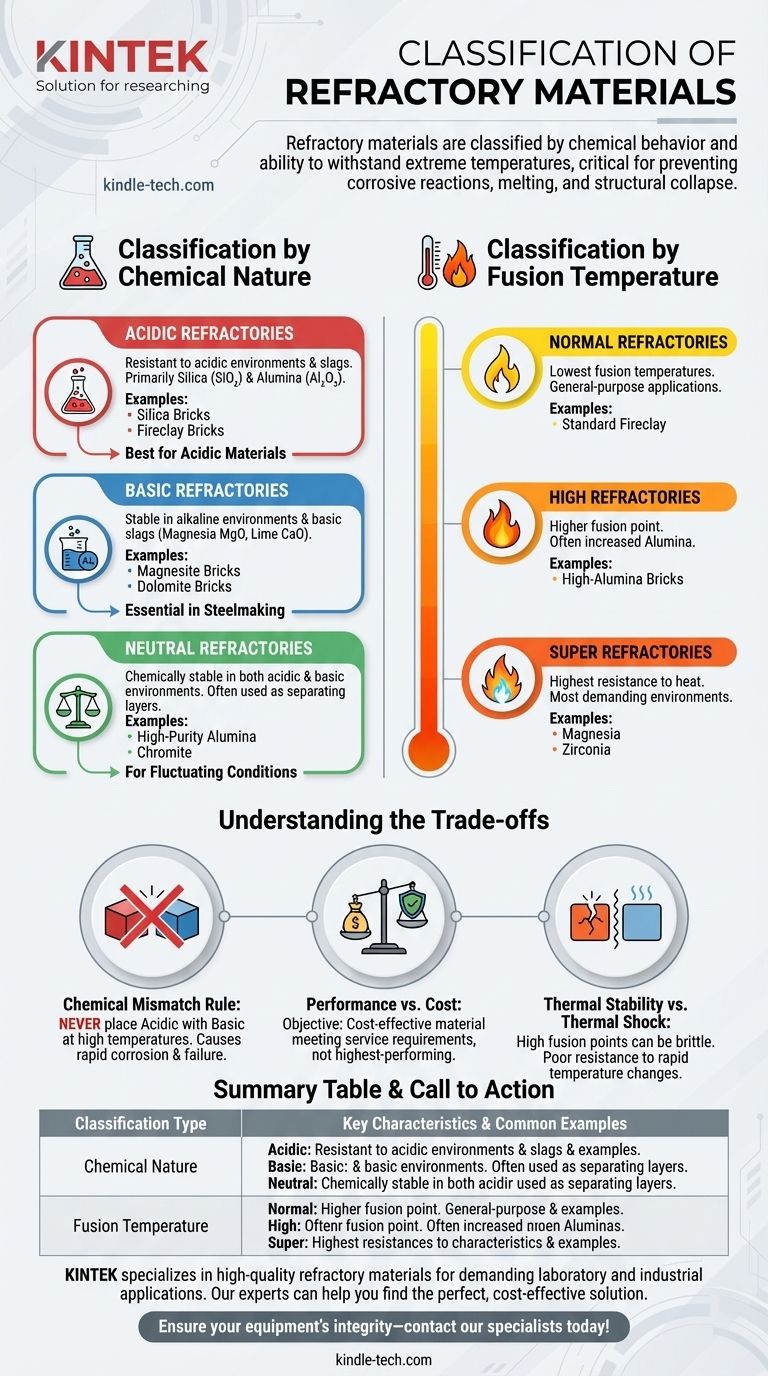
Refractory materials are primarily classified in two distinct ways: by their chemical behavior and by their ability to withstand extreme temperatures. The chemical classification—acidic, basic, or neutral—is critical for preventing corrosive reactions, while the temperature classification—normal, high, or super—dictates the material's physical stability and melting point.
The classification of a refractory is not an academic exercise; it is a critical guide for selection. Choosing the wrong chemical type can lead to rapid degradation and failure, while misjudging the temperature rating can result in melting and structural collapse.

Classification by Chemical Nature
The most fundamental classification relates to how a refractory material will react with its operational environment, particularly with substances like slag, fumes, or the product being processed. At high temperatures, these chemical reactions accelerate dramatically.
The Principle: Chemical Compatibility
The primary goal is to choose a refractory that is chemically inert within its specific environment. Using a chemically incompatible refractory will cause it to be "eaten away" or corroded, leading to premature failure of the furnace or vessel lining.
