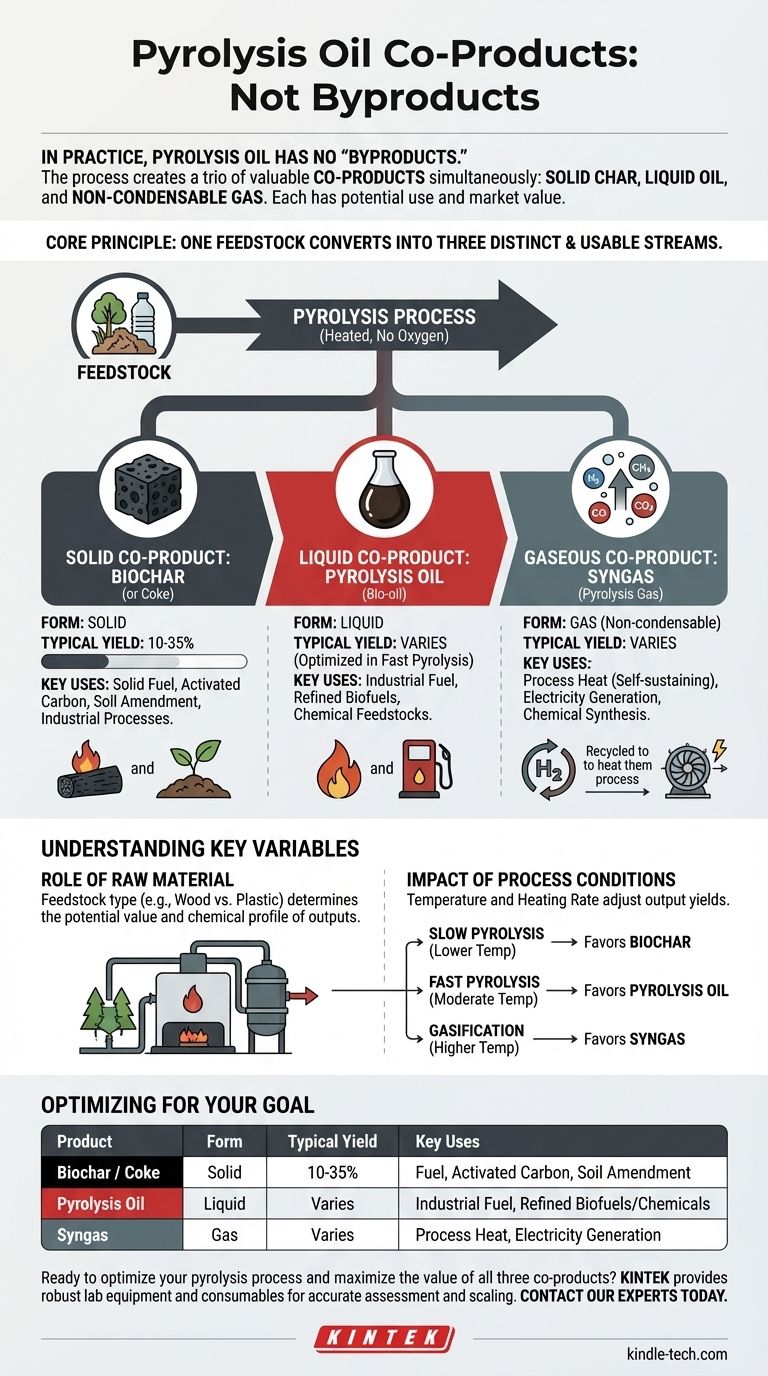
In practice, pyrolysis oil has no "byproducts." Instead, the pyrolysis process itself creates a trio of valuable outputs simultaneously: a solid char, a liquid oil, and a non-condensable gas. The materials often considered byproducts are actually co-products, each with its own potential use and market value.
The core principle of pyrolysis is the conversion of a single feedstock into three distinct and usable product streams. An economically and environmentally successful pyrolysis operation depends on finding value not just in the oil, but in the solid (biochar) and gaseous (syngas) outputs as well.

