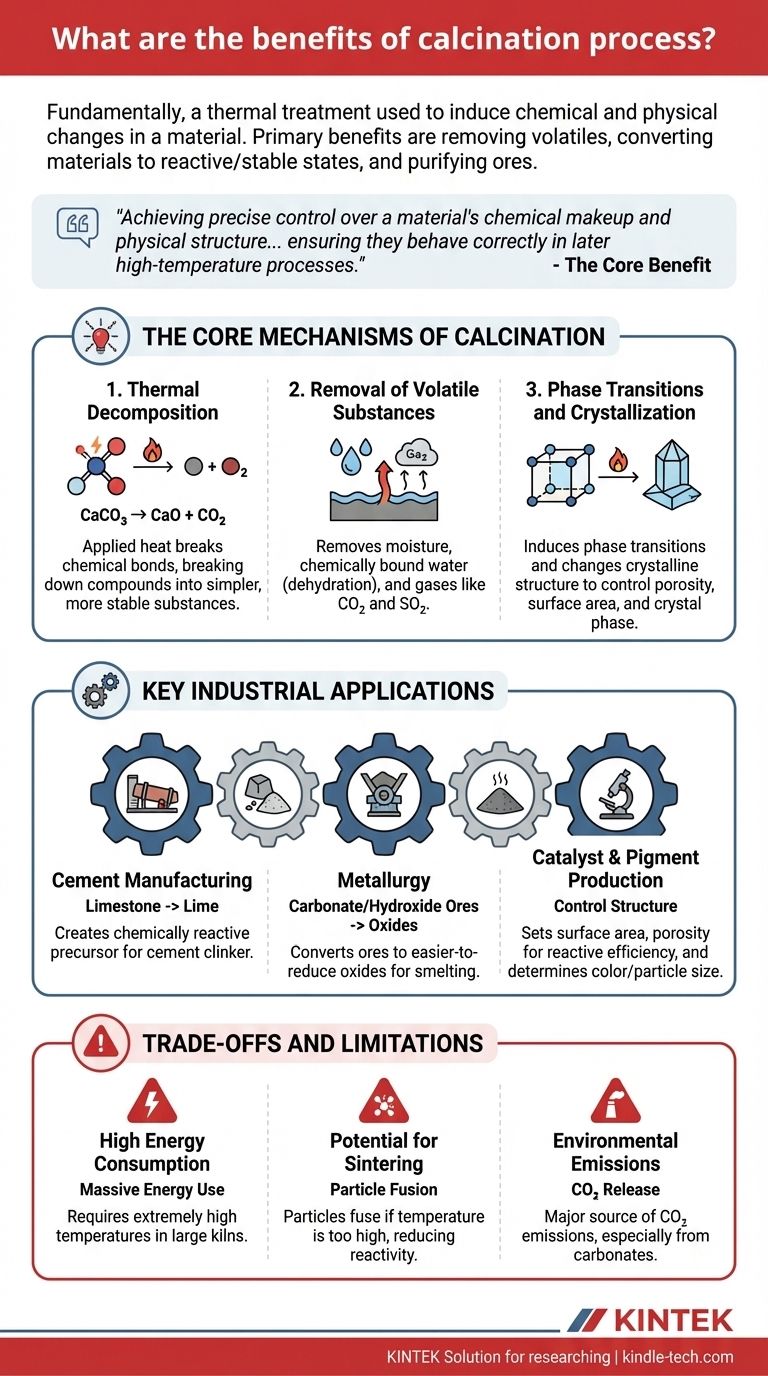
Fundamentally, the calcination process is a form of thermal treatment used to induce chemical and physical changes in a material. Its primary benefits are to remove volatile substances like water and carbon dioxide, convert materials into a more reactive or stable state, and purify ores before subsequent processing like smelting. This controlled heating prepares a raw material by fundamentally altering its composition.
The core benefit of calcination is not simply "cleaning" an ore, but rather achieving precise control over a material's chemical makeup and physical structure. It transforms materials into a more stable and predictable state, ensuring they behave correctly in later high-temperature processes like smelting or cement production.
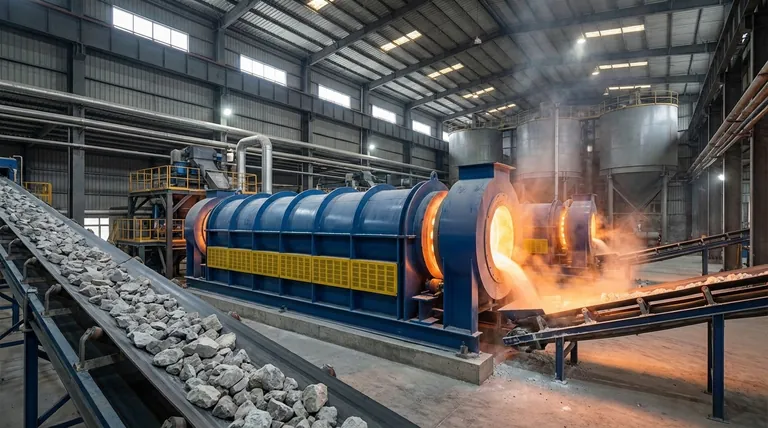

The Core Mechanisms of Calcination
Calcination achieves its benefits through several key mechanisms driven by high heat, typically in the absence of air or with limited oxygen to prevent combustion.