Acidic Refractories
These materials are resistant to acidic environments and slags. They are primarily composed of silica (SiO₂) and alumina (Al₂O₃).
Common examples include silica bricks and fireclay bricks. They perform best when in contact with other acidic materials.
Basic Refractories
Basic refractories are stable in alkaline environments and are used to resist basic slags, which are rich in oxides like magnesia (MgO) and lime (CaO).
These materials, such as magnesite and dolomite bricks, are essential in processes like steelmaking.
Neutral Refractories
These materials are chemically stable in both acidic and basic environments. They are often used as a separating layer between acidic and basic refractories or when the furnace conditions fluctuate.
High-purity alumina and chromite are the most common neutral refractories.
Classification by Fusion Temperature
This classification is a direct measure of a refractory's ability to withstand heat without melting or deforming. It is often measured by a standard known as the Pyrometric Cone Equivalent (PCE), which determines the temperature at which the material begins to soften.
Normal Refractories
This category includes materials with the lowest fusion temperatures, typically corresponding to common fireclay products. They are suitable for general-purpose applications where temperatures are high but not extreme.
High Refractories
These materials have a higher fusion point than normal refractories. This increased performance is often achieved by using materials with a higher percentage of alumina.
Super Refractories
This class represents materials with the highest resistance to heat, capable of serving in the most demanding thermal environments. They are typically made from very pure compounds like magnesia or zirconia.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a refractory is an exercise in balancing competing factors. No single material is perfect for all applications.
The Chemical Mismatch Rule
The most critical pitfall to avoid is chemical incompatibility. Never place an acidic refractory in direct contact with a basic environment (or vice-versa) at high temperatures. This will create a low-melting-point compound at the interface, causing rapid corrosion and destroying the lining.
Performance vs. Cost
As a rule, materials with higher fusion temperatures and greater chemical purity are significantly more expensive. The objective is to select the most cost-effective material that meets the specific service requirements of the application, not simply the highest-performing one available.
Thermal Stability vs. Thermal Shock
Some materials with exceptionally high fusion points can be brittle and may have poor resistance to rapid temperature changes (thermal shock). This can lead to cracking and spalling, where pieces of the refractory break away from the lining.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final selection should be guided entirely by the operational conditions of your furnace, kiln, or reactor.
- If your primary focus is containing acidic slags: You must select an acidic refractory, such as fireclay or silica-based bricks, to prevent chemical erosion.
- If your primary focus is containing basic slags (common in steelmaking): A basic refractory, such as magnesia, is non-negotiable to ensure furnace integrity.
- If your environment fluctuates or requires a separating layer: A neutral refractory like high-purity alumina or chromite provides the necessary chemical stability.
- If your main challenge is extreme temperature: Your selection will be a high or super refractory, but you must still match its chemical nature to the process environment.
Understanding these classifications moves you from simply choosing a brick to engineering a durable, reliable high-temperature system.
Summary Table:
| Classification Type | Key Categories | Primary Characteristics | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Nature | Acidic | Resistant to acidic slags and environments. | Silica bricks, Fireclay |
| Basic | Stable in alkaline environments, resists basic slags. | Magnesite, Dolomite | |
| Neutral | Chemically stable in both acidic and basic conditions. | High-purity Alumina, Chromite | |
| Fusion Temperature | Normal | Lower fusion point, suitable for general-purpose applications. | Standard Fireclay |
| High | Higher fusion point, often with increased alumina content. | High-Alumina Bricks | |
| Super | Highest temperature resistance for extreme environments. | Magnesia, Zirconia |
Selecting the right refractory is critical for your furnace's performance and longevity. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including refractory materials for demanding laboratory and industrial applications. Our experts can help you navigate chemical and thermal classifications to find the perfect, cost-effective solution for your specific process. Ensure your equipment's integrity—contact our specialists today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What temperature should a furnace run at? From Home Comfort to Industrial Processes
- What is the difference between a box furnace and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Lab Furnace for Your Application
- What is the use of muffle furnace in food analysis? Master Ashing for Accurate Mineral Content
- What are the disadvantages of a muffle furnace? Understanding the Trade-offs for Your Lab
- How is heat transferred in a furnace? Master Radiation, Convection & Conduction



















