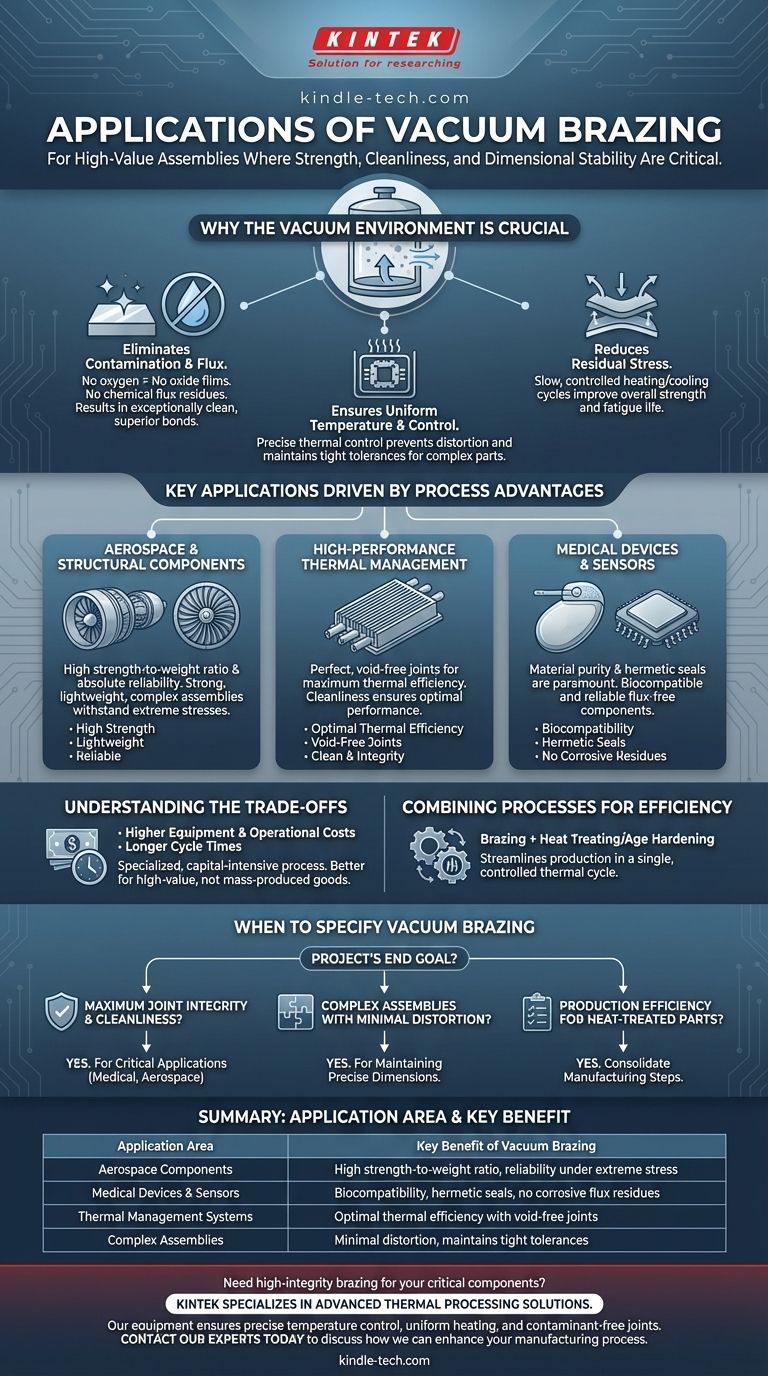
Vacuum brazing is primarily used for joining complex, high-value assemblies where strength, cleanliness, and dimensional stability are critical. Its applications span demanding industries, including the manufacturing of aircraft components, medical devices, sensors, and high-performance thermal management systems like micro-channel heat exchangers.
The decision to use vacuum brazing is driven by a need for metallurgical purity and precision that other joining methods cannot provide. It excels at creating strong, contaminant-free joints in complex assemblies while minimizing the internal stresses that cause distortion.

