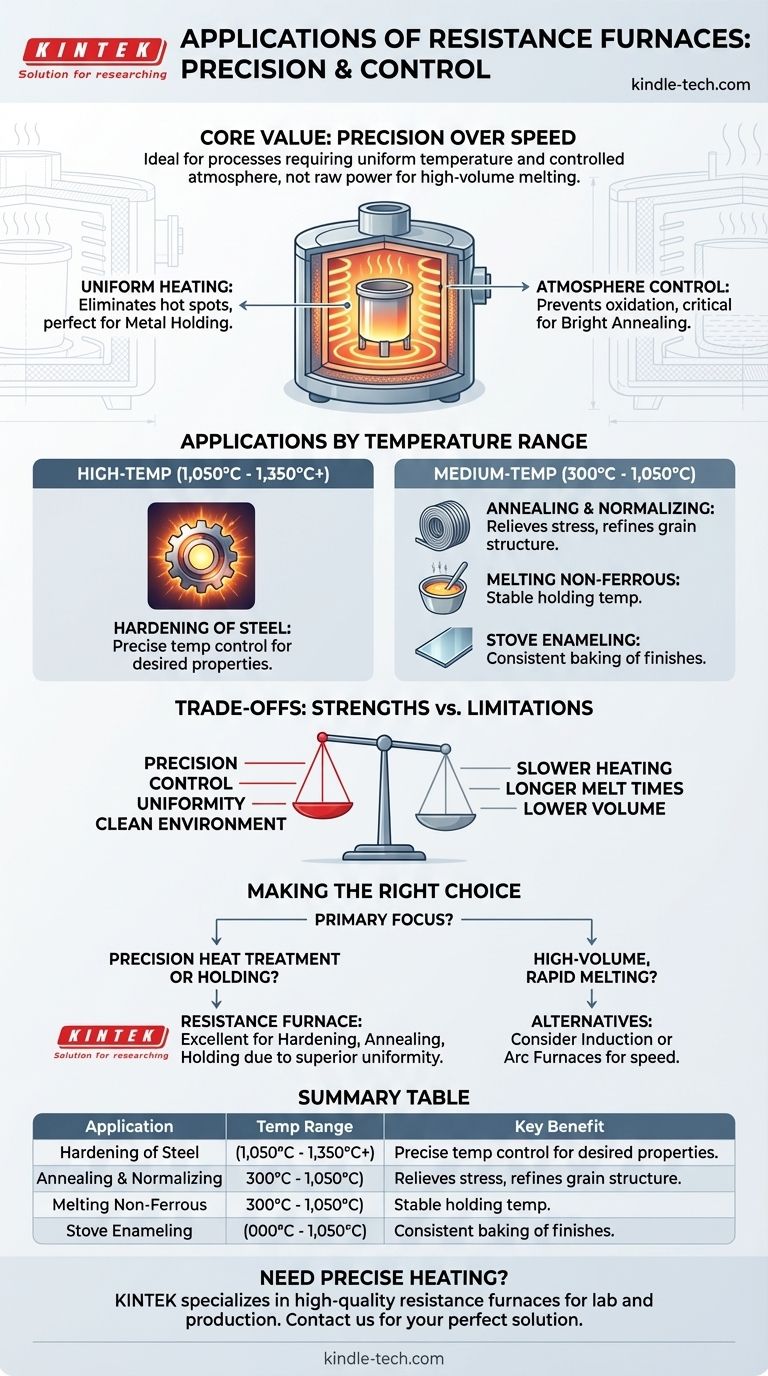
At their core, resistance furnaces are used for thermal processes that demand high precision and uniform temperature. Their primary applications include the heat treatment of metals—such as hardening, annealing, and normalizing—as well as holding molten non-ferrous metals at a specific temperature and for specialized processes like stove enameling.
A resistance furnace's value is not in its speed, but in its precision. It excels in applications where uniform, controllable heating in a controlled atmosphere is more critical than the raw power needed for high-volume melting.

The Principle: Control Over Power
The applications of a resistance furnace are a direct result of how it generates heat. Unlike fuel-fired or induction furnaces, it uses electrical resistance to create a clean, stable, and easily regulated thermal environment.
The Benefit of Uniform Heating
Resistance elements can be distributed around the furnace chamber, providing even, all-around heating. This eliminates hot spots and ensures the entire workpiece or crucible reaches and maintains a consistent temperature.
This quality makes them ideally suited for metal holding applications, where a batch of molten metal must be kept at a precise temperature without variation.
The Importance of Atmosphere Control
Modern resistance furnaces are often well-sealed, allowing for a vacuum or the introduction of a specific gaseous medium.
This controlled atmosphere prevents oxygen from reacting with the metal surface. This is critical for applications like bright annealing, where the goal is to soften the metal without causing oxidation or discoloration, preserving its surface finish.
Core Applications by Temperature Range
The specific use of a resistance furnace is often dictated by its operating temperature range.
High-Temperature Processes (1,050°C to 1,350°C+)
In this range, resistance furnaces are primarily employed for the hardening of steel. The process requires bringing the metal to a precise temperature before quenching, and the furnace's control is essential for achieving the desired material properties.
Some specialized models can exceed 1500°C, accommodating a wider range of materials and processes.
Medium-Temperature Processes (300°C to 1,050°C)
This is the most versatile range, covering several key industrial applications.
These include annealing and normalizing of both steel and non-ferrous metals to relieve internal stresses and refine grain structure. It also includes the melting of non-ferrous metals and processes like stove enameling, where a finish is baked onto a surface at a consistent temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is a universal solution. The primary strengths of a resistance furnace—precision and control—come with clear limitations.
Speed and Scale
Resistance furnaces take longer to reach temperature and melt metals compared to technologies like induction or arc furnaces. The heating process is fundamentally slower.
This makes them less suitable for operations where speed is the dominant economic driver.
Limitations in High-Volume Melting
Because of their slower heating rate, resistance furnaces are generally not the preferred choice for melting very large quantities of metal from a solid state, especially high-melting-point metals.
They are typically used for small to medium-sized operations. Their strength lies in holding, heat treatment, and lower-volume melting, not primary, large-scale production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right furnace technology requires aligning the tool with the specific goal of your operation.
- If your primary focus is precision heat treatment: A resistance furnace is an excellent choice for hardening, annealing, or normalizing due to its superior temperature uniformity and control.
- If your primary focus is holding molten metal: The even, all-around heating of a resistance furnace is ideal for maintaining a precise and stable temperature in a holding application.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, rapid melting: You should evaluate faster alternatives, such as induction or arc furnaces, which are designed for speed and throughput.
By understanding its core strengths, you can leverage a resistance furnace for processes where precision and quality are paramount.
Summary Table:
| Application | Temperature Range | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Hardening of Steel | 1,050°C to 1,350°C+ | Precise temperature control for material properties |
| Annealing & Normalizing | 300°C to 1,050°C | Uniform heating to relieve stress & refine grain structure |
| Holding Molten Non-Ferrous Metals | Varies by metal | Stable temperature maintenance without hot spots |
| Bright Annealing | Medium to High | Controlled atmosphere prevents oxidation & discoloration |
| Stove Enameling | 300°C to 1,050°C | Consistent baking of finishes on surfaces |
Need precise, uniform heating for your lab or production process? KINTEK specializes in high-quality resistance furnaces designed for applications like metal hardening, annealing, and controlled atmosphere heat treatment. Our equipment ensures temperature stability and reliability for your specific needs. Contact us today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory or industrial application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing



















