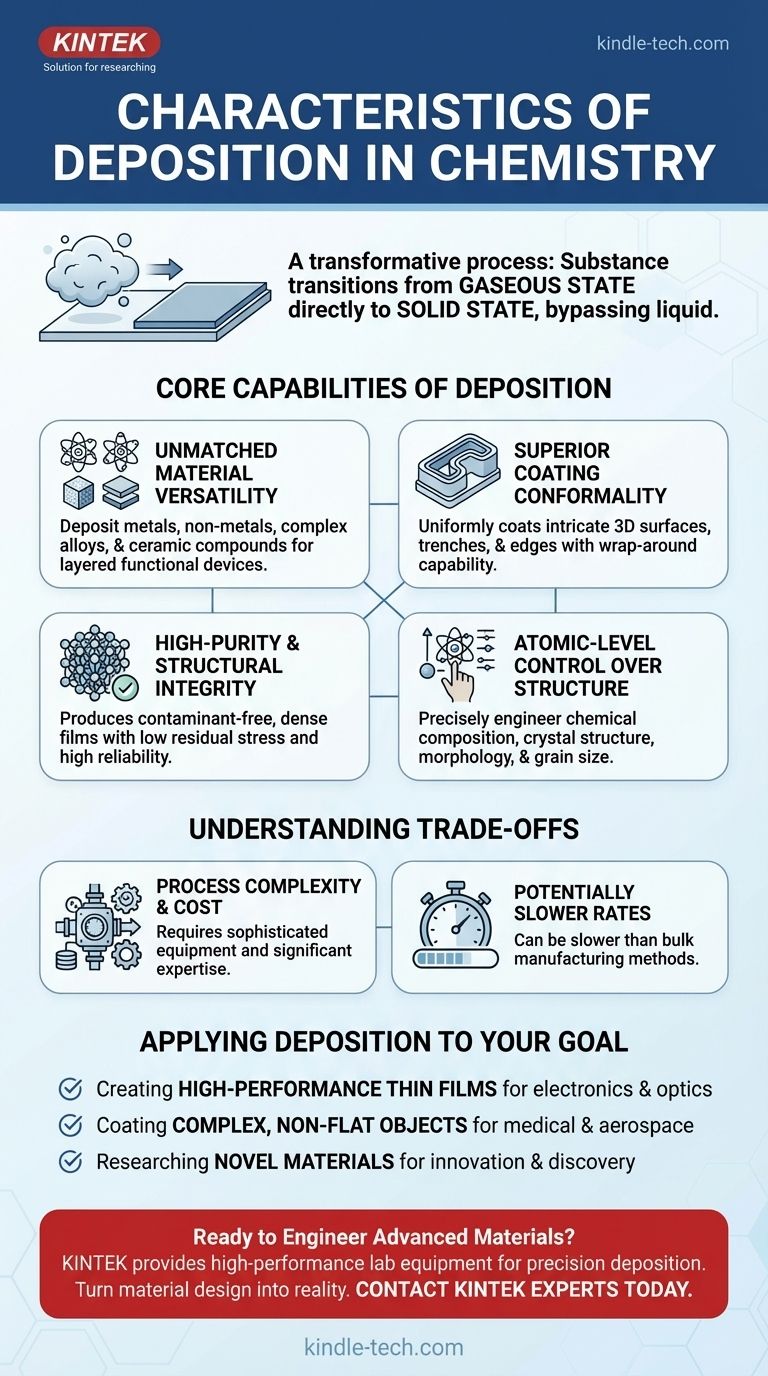
In chemistry, deposition is a transformative process where a substance transitions directly from a gaseous state to a solid state, bypassing the liquid phase. The key characteristics of this process, particularly in techniques like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), include the ability to create a wide variety of materials, produce exceptionally pure and dense films, and uniformly coat even the most complex surfaces.
The true value of deposition lies not just in its ability to create solid layers from gas, but in the exceptional level of control it provides. It allows for the precise engineering of a material's fundamental properties—from its chemical makeup to its crystal structure—at the microscopic level.
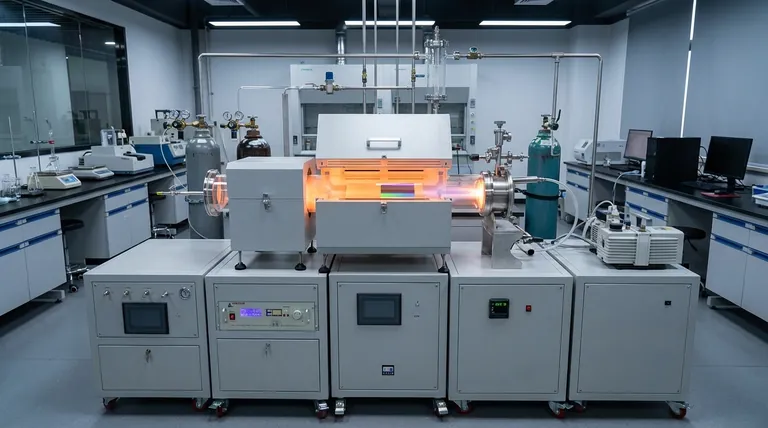

The Core Capabilities of Deposition
To understand if deposition is the right approach for a task, you must first understand its defining capabilities. These characteristics are what make it indispensable in fields ranging from microelectronics to aerospace engineering.