Why the Vacuum Environment is Crucial
The defining characteristic of this process is the vacuum itself. By removing atmospheric gases from the furnace, we fundamentally change the joining environment, which delivers several key advantages.
Eliminating Contamination and Flux
In a vacuum, there is no oxygen to create oxide films on the metal surfaces. This results in an exceptionally clean work surface, allowing the brazing filler metal to flow freely and form a superior bond.
This process eliminates the need for chemical fluxes, which can leave corrosive residues and create potential failure points within the joint. The final product is bright, clean, and requires no post-process cleaning.
Ensuring Uniform Temperature and Control
A vacuum furnace provides highly uniform heating and cooling. This controlled environment ensures that complex assemblies, regardless of size or shape, reach the target temperature evenly.
This precise thermal control is essential for preventing distortion and maintaining the tight tolerances required in aerospace and medical components.
Reducing Residual Stress
The slow, controlled heating and cooling cycles inherent to vacuum brazing significantly reduce the internal stresses that can build up within a component.
Lower residual stress improves the part's overall thermal and mechanical properties, increasing its strength and fatigue life in demanding service conditions.
Key Applications Driven by Process Advantages
The unique benefits of vacuum brazing make it the go-to solution for specific, high-stakes manufacturing challenges.
Aerospace and Structural Components
In aerospace, strength-to-weight ratios and absolute reliability are non-negotiable. Vacuum brazing is used to create strong, lightweight, and complex assemblies that can withstand extreme operational stresses.
High-Performance Thermal Management
Components like micro-channel heat exchangers and other heating or cooling assemblies rely on perfect, void-free joints for maximum thermal efficiency. The cleanliness and integrity of vacuum-brazed joints ensure optimal performance.
Medical Devices and Sensors
For medical implants and sensitive electronic sensors, material purity and hermetic seals are paramount. The flux-free, pristine nature of vacuum brazing makes it ideal for producing biocompatible and reliable components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum brazing is a specialized process with specific considerations. It is not a universal solution for all joining tasks.
Equipment and Operational Costs
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment and require skilled technicians to operate and maintain. This makes the process more expensive than conventional brazing or welding methods.
Longer Cycle Times
The controlled heating and cooling ramps necessary to ensure low distortion and high quality result in longer processing times compared to other methods. This makes it better suited for high-value components rather than mass-produced, low-cost goods.
Combining Processes for Efficiency
A significant advantage is the ability to combine processes. Brazing can be performed in the same thermal cycle as heat treating or age hardening, streamlining the production of parts that require both joining and specific metallurgical properties.
When to Specify Vacuum Brazing for Your Project
Choosing the right joining process depends entirely on your project's end goal and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint integrity and cleanliness: Vacuum brazing is the definitive choice for creating strong, flux-free bonds in critical applications like medical or aerospace hardware.
- If your primary focus is joining complex assemblies with minimal distortion: The uniform heating and controlled cooling of the vacuum process make it ideal for maintaining the precise dimensions of intricate parts.
- If your primary focus is production efficiency for heat-treated parts: Use vacuum brazing to consolidate manufacturing steps by performing brazing and hardening in a single, controlled furnace cycle.
Ultimately, selecting vacuum brazing is a strategic decision to prioritize metallurgical perfection and structural integrity for your most critical components.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Benefit of Vacuum Brazing |
|---|---|
| Aerospace Components | High strength-to-weight ratio, reliability under extreme stress |
| Medical Devices & Sensors | Biocompatibility, hermetic seals, no corrosive flux residues |
| Thermal Management Systems | Optimal thermal efficiency with void-free joints |
| Complex Assemblies | Minimal distortion, maintains tight tolerances |
Need high-integrity brazing for your critical components? KINTEK specializes in advanced thermal processing solutions, including vacuum brazing systems designed for aerospace, medical, and high-performance industrial applications. Our equipment ensures precise temperature control, uniform heating, and contaminant-free joints for your most demanding projects. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your manufacturing process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of brazing over braze welding? Achieve Stronger, Cleaner, and Repeatable Joints
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What is the most important factor influencing the strength of the brazed joint? Master Joint Clearance for Maximum Strength
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds



