Thermal Decomposition
The central principle of calcination is thermal decomposition. The applied heat provides enough energy to break the chemical bonds within a compound, causing it to break down into simpler, more stable substances.
A classic example is the calcination of limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) to produce lime (calcium oxide, CaO). The heat drives off carbon dioxide (CO₂), leaving behind a highly reactive oxide essential for making cement and steel.
Removal of Volatile Substances
A primary goal of calcination is to remove volatile components that could interfere with later stages of production. This goes beyond simple drying.
This includes removing physically bound moisture, chemically bound water (dehydration) from hydrates like bauxite, and gases like carbon dioxide from carbonates or sulfur dioxide from sulfates. The result is a more concentrated, purified base material.
Phase Transitions and Crystallization
Heat can also induce phase transitions, changing the crystalline structure of a material without altering its chemical formula.
This benefit is crucial for controlling a material's final properties. For example, calcination can be used to control the porosity, surface area, and crystal phase of materials like alumina, which is critical for their use as abrasives, ceramics, or catalyst supports.
Key Industrial Applications and Their Benefits
The benefits of calcination are most clearly seen in its large-scale industrial applications.
In Cement Manufacturing
Calcination is the heart of cement production. Limestone is heated in a kiln to produce calcium oxide (lime), the primary reactive ingredient that will later form cement clinker. The benefit here is creating a chemically reactive precursor.
In Metallurgy
As the reference indicates, calcination is a vital step in preparing metallic ores. It converts carbonate and hydroxide ores into their oxide forms, which are much easier to reduce to pure metal in a smelter.
For example, bauxite ore (hydrated aluminum oxide) is calcined to produce anhydrous alumina (Al₂O₃), the raw material for producing aluminum metal. This removes water that would otherwise consume vast amounts of energy in the smelting pot.
In Catalyst and Pigment Production
In more specialized fields, calcination provides precise control over a material’s physical structure. For catalysts, the process sets the final surface area and porosity, which dictates its reactive efficiency. For pigments, it can determine the final color and particle size.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly beneficial, calcination is not without its challenges. Understanding these trade-offs is critical for any technical application.
High Energy Consumption
Calcination requires maintaining extremely high temperatures in massive rotary kilns. This process is highly energy-intensive, representing a significant operational cost and a major factor in the overall energy footprint of industries like cement and metallurgy.
Potential for Sintering
If the temperature is too high or held for too long, the particles can begin to fuse together in a process called sintering. This agglomeration can reduce the material's surface area and reactivity, which is often the opposite of the intended goal. Precise temperature control is essential to avoid this.
Environmental Emissions
The process itself is a major source of emissions. The thermal decomposition of carbonates, particularly limestone, releases massive quantities of carbon dioxide (CO₂) directly into the atmosphere. This makes industries that rely on calcination a major focus for carbon capture and emission reduction strategies.
Applying Calcination for Specific Goals
To leverage the process effectively, you must align it with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is producing a reactive chemical intermediate: The main benefit is the creation of highly reactive oxides, like quicklime from limestone, for use in subsequent chemical processes.
- If your primary focus is preparing a metallic ore for smelting: The key advantage is converting the ore into a more easily reducible oxide form, which improves the efficiency and energy consumption of the smelting furnace.
- If your primary focus is controlling the physical properties of a material: Calcination is essential for modifying crystal structure, controlling porosity, and setting the final surface area for applications like catalysts and ceramics.
Ultimately, calcination provides critical control over a material's chemical and physical state, making it an indispensable step in manufacturing the world's most essential materials.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Mechanism | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Remove Volatile Substances | Thermal Decomposition | Purify ores, dehydrate materials |
| Create Reactive Oxides | Chemical Breakdown | Cement production, metallurgy |
| Control Physical Properties | Phase Transitions | Catalyst and pigment manufacturing |
Optimize Your Material Processing with KINTEK's Calcination Solutions
Calcination is a critical step for achieving the precise chemical and physical properties required in industries like metallurgy, cement production, and catalyst manufacturing. The process demands reliable, high-performance equipment to ensure consistent results and operational efficiency.
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored for high-temperature processes. Our solutions are designed to help you:
- Enhance Process Control: Achieve precise temperature management to avoid sintering and maximize material reactivity.
- Improve Product Quality: Produce consistent, high-purity oxides and intermediates for your downstream applications.
- Increase Operational Efficiency: Leverage energy-efficient designs to manage the high energy demands of calcination.
Whether you are developing new materials or optimizing existing production lines, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your goals.
Ready to transform your materials with precision? Contact our experts today to discuss how our calcination solutions can benefit your specific laboratory or industrial needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields



















