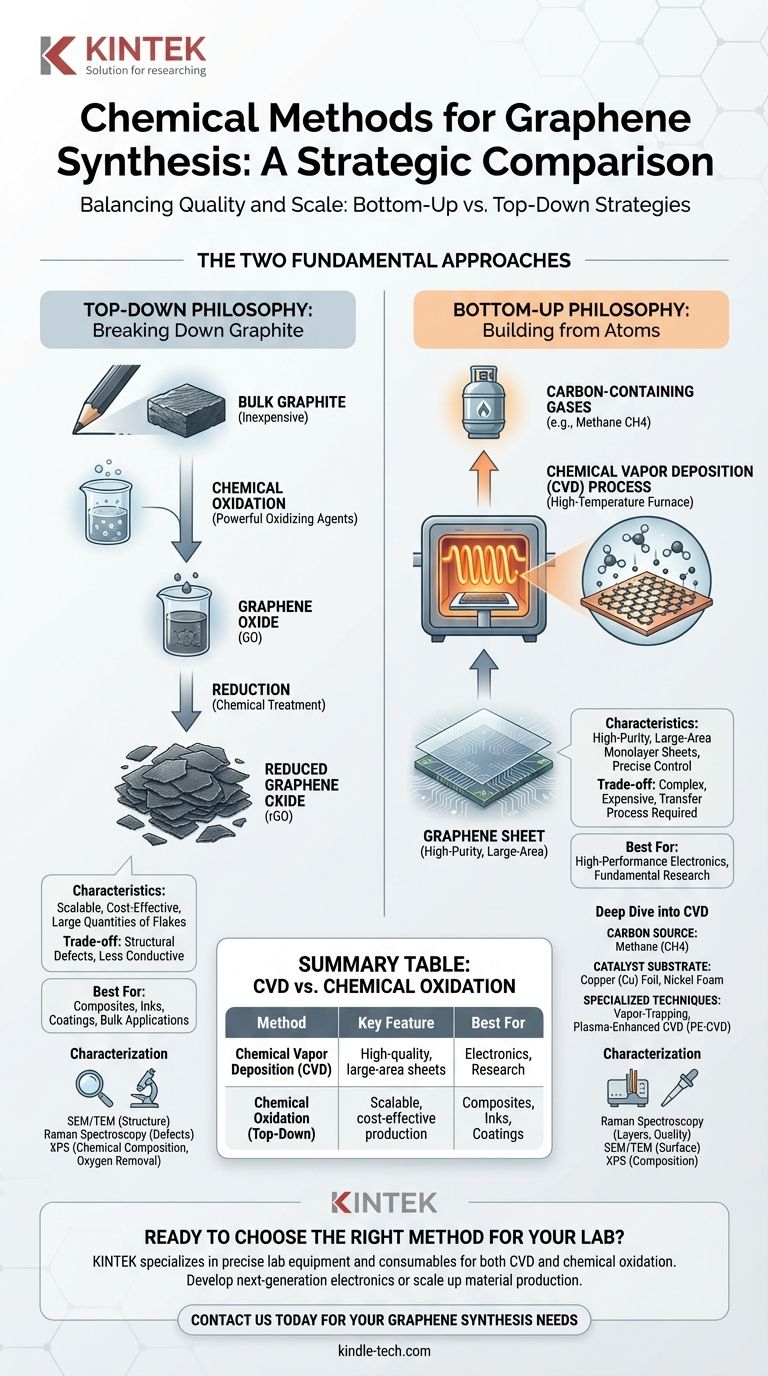
At its core, the chemical synthesis of graphene is divided into two primary strategies. The first is a "bottom-up" approach, where graphene is built atom-by-atom from carbon-containing gases, with Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) being the dominant method. The second is a "top-down" approach, which starts with bulk graphite and uses chemicals to break it down into single layers, a process known as chemical oxidation.
The choice between graphene synthesis methods is a strategic decision balancing quality against scale. Bottom-up CVD produces high-purity, large-area sheets ideal for electronics, while top-down chemical methods yield large quantities of graphene flakes perfect for composites and inks, but with more structural defects.
The Two Fundamental Approaches
The method you choose dictates the final quality, scalability, and cost of your graphene. Each philosophy—building up or breaking down—serves a different purpose.