The Three Core Products of Pyrolysis
When a feedstock like biomass or plastic is heated in the absence of oxygen, it doesn't just create oil. The material deconstructs into three fundamental states: a solid, a liquid, and a gas.
The Solid Product: Biochar (or Coke)
After the volatile components have been driven off, a solid, carbon-rich material remains. This is known as biochar when derived from biomass or often coke from other materials.
This solid typically accounts for 10-35% of the output yield. Its properties make it useful as a solid fuel, for creating activated carbon for filtration, as an agricultural soil amendment, or for various industrial processes.
The Liquid Product: Pyrolysis Oil (Bio-oil)
This is the product most people associate with pyrolysis. It is formed when the hot pyrolysis gas is rapidly cooled (quenched), causing the condensable compounds to turn into a liquid.
This dark, viscous liquid is a complex mixture of water, tars, and hundreds of organic compounds. It can be used directly as an industrial fuel, or it can be upgraded and refined into higher-grade biofuels or valuable chemical feedstocks.
The Gaseous Product: Syngas (Pyrolysis Gas)
Not all the gas produced during pyrolysis will condense into a liquid. This remaining stream of non-condensable gases is commonly called syngas or pyrolysis gas.
It is a mixture of hydrogen (H2), methane (CH4), carbon monoxide (CO), and carbon dioxide (CO2). While it has the lowest energy density of the three products, its most critical use is often to be recycled back into the system to provide the heat for the pyrolysis reaction, making the entire process more energy-efficient and self-sustaining.
Understanding the Key Variables
The exact ratio and composition of these three products are not fixed. They are heavily influenced by the inputs and the precise method used, which allows operators to target specific outputs.
The Role of Raw Material
The initial feedstock is the single most important factor. Pyrolyzing wood will produce biochar, bio-oil, and syngas with a different chemical profile than pyrolyzing waste plastic or tires. The input directly determines the potential value of the outputs.
The Impact of Process Conditions
The temperature and heating rate of the pyrolysis process can be adjusted to favor one type of output over another.
- Slow Pyrolysis (Lower Temperature): Favors a higher yield of solid biochar.
- Fast Pyrolysis (Moderate Temperature): Optimized to produce the maximum yield of liquid pyrolysis oil.
- Gasification (Higher Temperature): Pushed to its extreme, the process maximizes the yield of syngas.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding the full output stream is critical to assessing the viability of a pyrolysis project. A failure to account for all three products can lead to critical miscalculations.
The Myth of "Waste" Streams
A common mistake is to view the biochar and syngas as waste products from oil production. An operation that has to pay for disposal of its solid output and flares off its gas is almost never economically viable.
The Reality of Product Purity
The three product streams are rarely perfectly separated. The bio-oil often contains water and fine char particles that must be filtered out. The syngas may need to be "cleaned" before it can be used in an engine or turbine. Planning for this post-processing is essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" pyrolysis setup depends entirely on your primary objective. By understanding that you are managing a portfolio of outputs, you can optimize the process to meet a specific need.
- If your primary focus is producing a liquid fuel: You will use fast pyrolysis to maximize bio-oil yield and use the syngas and a portion of the biochar to power the system.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration or soil amendment: You will use slow, lower-temperature pyrolysis to maximize the output of stable biochar.
- If your primary focus is generating electricity from waste: You might use a higher-temperature process that maximizes syngas for use in a gas engine or turbine.
Ultimately, viewing pyrolysis as a system that produces a portfolio of valuable co-products is the key to unlocking its full technological and economic potential.
Summary Table:
| Product | Form | Typical Yield | Key Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biochar / Coke | Solid | 10-35% | Fuel, activated carbon, soil amendment |
| Pyrolysis Oil | Liquid | Varies | Industrial fuel, refined biofuels/chemicals |
| Syngas | Gas | Varies | Process heat, electricity generation |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process and maximize the value of all three co-products?
KINTEK specializes in providing robust lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you are characterizing feedstocks, analyzing product yields, or scaling up your process, our solutions help you accurately assess and optimize for bio-oil, biochar, and syngas production.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your specific laboratory needs and help you unlock the full potential of your pyrolysis projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions



















