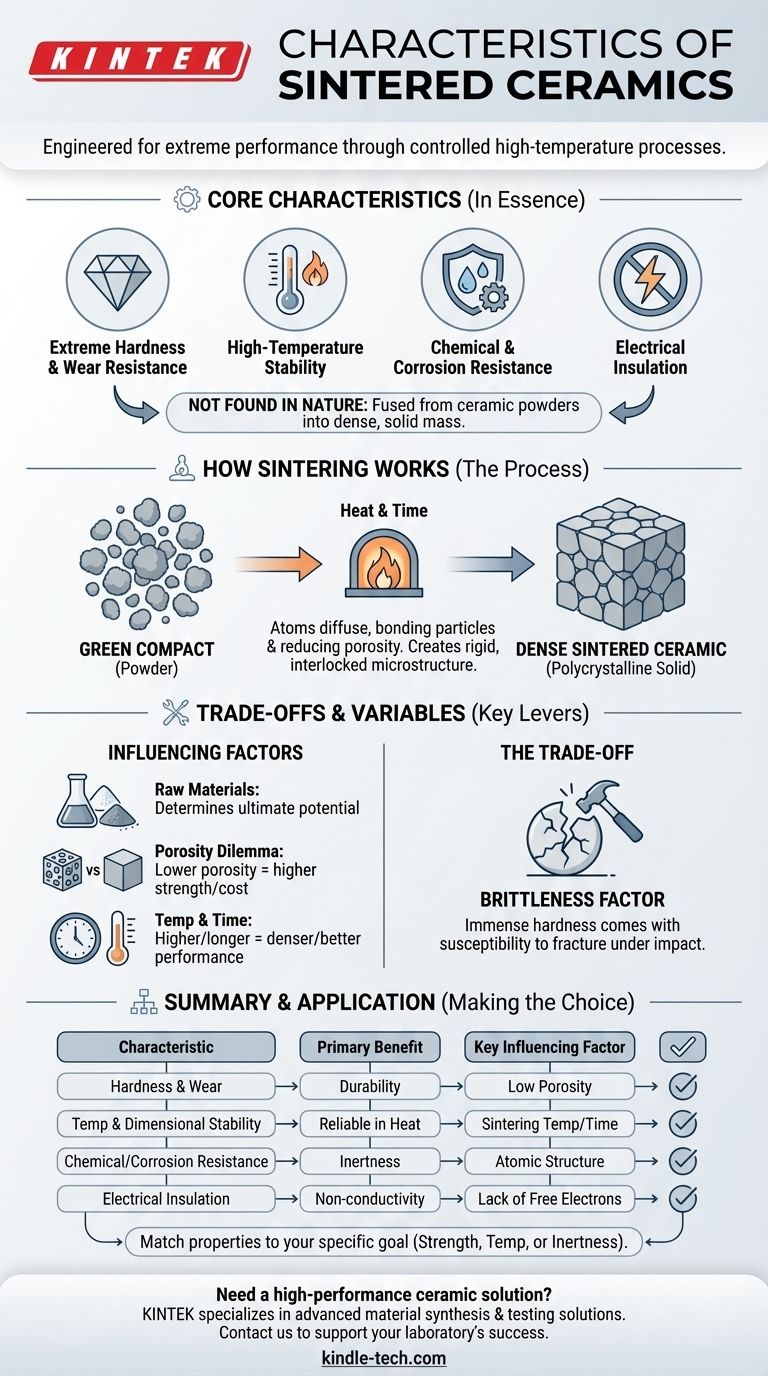
In essence, sintered ceramics are defined by their extreme hardness, stability under high temperatures, and resistance to wear, corrosion, and electricity. These materials are not found in nature but are engineered by compacting ceramic powders and heating them to just below their melting point, a process which fuses the particles into a dense, solid mass with a unique set of high-performance characteristics.
The exceptional properties of sintered ceramics are not accidental; they are the direct result of a controlled high-temperature process that fuses fine powders into a solid, highly stable material. Understanding this process is the key to leveraging their full potential for demanding applications.
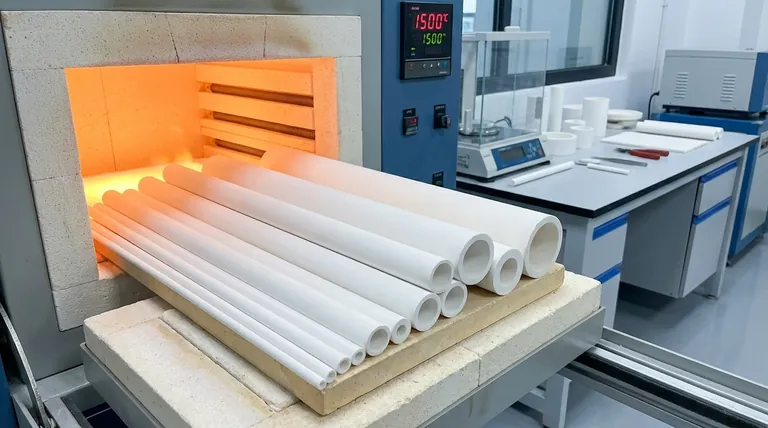

How Sintering Forges Exceptional Properties
The term "sintering" refers to the thermal treatment process that transforms a compacted powder (known as a "green compact") into a dense, polycrystalline solid. This transformation is the source of the material's most valuable traits.
