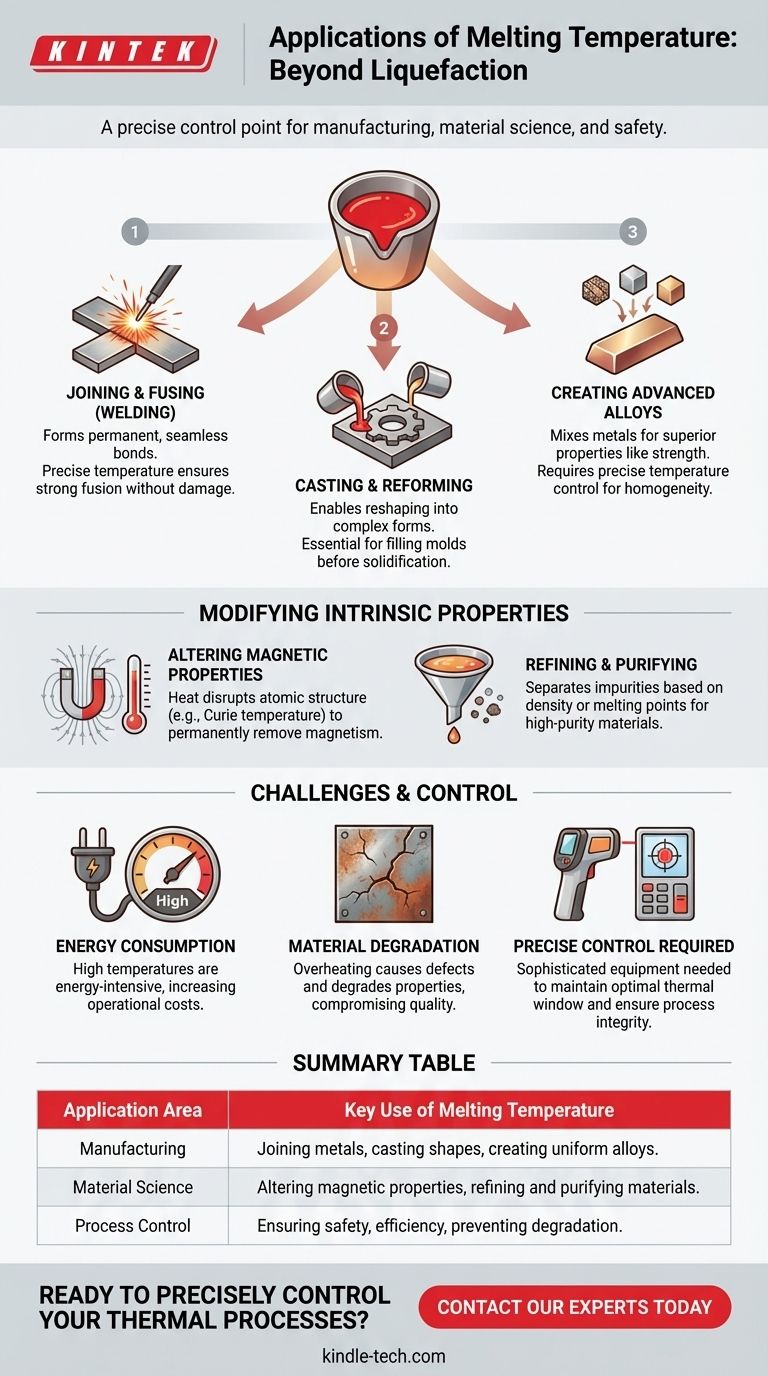
At its core, a material's melting temperature is a fundamental physical constant used for three primary applications: joining separate components, reforming materials into new shapes, and altering their intrinsic physical properties. For example, metals are liquefied for casting into molds, and magnetized steel can be heated to disrupt its atomic alignment, thereby removing its magnetism.
The true application of melting temperature is not simply about liquefying a substance. It is about leveraging a precise, predictable thermal threshold as a critical control point in manufacturing, material science, and process safety.

Foundational Applications in Manufacturing
The most common applications of melting temperature revolve around the physical manipulation of materials, particularly metals, to create new products or structures.
Joining and Fusing Materials
Melting is the principle behind many forms of welding and joining. By heating metals to their melting point, a permanent, often seamless bond can be formed between two or more pieces.
Knowing the precise melting temperature is crucial to ensure a strong fusion without overheating and damaging the parent materials.
Casting and Reforming Materials
Complete liquefaction allows a material to be reshaped. This is the basis of casting, where molten metal is poured into a mold to create complex shapes, from engine blocks to jewelry.
The process relies on reaching the melting temperature to ensure the material has the necessary fluidity to fill the mold completely before it cools and solidifies.
Creating Advanced Alloys
Alloys are mixtures of metals created to achieve superior properties like strength or corrosion resistance. This process involves melting two or more constituent metals together.
Controlling the temperature precisely at or above the respective melting points is essential to ensure the elements mix uniformly, resulting in a homogenous alloy with predictable characteristics.
Modifying Intrinsic Material Properties
Beyond simple shaping, melting temperature is a gateway to altering the fundamental nature of a material.
Altering Magnetic Properties
Heat can disrupt the internal atomic structure of a material. For instance, heating a piece of magnetized steel to a specific threshold known as the Curie temperature will cause it to lose its magnetism permanently.
This demonstrates how thermal energy, benchmarked by temperatures like the melting point, can be used to engineer specific physical properties.
Refining and Purifying Materials
Melting is a key step in refining ores and purifying materials. By liquefying a substance, impurities can be separated based on differences in density or their own distinct melting points.
This application is fundamental to producing high-purity metals and other industrial materials where contaminants would compromise performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, working with melting temperatures involves significant challenges that must be managed.
Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining the high temperatures required for melting is an energy-intensive process. This represents a significant operational cost in any manufacturing or refining operation.
Risk of Material Degradation
Exceeding the optimal melting temperature can be as problematic as not reaching it. Overheating can cause oxidation, introduce structural defects, or degrade the material's properties, compromising the quality of the final product.
Requirement for Precise Control
The benefits of using melting temperature can only be realized with precise control. As noted in process monitoring, this requires sophisticated equipment like optical pyrometers and automated control systems.
These systems use the target temperature as a critical setpoint, often cutting off energy input if it is exceeded to prevent equipment damage and ensure process integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Effectively applying the concept of melting temperature depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is fabrication and joining: Concentrate on reaching the melting point just enough to ensure complete fusion without damaging the surrounding material.
- If your primary focus is material creation: Use the melting points of constituent elements to design a heating profile that ensures a complete and homogenous mixture for your alloy.
- If your primary focus is process safety and efficiency: Implement precise temperature monitoring and control systems to operate within the optimal thermal window, preventing material degradation and energy waste.
Mastering a material's melting temperature is fundamental to controlling its final form, function, and integrity.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Use of Melting Temperature |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Joining metals (welding), casting shapes, creating uniform alloys. |
| Material Science | Altering magnetic properties, refining and purifying materials. |
| Process Control | Ensuring process safety, efficiency, and preventing material degradation. |
Ready to precisely control your thermal processes?
From alloy creation to material joining, mastering melting temperature is key to your success. KINTEK specializes in the high-temperature lab equipment and consumables you need for reliable, efficient, and safe operations.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve superior material control and enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?



