The "Top-Down" Philosophy: Starting with Graphite
This approach begins with inexpensive graphite, the same material found in pencils, and breaks it down into individual or few-layer graphene sheets.
The primary chemical method here is chemical oxidation. This process uses powerful oxidizing agents to force layers of graphite apart, creating a material called graphene oxide (GO). This GO is then "reduced" using other chemical treatments to remove most of the oxygen, resulting in reduced graphene oxide (rGO).
The "Bottom-Up" Philosophy: Building from Carbon Atoms
This strategy is the reverse of the top-down method. It involves constructing graphene from the ground up by assembling individual carbon atoms on a substrate.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the most prominent and powerful bottom-up technique. It offers precise control over the growth process, allowing for the creation of high-quality, large-area graphene sheets.
A Deep Dive into Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD has become the gold standard for producing the high-quality graphene required for advanced electronics and research.
How CVD Works: The Core Process
In a typical CVD process, a gaseous carbon source is introduced into a high-temperature furnace containing a catalyst substrate.
The high heat causes the gas to decompose, depositing carbon atoms onto the surface of the catalyst. These carbon atoms then self-assemble into the distinct hexagonal lattice structure of a graphene sheet.
The Role of Carbon Sources and Catalysts
The choice of gas and substrate is critical. Methane (CH4) is the most popular and reliable carbon source due to its simple structure.
The catalyst provides the surface for growth. Copper (Cu) foil is widely used because it has low carbon solubility, which naturally limits the growth to a single layer of graphene. Other catalysts like nickel foam and iron nanoparticles are also used for specific applications.
Specialized CVD Techniques
To further improve graphene quality, specialized variants of CVD exist. The vapor-trapping method, for instance, carefully controls the gas flow to grow exceptionally large, single-crystalline graphene domains.
Other variations like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PE-CVD) use a plasma to help decompose the carbon source, allowing for growth at lower temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single method is perfect. The right choice involves balancing the need for quality, quantity, and cost.
CVD: Quality at a Cost
CVD excels at producing continuous, monolayer graphene sheets over large areas, which is essential for electronic applications.
However, the process is complex and can be expensive. Furthermore, the graphene must be transferred from the metal catalyst to a final substrate (like silicon), a delicate step that can introduce wrinkles, tears, and contamination.
Chemical Oxidation: Scalability vs. Purity
The top-down oxidation of graphite is highly scalable and cost-effective, capable of producing large quantities of graphene flakes suspended in a liquid.
The major downside is quality. The harsh chemical process introduces structural defects and oxygen groups that are never fully removed during reduction. This makes the resulting rGO less conductive and less suitable for high-performance electronics.
Verifying Success: How Graphene is Characterized
Simply running a synthesis process isn't enough; you must verify that you've created what you intended. Several analytical techniques are essential for this.
Identifying Graphene and Its Quality
Raman Spectroscopy is the fastest and most common tool. It can confirm the presence of graphene, determine the number of layers, and quantify the level of defects in the atomic lattice.
Examining Structure and Composition
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) are used to visualize the graphene sheet's surface and internal structure.
X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) is used to analyze the chemical composition, which is critical for confirming the removal of oxygen after the chemical reduction of graphene oxide.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The best synthesis method is the one that meets the specific requirements of your end goal.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics: CVD is the superior method for creating the large-area, high-quality graphene sheets you need.
- If your primary focus is bulk production for composites, coatings, or inks: The top-down chemical oxidation method offers unmatched scalability and lower cost, making it the practical choice.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research on pristine properties: Specialized CVD methods for large single crystals are ideal for creating high-quality samples for scientific investigation.
Understanding this fundamental trade-off between bottom-up precision and top-down scale is the key to navigating the world of graphene synthesis.

Summary Table:
| Method | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | High-quality, large-area sheets | Electronics, Research |
| Chemical Oxidation (Top-Down) | Scalable, cost-effective production | Composites, Inks, Coatings |
Ready to choose the right graphene synthesis method for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for both CVD and chemical oxidation processes. Whether you're developing next-generation electronics or scaling up material production, our expertise ensures you have the right tools for success.
Contact us today to discuss your specific graphene synthesis needs and let our specialists help you optimize your workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method



















