sheet of metal, while blanking is the process of punching out a specific shape (a "blank") from a larger sheet for further processing. The fast cycle time of a mechanical press allows for thousands of parts to be produced per hour.
Coining and Embossing
These processes require a tremendous amount of force applied at the very bottom of the press stroke. Coining involves squeezing metal within a die to create fine details, like the features on a currency coin. The mechanical press's design naturally delivers its maximum tonnage at this specific point, making it perfect for the task.
Shallow Drawing and Forming
Mechanical presses are also used for drawing, which is the process of stretching sheet metal into a three-dimensional shape. They are best suited for shallow-drawn parts, where the depth is not extreme, and the speed of the operation is the primary concern.
Clarification: Mechanical vs. Hydraulic Presses
It is critical to distinguish between mechanical and hydraulic presses, as their applications differ significantly. The provided references primarily describe the uses of hydraulic presses, which operate on a different principle.
Where Hydraulic Presses Excel
A hydraulic press uses fluid pressure to exert a constant, controlled force throughout its entire stroke. This makes it better suited for applications requiring immense, sustained power rather than speed. This includes heavy-duty forging, deep drawing of complex parts, car crushing, and other tasks mentioned in the references.
The Key Distinction
Think of it this way: a mechanical press is like a hammer, delivering a rapid, powerful impact at a specific point. A hydraulic press is like a vise, applying a slow, deliberate, and sustained squeezing force.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the correct press type depends entirely on the requirements of the manufacturing process. Each has distinct advantages and limitations.
The Advantage: Unmatched Production Speed
For repetitive tasks with a consistent part design, nothing matches the output rate of a mechanical press. Its design is optimized for rapid cycling, making it the most cost-effective solution for mass production.
The Limitation: Fixed Stroke Length
The primary drawback of a mechanical press is its fixed stroke length, which is determined by the physical design of the crankshaft. This makes it less versatile than a hydraulic press, where stroke length and pressure can be easily adjusted.
The Limitation: Tonnage at the Bottom
A mechanical press only achieves its maximum rated tonnage at the very bottom of its stroke. The force available is significantly less at any other point in the cycle, which limits its use for jobs requiring sustained pressure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate technology comes down to a simple analysis of your primary manufacturing objective.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, high-volume production of relatively simple stamped parts: A mechanical press is unequivocally the correct choice for its efficiency and low cost-per-part.
- If your primary focus is forming complex, deep-drawn parts or you need precise control over pressure throughout the stroke: A hydraulic press offers the necessary power and flexibility that a mechanical press cannot.
Ultimately, the choice is dictated by the fundamental trade-off between manufacturing speed and operational versatility.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Stamping & Blanking | Cutting/shaping sheet metal | High-volume production of identical parts (e.g., automotive panels) |
| Coining | Squeezing metal for fine details | Creating detailed features like currency coins |
| Shallow Drawing | Forming 3D shapes from sheet metal | Manufacturing shallow-drawn components quickly |
| Embossing | Raising surface designs | Adding textures or logos to metal parts |
Ready to boost your production line's efficiency? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including robust mechanical presses designed for precision and speed. Whether you're in automotive, appliance, or electronics manufacturing, our solutions ensure consistent, high-volume output. Contact us today to find the perfect press for your laboratory or production needs and start maximizing your manufacturing potential!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- Does increasing hydraulic pressure increase speed? Focus on Flow Rate for True Performance Gains
- Why is a hydraulic press used for vacuum carbothermic magnesium reduction pellets? Protect Systems & Enhance Gas Flow
- What is the function of a laboratory hydraulic press in C/C-SiC preparation? Achieve Precision CFRP Green Body Densification
- How is a hydraulic press used to verify contaminated electrolyte solidification? Ensure 17-26 MPa Safety Compliance
- What is the maximum permissible temperature for hydraulic oil? Protect Your System from Costly Failure
- What are the safety precautions for KBr? Achieve Flawless FTIR Pellet Preparation and Data Accuracy
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press contribute to the preparation of fly ash composite samples? Precision Pressing
- Why was the hydraulic press important? Unlocking Unprecedented Industrial Power



