The Foundation of Hardness and Strength
During sintering, atoms diffuse across the boundaries of individual powder particles, causing them to bond and merge. This process significantly reduces the empty space, or porosity, between particles.
The result is a dense, interlocked microstructure that is incredibly rigid. This structure is what provides high mechanical resistance to force and an extremely hard surface that resists abrasion and wear.
Achieving Thermal and Dimensional Stability
The sintering process occurs at very high temperatures. This effectively "pre-shrinks" the material and locks its atomic structure into a stable state.
Because of this, the final ceramic part exhibits remarkable dimensional stability, maintaining its shape and integrity even when subjected to extreme heat later on. This is why they have a reputation for high-temperature withstand.
The Source of Chemical and Electrical Resistance
The strong atomic bonds formed during sintering, particularly in oxide ceramics, create a very stable and inert material. There are few free electrons available to conduct electricity, making most sintered ceramics excellent electrical insulators.
This same atomic stability makes the material highly resistant to attack from chemical products and corrosion, as it's difficult for external agents to break the existing bonds.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variables
The final characteristics of a sintered ceramic part are not fixed; they are controlled by several key variables in the manufacturing process. Understanding these trade-offs is critical for any application.
The Role of Raw Materials
The process begins with the selection of a specific ceramic powder, such as alumina, zirconia, or silicon carbide. The inherent properties of this base material determine the ultimate potential for hardness, strength, and chemical stability.
The Porosity Dilemma
The final porosity of the ceramic is a critical factor. A denser, less porous part is typically stronger and more wear-resistant.
However, achieving lower porosity often requires higher sintering temperatures, longer process times, or the application of external pressure. This increases manufacturing complexity and cost.
Temperature and Time as Control Levers
Engineers use sintering temperature and duration as key controls. A longer, hotter cycle will produce a denser, higher-performance part.
Conversely, a faster, lower-temperature cycle may be more cost-effective but could result in a more porous material with reduced mechanical properties.
The Brittleness Factor
The immense hardness of ceramics comes with a well-known trade-off: brittleness. While they can withstand enormous compressive force and surface wear, they can fracture under sharp, sudden impact. This must be a central consideration in any design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right sintered ceramic involves matching the material's engineered properties to the demands of your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and wear resistance: Opt for a ceramic engineered for low porosity, which may require a more advanced sintering process involving pressure.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability: Prioritize a material composition, like a pure oxide ceramic, known for its performance at extreme temperatures and ensure the sintering process is sufficient to achieve full density.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation or chemical inertness: Concentrate on the chemical composition of the ceramic, as these properties are fundamentally tied to the material's stable atomic structure.
Ultimately, the characteristics of a sintered ceramic part are a direct reflection of deliberate choices made in its material composition and manufacturing process.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | Primary Benefit | Key Influencing Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Hardness & Wear Resistance | Superior durability and longevity | Low porosity from sintering process |
| High-Temperature & Dimensional Stability | Reliable performance in extreme heat | Sintering temperature and duration |
| Excellent Chemical & Corrosion Resistance | Inertness in harsh environments | Stable atomic structure of oxide ceramics |
| High Electrical Insulation | Effective non-conductivity for electronics | Lack of free electrons in atomic bonds |
| Inherent Brittleness (Trade-off) | Susceptibility to fracture under impact | Rigid, interlocked microstructure |
Need a high-performance ceramic solution tailored to your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for material synthesis and testing. Our expertise can help you select or develop the ideal sintered ceramic for your needs, whether you require maximum wear resistance, thermal stability, or chemical inertness.
Let our experts guide you to the right material choice and manufacturing process. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's success with precision-engineered materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Alumina Ceramic Saggar for Fine Corundum
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Aluminum Oxide Al2O3 Heat Sink for Insulation
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What functions do high-purity alumina support rods serve in sCO2 experiments? Ensure High-Temp Material Integrity
- What is the process of alumina tube manufacturing? From Powder to High-Performance Ceramic
- What are the high temperature properties of alumina? Discover Its Stability, Strength, and Limits
- Why are high-purity alumina rods used in LOCA experiments? Simulating Nuclear Fuel Gap and Steam Starvation
- What is the maximum operating temperature of alumina? The Critical Role of Purity and Form



