Unmatched Material Versatility
Deposition techniques are not limited to a single class of material. They are remarkably flexible.
You can deposit pure metal films, non-metal layers like silicon nitride, complex multi-component alloys, and highly durable ceramic or compound layers. This versatility makes it a foundational process for building layered, functional devices.
Superior Coating Conformality
A defining feature of vapor deposition is its "wrap-around" capability, known as conformality. The gaseous precursors can access and coat all exposed areas of a substrate, no matter how intricate its shape.
This ensures a uniform film thickness not just on flat surfaces but also inside trenches, around curves, and over sharp edges. This is critical for protecting components or creating functional layers on complex 3D objects.
High-Purity and Structural Integrity
The process is inherently designed for high purity. By using refined precursor gases in a controlled environment, the resulting solid film is free from contaminants that could degrade performance.
These films are also characterized by their high density ("good denseness") and low residual stress. This means the resulting coating is strong, stable, and less prone to cracking or delamination, ensuring reliability and longevity.
Atomic-Level Control Over Structure
This is perhaps the most powerful characteristic of deposition. By carefully adjusting process parameters like temperature, pressure, and gas flow rates, you can directly manipulate the final material.
You gain precise control over the chemical composition, the surface morphology (texture), the internal crystal structure, and even the grain size of the material. This is akin to building a material atom-by-atom to meet exact specifications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, deposition is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires understanding its inherent limitations and challenges.
Process Complexity and Cost
The high degree of control comes at a price. Deposition systems often require vacuum chambers, precise temperature and gas flow controllers, and high-purity chemical precursors.
This equipment is expensive to acquire and maintain, and operating it effectively requires significant technical expertise.
Potentially Slower Rates
Building a high-quality, dense, and precisely structured film layer-by-layer can be a slow process compared to bulk manufacturing methods like casting or electroplating.
For applications requiring very thick coatings or extremely high throughput, deposition may become a bottleneck. The trade-off is often between quality and speed.
Substrate and Parameter Sensitivity
The success of deposition is highly dependent on the condition of the substrate surface and the stability of the process parameters.
Even minor temperature fluctuations, pressure changes, or surface impurities can introduce defects into the film. Achieving repeatable, high-quality results demands rigorous process control and a pristine environment.
Applying Deposition to Your Goal
Your decision to use deposition should be driven by your end goal. The process excels in specific scenarios where its unique characteristics provide a clear advantage.
- If your primary focus is creating high-performance thin films: Deposition is the ideal choice, as it offers the unparalleled purity, density, and structural control needed for electronics, optics, and sensors.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, non-flat objects: The excellent conformality of deposition ensures complete and uniform coverage that other methods cannot achieve, making it perfect for medical implants or turbine components.
- If your primary focus is researching novel materials: The fine-tuned control over composition and crystal structure makes deposition an essential tool for material science innovation and discovery.
Ultimately, deposition empowers you to move beyond simply using materials to actively designing and building them for a specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Material Versatility | Deposit metals, non-metals, alloys, and ceramics for diverse applications. |
| Superior Conformality | Achieve uniform coatings on complex 3D surfaces, trenches, and edges. |
| High Purity & Integrity | Produce dense, strong, and contaminant-free films with low residual stress. |
| Atomic-Level Control | Precisely engineer chemical composition, crystal structure, and morphology. |
| Process Complexity | Requires sophisticated equipment and expertise for optimal results. |
Ready to Engineer Advanced Materials with Precision Deposition?
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-performance lab equipment and consumables necessary to leverage the power of chemical deposition. Whether you are developing next-generation microelectronics, creating durable coatings for aerospace components, or conducting groundbreaking materials research, our solutions deliver the purity, control, and reliability you demand.
Let us help you turn material design into reality. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application needs and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- How thick is the thin film color? Unlocking the Nanometer Scale of Iridescent Effects
- What is deposition uniformity and how is it measured? Optimize Film Consistency & Quality Control
- What are some key film characteristics to consider? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition for Peak Performance
- What are the major functions of the synthetic graphene? Unlock Next-Gen Electronics and Materials
- What materials can be deposited with CVD? Discover the Full Spectrum from Semiconductors to Ceramics
- Is deposition a chemical process? Understanding Chemical vs. Physical Thin-Film Methods
- What makes nanotubes special? Discover the Revolutionary Material Combining Strength, Conductivity & Lightness
- Can you coat something in diamond? Unlock Unmatched Hardness and Thermal Conductivity



















